telescope
... Huygens about 350 years ago is shown on the front inside cover. Today, telescopes not only include optical telescopes such as these old ones, but any instrument that surveys the sky in any part of the electromagnetic spectrum, whether it is visible or invisible radiation. The idea of using a combina ...
... Huygens about 350 years ago is shown on the front inside cover. Today, telescopes not only include optical telescopes such as these old ones, but any instrument that surveys the sky in any part of the electromagnetic spectrum, whether it is visible or invisible radiation. The idea of using a combina ...
Day Laboratory Exercise #3: Optics and Telescopes
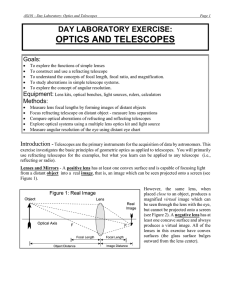
... Lenses and Refracting Telescopes - The focal length, f, of a lens is the distance between the lens and the image formed from originally parallel light rays (i.e., light rays from a very distant object). The focal length of a lens depends on the curvature of the lens surface. A basic refracting teles ...
... Lenses and Refracting Telescopes - The focal length, f, of a lens is the distance between the lens and the image formed from originally parallel light rays (i.e., light rays from a very distant object). The focal length of a lens depends on the curvature of the lens surface. A basic refracting teles ...
Chapter 18 - Firelands Local Schools
... –1852 James Clerk Maxwell proved that visible light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. –Each color of light is a different wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. –Humans can only see visible light, the rest of the spectrum is invisible to the human eye. –The earth’s atmosphere blocks most of ...
... –1852 James Clerk Maxwell proved that visible light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. –Each color of light is a different wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. –Humans can only see visible light, the rest of the spectrum is invisible to the human eye. –The earth’s atmosphere blocks most of ...
... sharp focus of the image in the focal plane. One imperfection intrinsic to refracting telescopes is chromatic aberration. The refraction of light through each lens tends to disperse shorter wavelength light through larger angles than for longer wavelength light. This results in blue light bending mo ...
Light and Telescopes - Otterbein University
... reflected at the same angle it was incident from • Proper design of a mirror (the shape of a parabola) can focus all rays incident on the mirror to a single place ...
... reflected at the same angle it was incident from • Proper design of a mirror (the shape of a parabola) can focus all rays incident on the mirror to a single place ...
Globular Clusters and Planetary Nebula
... three hands-on sessions. In one session, students will build their own planisphere and learn how to use it to find constellations. In another session, students will build their own refracting telescope and learn how to use it to observe the moon and planets. And, weather permitting, students will le ...
... three hands-on sessions. In one session, students will build their own planisphere and learn how to use it to find constellations. In another session, students will build their own refracting telescope and learn how to use it to observe the moon and planets. And, weather permitting, students will le ...
The Great Observatories - Center for STEM Education
... method is only accurate for stars within a few hundred light-years of Earth, since when the stars are very far away, the parallax shift is too small to measure. The method of measuring distance to stars beyond 100 light-years is to use Cepheid variable stars. These stars change in brightness over ti ...
... method is only accurate for stars within a few hundred light-years of Earth, since when the stars are very far away, the parallax shift is too small to measure. The method of measuring distance to stars beyond 100 light-years is to use Cepheid variable stars. These stars change in brightness over ti ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
Wide Angle Cross-Folded Telescope for Multiple
... be installations to accommodate the Focal Plane Assemblies. In both cases this generates a central obscuration, which has to be considered as a minimum. It is useful to size a central Secondary Mirror such that it generates not much more obscuration than already determined by the image size. III. ...
... be installations to accommodate the Focal Plane Assemblies. In both cases this generates a central obscuration, which has to be considered as a minimum. It is useful to size a central Secondary Mirror such that it generates not much more obscuration than already determined by the image size. III. ...
Tools of Astronomy
... • Astronomers often have to send their instruments into space to collect the information they seek. This is due to: • (1) Earth’s atmosphere blocking radiation • (2) When radiation is allowed to pass through atmosphere, the images are blurred • (3) To make close-up observations • (4) To obtain sampl ...
... • Astronomers often have to send their instruments into space to collect the information they seek. This is due to: • (1) Earth’s atmosphere blocking radiation • (2) When radiation is allowed to pass through atmosphere, the images are blurred • (3) To make close-up observations • (4) To obtain sampl ...
Chapter Six: Astronomical Tools
... 1) The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum can be divided into seven color bands of Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet (from long to short wavelength). A single photon of which of these colors has the greatest amount of energy? a. red b. orange c. green d. blue e. violet 2) ...
... 1) The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum can be divided into seven color bands of Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet (from long to short wavelength). A single photon of which of these colors has the greatest amount of energy? a. red b. orange c. green d. blue e. violet 2) ...
Lab 10: Refracting Telescopes
... Promota," which was published in 1663. He never actually made the telescope, which was to have used a parabolic (primary) and an ellipsoidal (secondary) mirror. In 1668, Newton used a concave mirror to actually make the first reflective telescope. We learn more of this history from two articles publ ...
... Promota," which was published in 1663. He never actually made the telescope, which was to have used a parabolic (primary) and an ellipsoidal (secondary) mirror. In 1668, Newton used a concave mirror to actually make the first reflective telescope. We learn more of this history from two articles publ ...
r 0 - Observatoire de Genève
... / D = 0.02 arc sec for = 1 mm, D = 10 m With turbulence, image size gets much larger ...
... / D = 0.02 arc sec for = 1 mm, D = 10 m With turbulence, image size gets much larger ...
Introduction to the Solar System
... Never Look at the Sun • NEVER look straight at the sun, especially with a telescope. Doing so can damage your eyes. • It is SAFE to look at other stars that are more distant than the sun. ...
... Never Look at the Sun • NEVER look straight at the sun, especially with a telescope. Doing so can damage your eyes. • It is SAFE to look at other stars that are more distant than the sun. ...
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.There are three primary types of optical telescope: refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics) reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics) catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrorsA telescope's light gathering power and ability to resolve small detail is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light). The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves.People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts.