“Stages” of Imaging Systems
... • Human visual system (HVS) is fine-tuned to focus, detect, and process (i.e., to create an “image” of) the particular wavelengths where the Sun emits most of its energy – evolutionary outcome: we see “best” in the dominant available band of wavelengths ...
... • Human visual system (HVS) is fine-tuned to focus, detect, and process (i.e., to create an “image” of) the particular wavelengths where the Sun emits most of its energy – evolutionary outcome: we see “best” in the dominant available band of wavelengths ...
Status of the Hybrid Doppler Wind Lidar (HDWL) Transceiver ACT
... • First move is 90 deg, next move is 180 deg, next move is 270 deg and last move is 180 deg • Operation speed is 1 sec for movement and stabilization Working with Pure Precision for a Precision Rotary Table that will meet our requirements. ...
... • First move is 90 deg, next move is 180 deg, next move is 270 deg and last move is 180 deg • Operation speed is 1 sec for movement and stabilization Working with Pure Precision for a Precision Rotary Table that will meet our requirements. ...
c. Section 2.3 Human Vision
... I. How to Bring an Image into Focus • to focus properly, the screen that is receiving the image must be the correct distance from the lens (where the light rays converge) • if the screen is too close or too far from the lens, the image will appear blurry • this is similar to near-sightedness and fa ...
... I. How to Bring an Image into Focus • to focus properly, the screen that is receiving the image must be the correct distance from the lens (where the light rays converge) • if the screen is too close or too far from the lens, the image will appear blurry • this is similar to near-sightedness and fa ...
Slide 1 - Physics and Astronomy
... HST orbits less than 400 miles above Earth – not much closer to stars & planets! But it can gather UV, visible, and IR light, unaffected by Earth’s atmosphere. ...
... HST orbits less than 400 miles above Earth – not much closer to stars & planets! But it can gather UV, visible, and IR light, unaffected by Earth’s atmosphere. ...
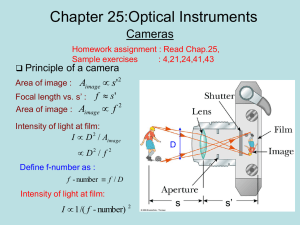
Chapter 25
... point of the eyepiece The two lenses are separated by the distance ƒo + ƒe which corresponds to the length of the tube The eyepiece forms an enlarged, inverted image of the first image ...
... point of the eyepiece The two lenses are separated by the distance ƒo + ƒe which corresponds to the length of the tube The eyepiece forms an enlarged, inverted image of the first image ...
Measuring the size of small things Stellar Diameters Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes
... found the distance of my eye from the cord, which amounts to the same thing as one of the sides which includes the angle formed at my eye and extending over the breadth of the cord.” “And . . . the apparent diameter of a fixed star of the first magnitude is no more than ...
... found the distance of my eye from the cord, which amounts to the same thing as one of the sides which includes the angle formed at my eye and extending over the breadth of the cord.” “And . . . the apparent diameter of a fixed star of the first magnitude is no more than ...
Tools of Astronomy Notes
... A radio telescope typically consists of a parabolic (bowlshaped) antenna similar to a modern satellite dish. This dish collects incoming radio or microwave radiation and focuses it onto a sensitive receiver located behind or below the antenna. Inside the receiver, the incoming waves are converted in ...
... A radio telescope typically consists of a parabolic (bowlshaped) antenna similar to a modern satellite dish. This dish collects incoming radio or microwave radiation and focuses it onto a sensitive receiver located behind or below the antenna. Inside the receiver, the incoming waves are converted in ...
Experiment 3 The Simple Magnifier, Microscope
... with telescopes) the object distance is functionally infinite, at which point this expression fails, so the angular magnification (ratio of subtended angles) is used instead. In Experiment 3, you will deal with a number of optical instruments in which the near point of the eye (taken as 25 cm for th ...
... with telescopes) the object distance is functionally infinite, at which point this expression fails, so the angular magnification (ratio of subtended angles) is used instead. In Experiment 3, you will deal with a number of optical instruments in which the near point of the eye (taken as 25 cm for th ...
E 3.1 Notes addition The James Webb and MOST Telescope
... Oscillation of Stars) was launched into space in 2003. It is the first Canadian scientific satellite in orbit in 33 years, and it is the first space telescope to be entirely designed and built in Canada. MOST is a small telescope dedicated entirely to asteroseismology, which is the study of star vib ...
... Oscillation of Stars) was launched into space in 2003. It is the first Canadian scientific satellite in orbit in 33 years, and it is the first space telescope to be entirely designed and built in Canada. MOST is a small telescope dedicated entirely to asteroseismology, which is the study of star vib ...
Astronomy 51 Introduction to Astronomy Fall 2016
... higher power and study the Moon’s surface some more. Discuss what you see in your report. What do you notice about the craters? What contrasting statements can you make between the dark surfaces and lighter surfaces (other than the different shades)? 5. With a low-power eyepiece, point the telescope ...
... higher power and study the Moon’s surface some more. Discuss what you see in your report. What do you notice about the craters? What contrasting statements can you make between the dark surfaces and lighter surfaces (other than the different shades)? 5. With a low-power eyepiece, point the telescope ...
Ch 05
... in the sky that supported the Copernican theory of the heliocentric cosmos like the moons of Jupiter • He also observed that the Milky Way was composed of millions of stars, Venus had phases, the Moon had geographical features similar to Earth (and the maria weren’t seas!) and the Sun had spots • Af ...
... in the sky that supported the Copernican theory of the heliocentric cosmos like the moons of Jupiter • He also observed that the Milky Way was composed of millions of stars, Venus had phases, the Moon had geographical features similar to Earth (and the maria weren’t seas!) and the Sun had spots • Af ...
Chapter5-Questions
... Diffraction limits resolution; larger telescopes & shorter wave light produces sharper images. ...
... Diffraction limits resolution; larger telescopes & shorter wave light produces sharper images. ...
Observing the Sun Description
... Light from the Sun enters the telescope, where it is focussed by lenses onto the viewing screen. The farther the eyepiece of the telescope is from the viewing screen, the larger the image will appear. However, increasing the magnification in this way also magnifies any motion. Thus it become more di ...
... Light from the Sun enters the telescope, where it is focussed by lenses onto the viewing screen. The farther the eyepiece of the telescope is from the viewing screen, the larger the image will appear. However, increasing the magnification in this way also magnifies any motion. Thus it become more di ...
Pressemitteilung - Micro
... the universe with its gigantic main mirror and adaptive optics (AO) technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we coul ...
... the universe with its gigantic main mirror and adaptive optics (AO) technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we coul ...
here.
... install the spectrograph into the telescope. When the instrument is first removed at each opening there is a bright red or orange covering which is to protect the instrument from collecting dust on its mirrors. Before starting these must be removed. Letter A is the telescope entrance and that is whe ...
... install the spectrograph into the telescope. When the instrument is first removed at each opening there is a bright red or orange covering which is to protect the instrument from collecting dust on its mirrors. Before starting these must be removed. Letter A is the telescope entrance and that is whe ...
Observing
... • We’ll meet at the observatory even if it is cloudy – If the weather is really bad (a foot of snow or something) I’ll send an email changing the meeting place, but otherwise… ...
... • We’ll meet at the observatory even if it is cloudy – If the weather is really bad (a foot of snow or something) I’ll send an email changing the meeting place, but otherwise… ...
How to Buy an Astronomical Telescope
... Achromatic: Literally, “free from color”. In amateur refractor telescopes, the use of a doublet objective lens to provide moderate correction for chromatic (color) aberrations in the refracted light (because all colors do not refract at the same angle). Altitude/Azimuth (Alt-Az): a type of telescope ...
... Achromatic: Literally, “free from color”. In amateur refractor telescopes, the use of a doublet objective lens to provide moderate correction for chromatic (color) aberrations in the refracted light (because all colors do not refract at the same angle). Altitude/Azimuth (Alt-Az): a type of telescope ...
5.2 Optical Instruments Optical systems Camera Limitations of Lens
... • For refracting optics there are problems of chromatic and spherical aberration. • Problems in precision in constructing the refracting and reflecting surfaces. • Diffraction – A basic problems having to do with the wave nature of light (discussed next) ...
... • For refracting optics there are problems of chromatic and spherical aberration. • Problems in precision in constructing the refracting and reflecting surfaces. • Diffraction – A basic problems having to do with the wave nature of light (discussed next) ...
Lecture 25: Optical Instruments
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
Mopra
... A 7mm spectrometer. This spectral window remains relatively unexplored (e.g. high dipole moment molecules), though is readily accessible from the Mopra site. Focal Plane Arrays. OTF mapping is limited to covering degree-sized regions if using just a single element detector. FPAs would greatly increa ...
... A 7mm spectrometer. This spectral window remains relatively unexplored (e.g. high dipole moment molecules), though is readily accessible from the Mopra site. Focal Plane Arrays. OTF mapping is limited to covering degree-sized regions if using just a single element detector. FPAs would greatly increa ...
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.There are three primary types of optical telescope: refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics) reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics) catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrorsA telescope's light gathering power and ability to resolve small detail is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light). The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves.People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts.