Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
star
... Life Cycle of Stars Small nebulas produce small, cool stars that are long-lived. A star can have a mass as low as a tenth of the sun’s mass. The gravitational force in such low-mass stars is just strong enough to create a small core where nuclear fusion takes place. This lower energy production res ...
... Life Cycle of Stars Small nebulas produce small, cool stars that are long-lived. A star can have a mass as low as a tenth of the sun’s mass. The gravitational force in such low-mass stars is just strong enough to create a small core where nuclear fusion takes place. This lower energy production res ...
ASTRONOMIA SPAIN inglés.qxd
... These are some of the results we present in ‘Astronomy made in Spain’, a project of the Spanish Astronomical Society (Sociedad Española de Astronomía, SEA) to commemorate the International Year of Astronomy 2009. This book is a collection of conversations with the Spanish astronomers who have publis ...
... These are some of the results we present in ‘Astronomy made in Spain’, a project of the Spanish Astronomical Society (Sociedad Española de Astronomía, SEA) to commemorate the International Year of Astronomy 2009. This book is a collection of conversations with the Spanish astronomers who have publis ...
2015 - Society for Astronomical Sciences
... recent, critical role in a play whose plot timeline extends from the early days of the Solar System to millennia yet to come. ...
... recent, critical role in a play whose plot timeline extends from the early days of the Solar System to millennia yet to come. ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... universe at distances of 12 billion to 16 billion light-years. The sun is in a galaxy called the Milky Way that contains more than 100 billion stars. There are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe, and the average number of stars per galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion tr ...
... universe at distances of 12 billion to 16 billion light-years. The sun is in a galaxy called the Milky Way that contains more than 100 billion stars. There are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe, and the average number of stars per galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion tr ...
Interpolation of Magnitude.
... it contains “noise”. You’ll learn that your observations can be very valuable, even while you’re learning to make better and better estimates. ...
... it contains “noise”. You’ll learn that your observations can be very valuable, even while you’re learning to make better and better estimates. ...
Spectroscopy-Heidelberg
... For low orders m (low spectral resolution, large free spectral range) one can use a filter that blocks light from the other orders For high orders m (the free spectral range is very small), use “cross disperser”: a second dispersive element (usually a prism), mounted with the dispersion direction pe ...
... For low orders m (low spectral resolution, large free spectral range) one can use a filter that blocks light from the other orders For high orders m (the free spectral range is very small), use “cross disperser”: a second dispersive element (usually a prism), mounted with the dispersion direction pe ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... trigonometric parallaxes had been measured. This enabled them to measure the absolute magnitude MV for these stars. ...
... trigonometric parallaxes had been measured. This enabled them to measure the absolute magnitude MV for these stars. ...
Studying gas in disks
... Study gas dissipation timescale: constrains pathways for giant planet formation, terrestrial planet architectures ...
... Study gas dissipation timescale: constrains pathways for giant planet formation, terrestrial planet architectures ...
Tasks - ESA Science
... found in the LMC and in other more distant galaxies can also be used for distance measurements, so a more precise distance to the LMC would be a stepping-stone to more precise distance measurements for other, more distant galaxies. ...
... found in the LMC and in other more distant galaxies can also be used for distance measurements, so a more precise distance to the LMC would be a stepping-stone to more precise distance measurements for other, more distant galaxies. ...
Chapter 26: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Stars
... Stars in the same constellation are often not close to each other in space. A star generates energy by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The color of a star is determined by its surface temperature. Stars are classified by color and temperature. The most common system uses the letters O (blue), ...
... Stars in the same constellation are often not close to each other in space. A star generates energy by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The color of a star is determined by its surface temperature. Stars are classified by color and temperature. The most common system uses the letters O (blue), ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 37-
... So in the 1800s astronomers wanted to name stars all the way down to about 9 th magnitude. Now, that’s about 300,000 stars. That’s a lot of stars. And so you can’t really give them nice names like Rigel. You can’t use Greek letters. And even if you start using numbers, it’s just gonna be a big numbe ...
... So in the 1800s astronomers wanted to name stars all the way down to about 9 th magnitude. Now, that’s about 300,000 stars. That’s a lot of stars. And so you can’t really give them nice names like Rigel. You can’t use Greek letters. And even if you start using numbers, it’s just gonna be a big numbe ...
PDF format - Princeton University Press
... circles passing under the earth, which is freely suspended in space. For Anaximenes the earth is still flat but, instead of resting on nothing, it is supported by air. The sun, the moon, and the planets are all made of fire, and they ride on the air because of their breadth. The sun derives its heat ...
... circles passing under the earth, which is freely suspended in space. For Anaximenes the earth is still flat but, instead of resting on nothing, it is supported by air. The sun, the moon, and the planets are all made of fire, and they ride on the air because of their breadth. The sun derives its heat ...
Beyond the Solar System By Patti Hutchison ANSWER THE
... the galaxies in the universe are spiral galaxies. A spiral galaxy looks like a twirling octopus. In the "arms" of the galaxy, new stars are formed. Some of them are very large. They cause the surrounding clouds of dust to glow brightly, also. Spiral galaxies are beautiful to see. New stars are not f ...
... the galaxies in the universe are spiral galaxies. A spiral galaxy looks like a twirling octopus. In the "arms" of the galaxy, new stars are formed. Some of them are very large. They cause the surrounding clouds of dust to glow brightly, also. Spiral galaxies are beautiful to see. New stars are not f ...
Word
... Analyzing this archive requires a parallel and distributed query system. We implemented a prototype query system. Each query received from the user interface is parsed into a query execution tree (QET) that is then executed by the query engine, which passes the requests to Objectivity/DB for actual ...
... Analyzing this archive requires a parallel and distributed query system. We implemented a prototype query system. Each query received from the user interface is parsed into a query execution tree (QET) that is then executed by the query engine, which passes the requests to Objectivity/DB for actual ...
argo and other tidal structures around the milky way
... Several features in these maps can be identified with known satellite galaxies, while others are new findings as the TriAnd + Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004) and Argo. It is apparent that there is a continuity between the Argo and CMa overdensities. We have verified that when these overden ...
... Several features in these maps can be identified with known satellite galaxies, while others are new findings as the TriAnd + Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004) and Argo. It is apparent that there is a continuity between the Argo and CMa overdensities. We have verified that when these overden ...
observing the universe
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Chapter 24
... Absolute Magnitude Apparent magnitudes were good approximations of the true brightness of stars when astronomers thought that the universe was very small—containing no more than a few thousand stars that were all at very similar distances from Earth. However, we now know that the universe is unimagi ...
... Absolute Magnitude Apparent magnitudes were good approximations of the true brightness of stars when astronomers thought that the universe was very small—containing no more than a few thousand stars that were all at very similar distances from Earth. However, we now know that the universe is unimagi ...
Chapter 2 User`s Guide to the Sky: Patterns and Cycles
... measure the intensity of starlight with high precision and then use a simple mathematical relationship that relates light intensity to apparent visual magnitude. • So, instead of saying that the star known by the charming name Chort (Theta Leonis) is about third magnitude, you can say its magnitude ...
... measure the intensity of starlight with high precision and then use a simple mathematical relationship that relates light intensity to apparent visual magnitude. • So, instead of saying that the star known by the charming name Chort (Theta Leonis) is about third magnitude, you can say its magnitude ...
11 01 04 Portable M Class Astro
... use of portable meter-class telescopes. These telescopes trace their origins to John Dobson and his innovative ideas for making relatively large aperture alt-az telescopes from low cost materials with ordinary tools. These alt-az telescopes more closely resembled their large mountaintop altaz brethr ...
... use of portable meter-class telescopes. These telescopes trace their origins to John Dobson and his innovative ideas for making relatively large aperture alt-az telescopes from low cost materials with ordinary tools. These alt-az telescopes more closely resembled their large mountaintop altaz brethr ...
On Sunspot and Starspot Lifetimes - Patrick M. Hartigan
... in the present work. Many sunspots persist for less than one day, and lifetimes of more than a week or two are relatively uncertain since the spots disappear over the limb and observations are interrupted. The data used to calculate W are probably biased toward smaller values of T than are obtained ...
... in the present work. Many sunspots persist for less than one day, and lifetimes of more than a week or two are relatively uncertain since the spots disappear over the limb and observations are interrupted. The data used to calculate W are probably biased toward smaller values of T than are obtained ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

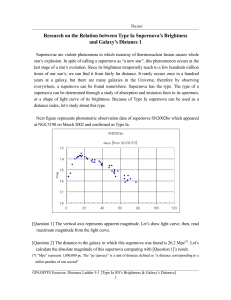
The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.