CHAPTER 4 FINAL REVIEW QUESTIONS MULTIPLE CHOICE
... The distance from Alexandria to Syene is about 500 miles. On the summer solstice the sun is directly overhead at noon in Syene. At Alexandria on the summer solstice, the sun is 1/50th of the circumference of the sky (about 7°) south of the zenith. Based on this information, what is the circumference ...
... The distance from Alexandria to Syene is about 500 miles. On the summer solstice the sun is directly overhead at noon in Syene. At Alexandria on the summer solstice, the sun is 1/50th of the circumference of the sky (about 7°) south of the zenith. Based on this information, what is the circumference ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... At distance R, radiation spread over sphere of radius R: energy falling on each unit area of that sphere is Flux or ...
... At distance R, radiation spread over sphere of radius R: energy falling on each unit area of that sphere is Flux or ...
X-RAY VISION
... Until now, no NASA mission has been able to focus high-energy x-rays to make a clear, high-quality image. The Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), to be launched in early 2012, will be the first. Made up of two mirrors, including the one at the right, plus a detector and an expandable mast ...
... Until now, no NASA mission has been able to focus high-energy x-rays to make a clear, high-quality image. The Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), to be launched in early 2012, will be the first. Made up of two mirrors, including the one at the right, plus a detector and an expandable mast ...
SkyMatters Jan-2017 - CIT Blackrock Castle Observatory
... of the 4th will be the best time for viewing because the first-quarter Moon will have set and the skies should be dark. Don’t be discouraged if you live in a city or town. If you can see some stars you can see some meteors! The Quadrantids are believed to be the leftover debris from an extinct comet ...
... of the 4th will be the best time for viewing because the first-quarter Moon will have set and the skies should be dark. Don’t be discouraged if you live in a city or town. If you can see some stars you can see some meteors! The Quadrantids are believed to be the leftover debris from an extinct comet ...
c - Fsusd
... 7) A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a ______. a) quasar b) binary system c) black hole d) pulsar ...
... 7) A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a ______. a) quasar b) binary system c) black hole d) pulsar ...
Lecture 2
... Class will be in Fiske Planetarium on Tuesday (geodesic dome west of events center) ...
... Class will be in Fiske Planetarium on Tuesday (geodesic dome west of events center) ...
1 - Northwest ISD Moodle
... identified Cepheid variables (a kind of star) in several spiral nebulae, including the Andromeda Nebula and Triangulum. Long after his death, the launching of the Hubble Space His observations, in 1922–1923, proved conclusively Telescope (namedmade in honor of Hubble) in 1990 on the Space that these ...
... identified Cepheid variables (a kind of star) in several spiral nebulae, including the Andromeda Nebula and Triangulum. Long after his death, the launching of the Hubble Space His observations, in 1922–1923, proved conclusively Telescope (namedmade in honor of Hubble) in 1990 on the Space that these ...
(and 4m) NGST - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... M2: rather slow, large stroke DM to compensate ground layer and telescope figure, or to use as single DM at >3 m. (~8000 actuators) Dedicated, small field (1-2’) MCAO system (~4-6DMs). ...
... M2: rather slow, large stroke DM to compensate ground layer and telescope figure, or to use as single DM at >3 m. (~8000 actuators) Dedicated, small field (1-2’) MCAO system (~4-6DMs). ...
Expansion of the Universe
... helium on the main sequence Massive stars need higher central temperatures and pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse, and for this reason, fusion reactions in these stars proceed at a faster rate than in lower mass stars IMPORTANT: The result is that massive stars use up t ...
... helium on the main sequence Massive stars need higher central temperatures and pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse, and for this reason, fusion reactions in these stars proceed at a faster rate than in lower mass stars IMPORTANT: The result is that massive stars use up t ...
CT9
... Astronaut Dave Bowman is standing in the centrifuge of the spaceship Discovery. He drops his pen and observes it fall to the floor. Which statement below is most accurate? A: After Bowman releases the pen, the net force on the pen is zero. B: The pen falls because the centrifugal force pulls it towa ...
... Astronaut Dave Bowman is standing in the centrifuge of the spaceship Discovery. He drops his pen and observes it fall to the floor. Which statement below is most accurate? A: After Bowman releases the pen, the net force on the pen is zero. B: The pen falls because the centrifugal force pulls it towa ...
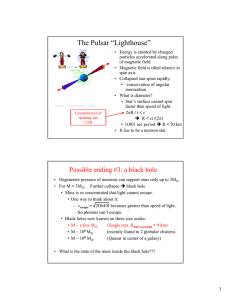
Weighing a Black Hole
... Angles for Distances? Astronomers like to measure objects in terms of angular scale (most often very small angular scales); because the objects they observe are very far away. This is done for two reasons, foremost for the practical reason that angular size on the sky is what astronomers can measure ...
... Angles for Distances? Astronomers like to measure objects in terms of angular scale (most often very small angular scales); because the objects they observe are very far away. This is done for two reasons, foremost for the practical reason that angular size on the sky is what astronomers can measure ...
Riaz - protostar sha.. - University of Hertfordshire
... molecular cloud, with the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) 4-m telescope in Chile. They found an odd feature in their image – a shadowed dark lane just to the west of the protostar with a thickness of about 54 billion kilometres (360 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun). Silho ...
... molecular cloud, with the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) 4-m telescope in Chile. They found an odd feature in their image – a shadowed dark lane just to the west of the protostar with a thickness of about 54 billion kilometres (360 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun). Silho ...
Document
... • Most stars have masses calculated this way. • Result: – The more massive the star, the more luminous it is. – The more massive the star, the hotter it is. ...
... • Most stars have masses calculated this way. • Result: – The more massive the star, the more luminous it is. – The more massive the star, the hotter it is. ...
OverviewJuly2007 - Magdalena Ridge Observatory
... mission, designed to assess and validate the technology that one day could be used to deflect or destroy an asteroid threatening the Earth. July 11, 2007 ...
... mission, designed to assess and validate the technology that one day could be used to deflect or destroy an asteroid threatening the Earth. July 11, 2007 ...
Lecture 37: The Pale Blue Dot
... planets around other stars, but the hunt is on… The ultimate goal is to find Earth-like planets in the Habitable Zones of their parent stars. The RV method is currently insensitive to Earth-mass planets. Transit methods are most sensitive to large planets, but the Kepler mission launched in 2008 is ...
... planets around other stars, but the hunt is on… The ultimate goal is to find Earth-like planets in the Habitable Zones of their parent stars. The RV method is currently insensitive to Earth-mass planets. Transit methods are most sensitive to large planets, but the Kepler mission launched in 2008 is ...
octl
... independent cloud visibility data from real time weather maps and star attenuation. Background corrected signals can be seen for an example case shown in Fig. 3 where the cloud signals follow the strong Raleigh backscatter. Tracking several satellites over the course of a cloudy night verified the a ...
... independent cloud visibility data from real time weather maps and star attenuation. Background corrected signals can be seen for an example case shown in Fig. 3 where the cloud signals follow the strong Raleigh backscatter. Tracking several satellites over the course of a cloudy night verified the a ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.