SPIE Cox Lallo Focus Model - Space Telescope Science Institute
... the two components are 450 days or 1.2 years and 2464 days or 6.7 years. The modeling of the temperature dependence has been attempted several times with gradually improving results. The first attempt in 1993 by Bély, Hasan and Meibach2 remains the basis for our current model. The main component app ...
... the two components are 450 days or 1.2 years and 2464 days or 6.7 years. The modeling of the temperature dependence has been attempted several times with gradually improving results. The first attempt in 1993 by Bély, Hasan and Meibach2 remains the basis for our current model. The main component app ...
Unit 1
... • In the 1700’s, Charles Messier was observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is ...
... • In the 1700’s, Charles Messier was observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is ...
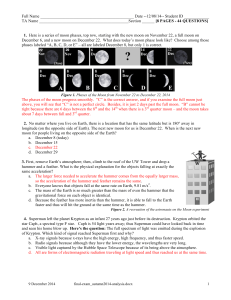
Field of View of a Small Telescope Observational
... long it took a star to move through the eyepiece and divided the result in seconds by four, you would know the field of view in arcminutes. Now, this result is only valid for objects at the celestial equator. Think about a spinning globe. A point on the equator moves a lot farther and faster than a ...
... long it took a star to move through the eyepiece and divided the result in seconds by four, you would know the field of view in arcminutes. Now, this result is only valid for objects at the celestial equator. Think about a spinning globe. A point on the equator moves a lot farther and faster than a ...
Assignment 4A
... a. a unit of wavelength b. a unit of frequency c. a unit of velocity d. a unit of loudness e. a wellknown carrental company ____ 12. A fashion designer decides to bring out a new line of clothing which reflects the longest wavelength of visible light. These articles of clothing will be what color ...
... a. a unit of wavelength b. a unit of frequency c. a unit of velocity d. a unit of loudness e. a wellknown carrental company ____ 12. A fashion designer decides to bring out a new line of clothing which reflects the longest wavelength of visible light. These articles of clothing will be what color ...
Line Survey of Large Organic Molecules toward Orion IRc2 in the 73
... IRc2, which is an infrared star, is located at the center of this cloud and the region toward this star has been investigated so far. In this survey, we observed between 73 and 89 GHz by using 45m telescope of the Nobeyama Radio Observatory (NRO), which has a narrow beam size of ~20". As major examp ...
... IRc2, which is an infrared star, is located at the center of this cloud and the region toward this star has been investigated so far. In this survey, we observed between 73 and 89 GHz by using 45m telescope of the Nobeyama Radio Observatory (NRO), which has a narrow beam size of ~20". As major examp ...
Solutions Set #2 1. What is the B
... telescope at the sun; its like your pupil just got a thousand times bigger. (Although the secondary blocks some of that.) d) The star Sirius is roughly 25 magnitudes dimmer than the Sun. When you look through the 8” telescope at Sirius, roughly how many photons enter your eye each second? By the mag ...
... telescope at the sun; its like your pupil just got a thousand times bigger. (Although the secondary blocks some of that.) d) The star Sirius is roughly 25 magnitudes dimmer than the Sun. When you look through the 8” telescope at Sirius, roughly how many photons enter your eye each second? By the mag ...
Death by Black Hole Study Guide-Answers - crespiphysics
... 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly distributed in the sky 5. In 1923, how did Edwin Hubble determine the distance to the Andromeda nebula? What did this prov ...
... 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly distributed in the sky 5. In 1923, how did Edwin Hubble determine the distance to the Andromeda nebula? What did this prov ...
here - Atomki
... The Virial theorem can be obtain by multiplying the hydrostatic equil. Eqn. (2) by the volume (V=4/3 πr3) and integrate over the total mass, M: ∫V dP/dm = - 1/3 ∫(Gm/r) dm = 1/3 Egrav The left hand-side term is related to the internal energy, E int. After some algebra, one obtains for an ideal mono- ...
... The Virial theorem can be obtain by multiplying the hydrostatic equil. Eqn. (2) by the volume (V=4/3 πr3) and integrate over the total mass, M: ∫V dP/dm = - 1/3 ∫(Gm/r) dm = 1/3 Egrav The left hand-side term is related to the internal energy, E int. After some algebra, one obtains for an ideal mono- ...
What are the Spectral Lines? - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... The History and Philosophy of Astronomy (Lecture 16: Birth of Astrophysics I) ...
... The History and Philosophy of Astronomy (Lecture 16: Birth of Astrophysics I) ...
powerpoint - Physics @ IUPUI
... Why variable stars are important • Variable stars have a relationship between their period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure d ...
... Why variable stars are important • Variable stars have a relationship between their period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure d ...
E1 Introduction to the universe
... the matter could be found in Massive Astronomical Compact Halo Objects or MACHOs for short. There is some evidence that lots of ordinary matter does exist in these groupings. These can be thought of as low-mass failed stars or high-mass planets. They could even be black holes. These would produce li ...
... the matter could be found in Massive Astronomical Compact Halo Objects or MACHOs for short. There is some evidence that lots of ordinary matter does exist in these groupings. These can be thought of as low-mass failed stars or high-mass planets. They could even be black holes. These would produce li ...
Ch 3 PPT - Blountstown Middle School
... • A spectroscope spreads light into different wavelengths. • Using spectroscopes, astronomers can study stars’ characteristics, including temperatures, compositions, and energies. ...
... • A spectroscope spreads light into different wavelengths. • Using spectroscopes, astronomers can study stars’ characteristics, including temperatures, compositions, and energies. ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... schmushed it all together into what is now the central bulge. • Then, more slowly, gas fell in from farther out, had angular momentum, and so settled into a flat disk, and only gradually is forming itself into stars. • Globular clusters formed during the proto-galaxy stage and during the time they c ...
... schmushed it all together into what is now the central bulge. • Then, more slowly, gas fell in from farther out, had angular momentum, and so settled into a flat disk, and only gradually is forming itself into stars. • Globular clusters formed during the proto-galaxy stage and during the time they c ...
Stars: the Hertzsprung
... star with a given mass and chemical composition – if we start with a just formed protostar of a given mass and chemical composition, we can calculate how that star will evolve over its entire life. • This is extremely useful because it greatly simplifies the study of stars and is the basic reason wh ...
... star with a given mass and chemical composition – if we start with a just formed protostar of a given mass and chemical composition, we can calculate how that star will evolve over its entire life. • This is extremely useful because it greatly simplifies the study of stars and is the basic reason wh ...
It`s cosmic! - NSW Department of Education
... Each galaxy is a very large spinning structure. It contains billions of stars. It also contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Some of the stars, like our Sun, have planets. All these things are held together in each galaxy by gravitational forces. (You feel a gravitational force on Earth. I ...
... Each galaxy is a very large spinning structure. It contains billions of stars. It also contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Some of the stars, like our Sun, have planets. All these things are held together in each galaxy by gravitational forces. (You feel a gravitational force on Earth. I ...
telescope field of view
... The Sun, stars, and any object seen in the sky rise somewhere near east and set somewhere near west (with a few exceptions – circumpolar stars). Exact locations of rising/setting depend on the object’s declination. During the time between rising and setting, the object must move from east to west, a ...
... The Sun, stars, and any object seen in the sky rise somewhere near east and set somewhere near west (with a few exceptions – circumpolar stars). Exact locations of rising/setting depend on the object’s declination. During the time between rising and setting, the object must move from east to west, a ...
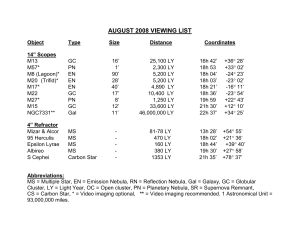
August
... pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraordinary color contrast. If it is a binary it would have an orbital period of about 75,000 years. The yel ...
... pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraordinary color contrast. If it is a binary it would have an orbital period of about 75,000 years. The yel ...
Solutions - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... 1. (a) Assuming that the surface temperature of the Sun is T = 5800 K, use Stefan’s law to determine the rest mass lost per second to radiation by the Sun. Take the Sun’s radius to be R = 7.0 × 108 meters. (b) What fraction of the Sun’s rest mass is lost each year from electromagnetic radiation? T ...
... 1. (a) Assuming that the surface temperature of the Sun is T = 5800 K, use Stefan’s law to determine the rest mass lost per second to radiation by the Sun. Take the Sun’s radius to be R = 7.0 × 108 meters. (b) What fraction of the Sun’s rest mass is lost each year from electromagnetic radiation? T ...
inaugural091112
... • Process is rapid: clouds consumed within few hundred million years • Yet we detect plenty of clouds: clouds exist • Some Unknown Unknown (UU) holds up the clouds ...
... • Process is rapid: clouds consumed within few hundred million years • Yet we detect plenty of clouds: clouds exist • Some Unknown Unknown (UU) holds up the clouds ...
TOP 78 ASTRONOMY FACTS 1. The solar system consists of the
... 56. Galileo Galilei (February 15, 1564 – January 8, 1642) was an Italian physicist, astronomer, and philosopher who is closely associated with the scientific revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope, a variety of astronomical observations, the first and second laws of motio ...
... 56. Galileo Galilei (February 15, 1564 – January 8, 1642) was an Italian physicist, astronomer, and philosopher who is closely associated with the scientific revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope, a variety of astronomical observations, the first and second laws of motio ...
Feb 2015 - Bluewater Astronomical Society
... lobe of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Along the horizon a relatively broad, raised portion of material appears to be abruptly truncated in the top left. Zooming into either side of the inner portion of the wall suggests the presence of slightly brighter material – perhaps more recently exposed th ...
... lobe of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Along the horizon a relatively broad, raised portion of material appears to be abruptly truncated in the top left. Zooming into either side of the inner portion of the wall suggests the presence of slightly brighter material – perhaps more recently exposed th ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.