Geometric Optics
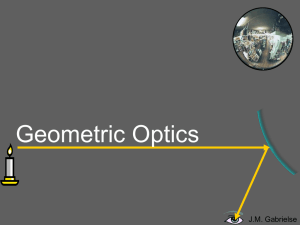
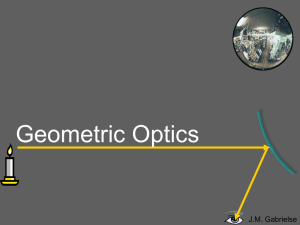
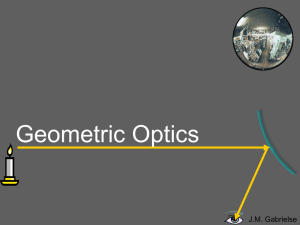
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
Geometric Optics
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
The basic purpose of a lens of any kind is to collect the light
... where a, b and c are constant values that define the distortion curve behavior; note that “a” is usually zero as the distortion is usually zero at the image center. In some cases, a third order polynomial could be required to get a perfect fit of the curve. In addition to radial distortion, also tra ...
... where a, b and c are constant values that define the distortion curve behavior; note that “a” is usually zero as the distortion is usually zero at the image center. In some cases, a third order polynomial could be required to get a perfect fit of the curve. In addition to radial distortion, also tra ...
AstroMaster Series Telescopes
... The telescope optical tube attaches to the mount via a dovetail slide bar mounting bracket at the top of the mount (Figure 2-16). For the 114 EQ Newtonian, the mounting bar is the bracket which is attached to the tube rings. For the 70 EQ refractor and the 76 EQ Newtonian the mounting bar is attache ...
... The telescope optical tube attaches to the mount via a dovetail slide bar mounting bracket at the top of the mount (Figure 2-16). For the 114 EQ Newtonian, the mounting bar is the bracket which is attached to the tube rings. For the 70 EQ refractor and the 76 EQ Newtonian the mounting bar is attache ...
WAVEFRONT SENSOR FOR THE GAIA MISSION
... The ESA Gaia mission is a successor to the ESA Hipparcos mission. It’s ambitious objective is to create the largest and most precise three dimensional chart of our galaxy by providing unprecedented positional and radial velocity measurements for about one billion stars in our Galaxy and throughout t ...
... The ESA Gaia mission is a successor to the ESA Hipparcos mission. It’s ambitious objective is to create the largest and most precise three dimensional chart of our galaxy by providing unprecedented positional and radial velocity measurements for about one billion stars in our Galaxy and throughout t ...
Phénomènes de diffraction
... • It is definitively a solution for some applications But extremely difficult and expensive to make large telescopes… Telescope under study for first light around 2015-2020: USA : TMT diameter of 30 meter Europe : E-ELT diameter 42 meter ...
... • It is definitively a solution for some applications But extremely difficult and expensive to make large telescopes… Telescope under study for first light around 2015-2020: USA : TMT diameter of 30 meter Europe : E-ELT diameter 42 meter ...
AOS_technical_4-24-07
... in-vacuum optics in the correct positions with the correct orientations Optical Lever System (OpLev)- sensors to monitor the orientation of the optics as they swing in their suspensions Photon Calibrator- applies a known radiation pressure force to the End Test Masses for interferometer calibration ...
... in-vacuum optics in the correct positions with the correct orientations Optical Lever System (OpLev)- sensors to monitor the orientation of the optics as they swing in their suspensions Photon Calibrator- applies a known radiation pressure force to the End Test Masses for interferometer calibration ...
Phase Contrast
... Pinhole prevents out-of-focus light getting to the sensor(s) (PMT - Photomultiplier) (30 – 70 µm) Multi Photon does not require pinhole (90 – 500 µm) ...
... Pinhole prevents out-of-focus light getting to the sensor(s) (PMT - Photomultiplier) (30 – 70 µm) Multi Photon does not require pinhole (90 – 500 µm) ...
THE CITY OF GRETNA PUBLIC OBSERVATORY Educational and
... end of Huey P. Long Avenue) . GPS users can use the address of the Gretna Middle School (910 Gretna Boulevard) to get close. The observatory is located just around the left side corner of the school and adjacent to the Gretna City Park. The observatory is open to the general public with free admissi ...
... end of Huey P. Long Avenue) . GPS users can use the address of the Gretna Middle School (910 Gretna Boulevard) to get close. The observatory is located just around the left side corner of the school and adjacent to the Gretna City Park. The observatory is open to the general public with free admissi ...
Basic Principles of the Surgical Microscope
... (on the footswitch) until a sharp image is obtained. E. Being careful not to physically shift the microscope position, change the magnification setting to its lowest position. Focus left and right eyepieces, one at a time, by turning the diopter ring until the image is clear and sharp. Tighten the d ...
... (on the footswitch) until a sharp image is obtained. E. Being careful not to physically shift the microscope position, change the magnification setting to its lowest position. Focus left and right eyepieces, one at a time, by turning the diopter ring until the image is clear and sharp. Tighten the d ...
[75-79] Privett Review Skywatcher Apr06.indd
... The champagne-coloured tubes with stylish white fittings and tube rings seemed rugged and robust and the dew shields worked well on the nights I used them. The tube caps included differed in style between the models, with some more secure than others, but all were adequate. The tube rings were easy ...
... The champagne-coloured tubes with stylish white fittings and tube rings seemed rugged and robust and the dew shields worked well on the nights I used them. The tube caps included differed in style between the models, with some more secure than others, but all were adequate. The tube rings were easy ...
PDF only
... required demand, that is, a significantly stronger eyepiece with a standard (weak) objective. The implications are, 1. Contrary to the received view, an objective of 1.5 diopter is not a significantly long-focal-length lens. 2. Contrary to the received view, an eyepiece of 13.7 diopter is not a stan ...
... required demand, that is, a significantly stronger eyepiece with a standard (weak) objective. The implications are, 1. Contrary to the received view, an objective of 1.5 diopter is not a significantly long-focal-length lens. 2. Contrary to the received view, an eyepiece of 13.7 diopter is not a stan ...
104-cm Sampurnanand Telescope
... mm, f/14, reflector), 8-inch (200 mm, f/15, refractor) and 4-inch (110 mm, f/7, refrator type). The 8 and 4-inch finder telescopes are equipped with eyepieces which covers around 20 and 90 arcmin field of view respectively. The 8-inch refractor is also used for guiding the main (104-cm) telescope. A ...
... mm, f/14, reflector), 8-inch (200 mm, f/15, refractor) and 4-inch (110 mm, f/7, refrator type). The 8 and 4-inch finder telescopes are equipped with eyepieces which covers around 20 and 90 arcmin field of view respectively. The 8-inch refractor is also used for guiding the main (104-cm) telescope. A ...
How We See The Sky
... Diffraction places a limit on the resolution of an optical system. As detail becomes smaller, diffraction has a proportionally stronger “smearing” effect (failure to fully “transfer” scene contrast), diminishing the ability of the optical system to resolve fine detail. High MTF at low contrast level ...
... Diffraction places a limit on the resolution of an optical system. As detail becomes smaller, diffraction has a proportionally stronger “smearing” effect (failure to fully “transfer” scene contrast), diminishing the ability of the optical system to resolve fine detail. High MTF at low contrast level ...
SIMG-716 Linear Imaging Mathematics I 01 - Motivation 1
... the galaxy NGC 7469 (http://cfao.ucolick.org/ao/why.php), and Titan (largest moon of Saturn) through a ground-based conventional telescope, the Hubble Space telescope, and the Keck Telescope with adaptive optics (http://cfao.ucolick.org/ao/why.php). ...
... the galaxy NGC 7469 (http://cfao.ucolick.org/ao/why.php), and Titan (largest moon of Saturn) through a ground-based conventional telescope, the Hubble Space telescope, and the Keck Telescope with adaptive optics (http://cfao.ucolick.org/ao/why.php). ...
Autostar Manual
... -7outside area with few obstructions and an open sky . The telescope should be prepared for observing with lens covers removed, a low power eyepiece installed and the viewfinder aligned. Use MODE to return to the main menu (“Select Item:”). Chose the “Setup” menu and press ENTER. Press ENTER again ...
... -7outside area with few obstructions and an open sky . The telescope should be prepared for observing with lens covers removed, a low power eyepiece installed and the viewfinder aligned. Use MODE to return to the main menu (“Select Item:”). Chose the “Setup” menu and press ENTER. Press ENTER again ...
Introduction to Adaptive Optics
... • How is it supposed to work? • How does it really work? • Astronomy with adaptive optics. ...
... • How is it supposed to work? • How does it really work? • Astronomy with adaptive optics. ...
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.There are three primary types of optical telescope: refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics) reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics) catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrorsA telescope's light gathering power and ability to resolve small detail is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light). The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves.People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts.











![[75-79] Privett Review Skywatcher Apr06.indd](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/023366319_1-a76758b4d0090512e8b7a8bcf6b3580b-300x300.png)