Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
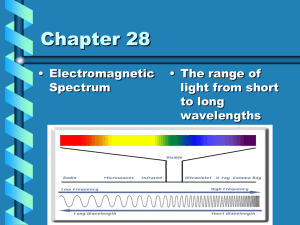
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
Study Questions for Test 2
... Study Questions for Test 2 Chapters 6, 8, 19 and 20 What forms of electromagnetic radiation have wavelengths shorter and longer than visible light? How is the energy of a photon related to its wavelength? The largest optical telescopes in the world today are what type? What are observational advanta ...
... Study Questions for Test 2 Chapters 6, 8, 19 and 20 What forms of electromagnetic radiation have wavelengths shorter and longer than visible light? How is the energy of a photon related to its wavelength? The largest optical telescopes in the world today are what type? What are observational advanta ...
13.12 & 14.6 Technolgy and Space
... A reflecting telescope uses a concave mirror at the bottom of the scope. ...
... A reflecting telescope uses a concave mirror at the bottom of the scope. ...
8th Grade - Astronomy
... trillion miles). Astronomers use the light-year to measure distances between the stars. Light-year Light travels at about 300,000 kilometers a second. A light-year is a unit of distance not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602 ...
... trillion miles). Astronomers use the light-year to measure distances between the stars. Light-year Light travels at about 300,000 kilometers a second. A light-year is a unit of distance not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602 ...
18.2 Telescopes
... focus light. A large concave mirror (the center is thinner than the edges) collects and reflects the light to make an image. Once the image forms, the lens in the eyepiece magnifies the image. Reflecting telescopes are very helpful for viewing dim or dark objects. Large reflecting telescopes can see ...
... focus light. A large concave mirror (the center is thinner than the edges) collects and reflects the light to make an image. Once the image forms, the lens in the eyepiece magnifies the image. Reflecting telescopes are very helpful for viewing dim or dark objects. Large reflecting telescopes can see ...
Galaxies
... clouds of gas and dust. Elliptical - Elliptical galaxies contain older stars and very little gas and dust. They can be different shapes ranging from round, to flattened, ...
... clouds of gas and dust. Elliptical - Elliptical galaxies contain older stars and very little gas and dust. They can be different shapes ranging from round, to flattened, ...
Telescopes and Astronomical Observations
... What can we observe? Telescopes Optical, IR, Radio, High Energy ++ Limitations Angular resolution Spectroscopy Data Handling ...
... What can we observe? Telescopes Optical, IR, Radio, High Energy ++ Limitations Angular resolution Spectroscopy Data Handling ...
Novel technique water on exoplanets
... Very Large Telescope (VLT), endorsesa new techniquethat will let astronomersefficiently search for ,water on hundreds of worlds without the need for space-basedtelescopes. Since the early 1990s scientists have found almost 1000 planets in orbit around other stars.These so-calledexoplanets are mostly ...
... Very Large Telescope (VLT), endorsesa new techniquethat will let astronomersefficiently search for ,water on hundreds of worlds without the need for space-basedtelescopes. Since the early 1990s scientists have found almost 1000 planets in orbit around other stars.These so-calledexoplanets are mostly ...
il 3 ~ )
... 1. Consider launching a spacecraft on a least-energy orbit to Mercury. That orbit is an elliptical orbit with the Sun at the focus, and with Earth and Mercury at aphelion and perihelion, respectively. Consider the orbits of Earth and Mercury circular. (a) What is the semi-major ...
... 1. Consider launching a spacecraft on a least-energy orbit to Mercury. That orbit is an elliptical orbit with the Sun at the focus, and with Earth and Mercury at aphelion and perihelion, respectively. Consider the orbits of Earth and Mercury circular. (a) What is the semi-major ...
Hubble Telescope Pictures
... distance of these objects from earth, i.e. one(1) light year = 5,865,696,000,000 or 6 trillion miles. ...
... distance of these objects from earth, i.e. one(1) light year = 5,865,696,000,000 or 6 trillion miles. ...
Chapter 8, Lesson 1, pdf
... ▪ The angle is greatest in Summer and least in winter. This means the Sun is higher in the sky at noon in summer than at noon in winter. ...
... ▪ The angle is greatest in Summer and least in winter. This means the Sun is higher in the sky at noon in summer than at noon in winter. ...
Lesson 1, The Earth
... planetary images taken from Earth and those taken from space? The sharpness and detail of the images would increase, from ground-based to satellite to probe, because there is no air in space. ...
... planetary images taken from Earth and those taken from space? The sharpness and detail of the images would increase, from ground-based to satellite to probe, because there is no air in space. ...
The First Revolution Newton`s Telescope
... Red light is bent more than blue light and therefore focuses closer to the lens. Each color focuses to a different point. While this can be compensated for to some extent by using different types of glass, Newton concluded that chromatic aberration would always be present in a refractor. Modern glas ...
... Red light is bent more than blue light and therefore focuses closer to the lens. Each color focuses to a different point. While this can be compensated for to some extent by using different types of glass, Newton concluded that chromatic aberration would always be present in a refractor. Modern glas ...
Tools for Studying Space
... A narrow band of radio waves is able to penetrate the atmosphere, by measuring these waves we can map the galactic distribution of hydrogen Radio Telescope – a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which absorbs ...
... A narrow band of radio waves is able to penetrate the atmosphere, by measuring these waves we can map the galactic distribution of hydrogen Radio Telescope – a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which absorbs ...
Who`s Who in Astronomy
... of astronomy that he could find His theory predicted the motions of the planets better than any other theory at the time His theory was widely accepted (most popular) for over 1500 years ...
... of astronomy that he could find His theory predicted the motions of the planets better than any other theory at the time His theory was widely accepted (most popular) for over 1500 years ...
Earth Science Chapter 24 File
... the universe that uses a lens to bend or refract light in order to magnify distant objects The most important lens in a refracting telescope, the objective lens, produces an image by bending light from a distant object so that the light converges at an area called the focus (central ...
... the universe that uses a lens to bend or refract light in order to magnify distant objects The most important lens in a refracting telescope, the objective lens, produces an image by bending light from a distant object so that the light converges at an area called the focus (central ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... 5: Draw a refracting telescope and reflecting telescopes with Newtonian, Cassegrain, prime, and coude’ focus locations, showing the path of parallel light ...
... 5: Draw a refracting telescope and reflecting telescopes with Newtonian, Cassegrain, prime, and coude’ focus locations, showing the path of parallel light ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
Section 24.2 Astronomical Tools
... A radio telescope is a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths. A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which, just like a radio antenna, absorbs and transmits these waves to an amplifier. ...
... A radio telescope is a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths. A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which, just like a radio antenna, absorbs and transmits these waves to an amplifier. ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.