kowinsky-apphysics-1-lp-2014-08-25
... Students will create solutions for reflections, refractions for substances. Use equations for thin lenses and mirrors to find object, image, and ...
... Students will create solutions for reflections, refractions for substances. Use equations for thin lenses and mirrors to find object, image, and ...
Lab 12 - Cabrillo College
... only be seen by looking "through" a lens or mirror. They look very real, but the light isn’t really there where the image seems to be. Other images can be projected onto a surface—these are called “real” images—but they are sometimes difficult to see without the help of a screen. We will meet both t ...
... only be seen by looking "through" a lens or mirror. They look very real, but the light isn’t really there where the image seems to be. Other images can be projected onto a surface—these are called “real” images—but they are sometimes difficult to see without the help of a screen. We will meet both t ...
PARTS LIST FOR AT50 Telescope
... The popular and more familiar constellations often provide the easiest landmarks to help find the planet’s locations and paths of orbit. Most people have looked up at the sky at night and seen some of the planets without even realizing it. A planet looks like a bright star but does not twinkle like ...
... The popular and more familiar constellations often provide the easiest landmarks to help find the planet’s locations and paths of orbit. Most people have looked up at the sky at night and seen some of the planets without even realizing it. A planet looks like a bright star but does not twinkle like ...
Lab 12 - Cabrillo College
... only be seen by looking "through" a lens or mirror. They look very real, but the light isn’t really there where the image seems to be. Other images can be projected onto a surface—these are called “real” images—but they are sometimes difficult to see without the help of a screen. We will meet both t ...
... only be seen by looking "through" a lens or mirror. They look very real, but the light isn’t really there where the image seems to be. Other images can be projected onto a surface—these are called “real” images—but they are sometimes difficult to see without the help of a screen. We will meet both t ...
astronomical observatories of the canary islands
... The GTC, which began its scientific production in 2009, is considered one of the most advanced telescopes in the world and the largest in the optical-infrared range, with a segmented 10.4 meter diameter primary mirror. Its cutting edge technology has helped answer many questions about the creation ...
... The GTC, which began its scientific production in 2009, is considered one of the most advanced telescopes in the world and the largest in the optical-infrared range, with a segmented 10.4 meter diameter primary mirror. Its cutting edge technology has helped answer many questions about the creation ...
Looking Deeper into Astronomy
... much the same technology as is found inside a video camera. (In Chapter 6 of Universe we will see the advantages of this technology over the human eye.) Other telescopes are sensitive to invisible forms of light such as X rays or radio waves; there is no way that one could “look through” such telesc ...
... much the same technology as is found inside a video camera. (In Chapter 6 of Universe we will see the advantages of this technology over the human eye.) Other telescopes are sensitive to invisible forms of light such as X rays or radio waves; there is no way that one could “look through” such telesc ...
Design parameters – Summary
... Diffraction-limited field of view (Strehl Ratio ≥ 0.80) λ=0.5 µm (on curved field with R=2209.8 mm) λ=2.2 µm (on curved field with R=2215.4 mm) λ=5.0 µm (on curved field with R=2243.1 mm) Image quality at edge of field (10 arc mins) Wavefront RMS RMS spot size Field curvature Central obscuration Dis ...
... Diffraction-limited field of view (Strehl Ratio ≥ 0.80) λ=0.5 µm (on curved field with R=2209.8 mm) λ=2.2 µm (on curved field with R=2215.4 mm) λ=5.0 µm (on curved field with R=2243.1 mm) Image quality at edge of field (10 arc mins) Wavefront RMS RMS spot size Field curvature Central obscuration Dis ...
5.4 AND 10 MM ULTRA TELESCOPES
... * 5.4mm ULTRA telescope compared to endoscope with 70° field of view and 10mm ULTRA telescope compared to endoscope with 75° field of view. ...
... * 5.4mm ULTRA telescope compared to endoscope with 70° field of view and 10mm ULTRA telescope compared to endoscope with 75° field of view. ...
VOYAGER® 8 INCH DOBSONIAN TELESCOPE MODEL 78-8000
... 1. First determine your targeted object. Any bright object in the night sky is a good starting point. One of the favorite starting points in astronomy is the moon. This is an object sure to please any budding astronomer or experienced veteran. When you have developed proficiency at this level, other ...
... 1. First determine your targeted object. Any bright object in the night sky is a good starting point. One of the favorite starting points in astronomy is the moon. This is an object sure to please any budding astronomer or experienced veteran. When you have developed proficiency at this level, other ...
X-ray allow doctors and others to see inside our bodies and identify
... How much of this light reaches the eye will depend on telescope's light transmission efficiency. Transmission losses at mirror surface range from ~2% to ~20%, or more. Light loss in glass elements, therefore, increases with the number of uncoated surfaces and the in-glass path length. For uncoated d ...
... How much of this light reaches the eye will depend on telescope's light transmission efficiency. Transmission losses at mirror surface range from ~2% to ~20%, or more. Light loss in glass elements, therefore, increases with the number of uncoated surfaces and the in-glass path length. For uncoated d ...
Space telescopes - International Space Science Institute
... orbit around a bright star require coronagraphs with very low scatter (about 10−10 in the visible or 10−7 in the near mid-infrared). These numbers are for a separation of 0.1′′ of the two-component star/planet system located at a distance from the ...
... orbit around a bright star require coronagraphs with very low scatter (about 10−10 in the visible or 10−7 in the near mid-infrared). These numbers are for a separation of 0.1′′ of the two-component star/planet system located at a distance from the ...
d - Madison Public Schools
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
David Gill and his work
... Gill watched with envy the rise of astrophysics (the study of the physics of the stars) but could not persuade his superiors to support him in this type of work. His prayers were answered when his friend and frequent visitor, Frank McClean, offered to finance the 24-inch telescope ...
... Gill watched with envy the rise of astrophysics (the study of the physics of the stars) but could not persuade his superiors to support him in this type of work. His prayers were answered when his friend and frequent visitor, Frank McClean, offered to finance the 24-inch telescope ...
Alternate Surface Measurements for GMT Primary Mirror
... surface by sending parallel rays into the mirror and measuring where they intercept the focal plane. The scanning pentaprism system uses a collimated light source and a pentaprism to create parallel beams that are scanned over the surface, as shown above. For an off-axis mirror, several scans across ...
... surface by sending parallel rays into the mirror and measuring where they intercept the focal plane. The scanning pentaprism system uses a collimated light source and a pentaprism to create parallel beams that are scanned over the surface, as shown above. For an off-axis mirror, several scans across ...
Adaptive Optics: basic principles and applications Short course of
... • The only way to use AO for everyday vision correction is the incorporation of the AO within the human eye. • There are two ways to incorporate the AO: a contact lens and an intra-ocular implant. ...
... • The only way to use AO for everyday vision correction is the incorporation of the AO within the human eye. • There are two ways to incorporate the AO: a contact lens and an intra-ocular implant. ...
COrE+ Optics options
... – Crossed Dragonian design (side fed or front fed) – Off axis Gregorian ...
... – Crossed Dragonian design (side fed or front fed) – Off axis Gregorian ...
SPIE Cox Lallo Focus Model - Space Telescope Science Institute
... In the first year of operation the separation shrank by over 80 microns but currently the rate is about 0.8 microns per year. In the first year of operations, adjustments to the secondary mirror position were made every month or two with the aim of staying within 5 microns of best focus. Initially t ...
... In the first year of operation the separation shrank by over 80 microns but currently the rate is about 0.8 microns per year. In the first year of operations, adjustments to the secondary mirror position were made every month or two with the aim of staying within 5 microns of best focus. Initially t ...
Optics requirements for the Generation-X x
... Astronomical x-ray telescopes need large area and high-resolution imaging. International X-ray Observatory (IXO) ...
... Astronomical x-ray telescopes need large area and high-resolution imaging. International X-ray Observatory (IXO) ...
hirshhorn museum and sculpture garden
... design provided a state-of-the-art solution to the technological limitation in casting large mirrors at that time. Following advances in mirror-casting technology developed by the University of Arizona, SAO replaced the six smaller mirrors of the original MMT with a single mirror 6.5 meters in diame ...
... design provided a state-of-the-art solution to the technological limitation in casting large mirrors at that time. Following advances in mirror-casting technology developed by the University of Arizona, SAO replaced the six smaller mirrors of the original MMT with a single mirror 6.5 meters in diame ...
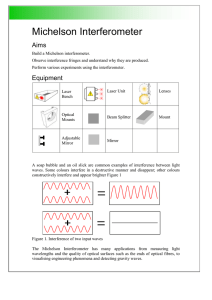
Michelson Interferometer - Research School of Physics and
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
Part F
... Multi Pixel Photon Counter (MPPC) and Charge Coupled Devices (CCDs) Charge-Coupled device (CCD) has been incorporated into the MPPC thereby providing track information. The figure below shows a CCD used in digital photography. A CCD is a device used for the movement of electrical charge, usually fro ...
... Multi Pixel Photon Counter (MPPC) and Charge Coupled Devices (CCDs) Charge-Coupled device (CCD) has been incorporated into the MPPC thereby providing track information. The figure below shows a CCD used in digital photography. A CCD is a device used for the movement of electrical charge, usually fro ...
Quo Vadis
... angle dependence, the showers of different E will reach their maxima on different distances from the telescope. • This means that their images will be smeared out depending on their angular deviation from the telescope‘s axis and the best focus plane of the telescope. Needs to be studied what is the ...
... angle dependence, the showers of different E will reach their maxima on different distances from the telescope. • This means that their images will be smeared out depending on their angular deviation from the telescope‘s axis and the best focus plane of the telescope. Needs to be studied what is the ...
Entry Task
... Please have on desk: light is • Work from yesterday will What mirrors do to light be checked off tomorrow waves to form images ...
... Please have on desk: light is • Work from yesterday will What mirrors do to light be checked off tomorrow waves to form images ...
Refraction - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • The speed of light differs in different transparent materials. • The denser the material the slower light travels as it passes through. ...
... • The speed of light differs in different transparent materials. • The denser the material the slower light travels as it passes through. ...
Reflecting telescope

A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a ""catoptric"" telescope.