Sky & Astronomy - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Galileo (2) His telescope enabled him to see many, many new fainter stars that had never been seen before The superior resolution and magnification of his telescope enabled him to see pits and craters on the Moon see spots on the Sun : these objects are not static they decay, they are not god-like. ...
... Galileo (2) His telescope enabled him to see many, many new fainter stars that had never been seen before The superior resolution and magnification of his telescope enabled him to see pits and craters on the Moon see spots on the Sun : these objects are not static they decay, they are not god-like. ...
The Spitzer Space Telescope
... Fun Facts The Spitzer ran out of liquid helium on May 15, 2009 Only IRAC instrument is functional Spitzer Warm Mission The only one of the Great Observatories not launched ...
... Fun Facts The Spitzer ran out of liquid helium on May 15, 2009 Only IRAC instrument is functional Spitzer Warm Mission The only one of the Great Observatories not launched ...
Learning About Stars
... Earth rotates on its axis. Part of the Earth faces the sun, while the other part of Earth is in shadow. Earth’s rotation is why we have night and day. http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/Images/StarChild/questions/dayandnight.gif ...
... Earth rotates on its axis. Part of the Earth faces the sun, while the other part of Earth is in shadow. Earth’s rotation is why we have night and day. http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/Images/StarChild/questions/dayandnight.gif ...
How big are stars? How do we know?
... a) relatively hot main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. b) relatively cool giant stars that are relatively close to the Sun. c) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively far from the Sun. d) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. e ...
... a) relatively hot main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. b) relatively cool giant stars that are relatively close to the Sun. c) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively far from the Sun. d) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. e ...
1-structure-of-the-universe-and-the-big-bang
... C) shift toward the blue end of the spectrum D) shift toward the red end of the spectrum 17. In a Doppler red shift, the observed wavelengths of light from distant celestial objects appear closer to the red end of the spectrum than light from similar nearby celestial objects. The explanation for the ...
... C) shift toward the blue end of the spectrum D) shift toward the red end of the spectrum 17. In a Doppler red shift, the observed wavelengths of light from distant celestial objects appear closer to the red end of the spectrum than light from similar nearby celestial objects. The explanation for the ...
star - TeacherWeb
... A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s Light travels about 9.46 trillion km. per year. The light you see when you look at a star left that star sometime in the past. ...
... A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s Light travels about 9.46 trillion km. per year. The light you see when you look at a star left that star sometime in the past. ...
aaswinter06
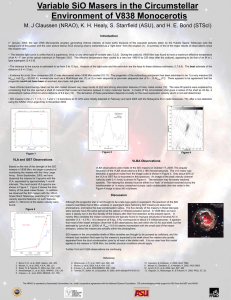
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
Wh t i C l ? What is Cosmology?
... Consider spherical shell of radius r and thickness dr Number of stars in this shell is 4πr2n dr, where n is number density of stars Light from each star is L/4πr2, therefore light from shell is nL dr, independent of r therefore, in infinite universe, night sky should be infinitely bright (or at leas ...
... Consider spherical shell of radius r and thickness dr Number of stars in this shell is 4πr2n dr, where n is number density of stars Light from each star is L/4πr2, therefore light from shell is nL dr, independent of r therefore, in infinite universe, night sky should be infinitely bright (or at leas ...
Characteristics of Stars
... distance from Earth and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in two different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightness fairly easily using el ...
... distance from Earth and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in two different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightness fairly easily using el ...
Distance Between Stars - cK-12
... Distances to stars that are relatively close to us can be measured using parallax. Parallax is an apparent shift in position that takes place when the position of the observer changes. To see an example of parallax, try holding your finger about 1 foot (30 cm) in front of your eyes. Now, while focus ...
... Distances to stars that are relatively close to us can be measured using parallax. Parallax is an apparent shift in position that takes place when the position of the observer changes. To see an example of parallax, try holding your finger about 1 foot (30 cm) in front of your eyes. Now, while focus ...
Series Telescopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... A Newtonian reflector uses a single concave mirror as its primary. Light enters the tube traveling to the mirror at the back end. There light is bent forward in the tube to a single point, its focal point. Since putting your head in front of the telescope to look at the image with an eyepiece would ...
... A Newtonian reflector uses a single concave mirror as its primary. Light enters the tube traveling to the mirror at the back end. There light is bent forward in the tube to a single point, its focal point. Since putting your head in front of the telescope to look at the image with an eyepiece would ...
Lecture Eight (Powerpoint format) - Flash
... As time progressed, astronomers have discovered increasingly complex molecules like formaldehyde (H2CO) and ethyl alcohol (C2H6O) in molecular clouds. These complex molecules would require not only two atoms colliding and sticking, but many such collisions. Such a gaseous phase process is inde ...
... As time progressed, astronomers have discovered increasingly complex molecules like formaldehyde (H2CO) and ethyl alcohol (C2H6O) in molecular clouds. These complex molecules would require not only two atoms colliding and sticking, but many such collisions. Such a gaseous phase process is inde ...
TELESCOPE CONCEPTS SUPER VIEWS OF SPACE
... track of moving objects. If your eye did not constantly update its information about where things are, moving objects would become a blur. When collecting light from faint objects such as distant galaxies, however, a twentieth of a second is not enough time for your eye to see anything at all, even ...
... track of moving objects. If your eye did not constantly update its information about where things are, moving objects would become a blur. When collecting light from faint objects such as distant galaxies, however, a twentieth of a second is not enough time for your eye to see anything at all, even ...
Stellar Evolution Before…..During……and After…. The Main
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime ...
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime ...
5-E Galaxy T - McDonald Observatory
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
The Mystery of Gamma Ray Bursts
... energy gamma rays. Some astronomers suggest that a short GRB may simply be an observational artefact - recording the edge of the energy cone from a long GRB. X-ray flashes are also observed, and may be classified as ‘soft’ gamma ray bursts, perhaps also seen as the edge of a long GRB cone (Imaginewe ...
... energy gamma rays. Some astronomers suggest that a short GRB may simply be an observational artefact - recording the edge of the energy cone from a long GRB. X-ray flashes are also observed, and may be classified as ‘soft’ gamma ray bursts, perhaps also seen as the edge of a long GRB cone (Imaginewe ...
giant molecular clouds
... Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
... Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
May 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... Imaging Conference) and the astronomy convention was called NEAF (Northeast Astronomy Forum). Some of you may have heard of them or may have even been to one or both. If you have not, I highly recommend taking the time to go one year. The events are held in Suffern, NY, just outside of New York City. ...
... Imaging Conference) and the astronomy convention was called NEAF (Northeast Astronomy Forum). Some of you may have heard of them or may have even been to one or both. If you have not, I highly recommend taking the time to go one year. The events are held in Suffern, NY, just outside of New York City. ...
Searching for stars in high-velocity clouds
... In 2001 May we used the imaging CCD camera on the 1.0-m Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope to image the central regions of three compact HVCs from the list of Braun & Burton (1999). A single 10-arcmin field was observed for each HVC in two colours (V and I). The field of view is somewhat smaller than the typ ...
... In 2001 May we used the imaging CCD camera on the 1.0-m Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope to image the central regions of three compact HVCs from the list of Braun & Burton (1999). A single 10-arcmin field was observed for each HVC in two colours (V and I). The field of view is somewhat smaller than the typ ...
Spring 2017 - Astronomers of Humboldt
... the research being done in his “Gravitational Research Lab” and the work they are doing to test Einstein’s theory of relativity. As one of our members remarked, “I am so proud to live so near to a top tier university that is always at the cutting edge of contemporary research”. HSU Professor Paola H ...
... the research being done in his “Gravitational Research Lab” and the work they are doing to test Einstein’s theory of relativity. As one of our members remarked, “I am so proud to live so near to a top tier university that is always at the cutting edge of contemporary research”. HSU Professor Paola H ...
An Introduction to Adaptive Optics
... corrections than monolithic types. – Requires frequent calibration – Diffraction due to gaps between segments ...
... corrections than monolithic types. – Requires frequent calibration – Diffraction due to gaps between segments ...
The Stellar Graveyard
... that is simply cooling off and producing no additional energy of its own. After billion of years, the white dwarf will cool down so that it no longer emits much light in the optical part of the spectrum. The timescale for this to occur is longer than the age of the Galaxy so this configuration has n ...
... that is simply cooling off and producing no additional energy of its own. After billion of years, the white dwarf will cool down so that it no longer emits much light in the optical part of the spectrum. The timescale for this to occur is longer than the age of the Galaxy so this configuration has n ...
Dobsonians Reflector Telescopes
... wave distortion inside telescope tube (tube currents). Allow a longer cooling time for larger optics. If you are using an equatorial mount, use this time for polar alignment. ...
... wave distortion inside telescope tube (tube currents). Allow a longer cooling time for larger optics. If you are using an equatorial mount, use this time for polar alignment. ...
Document
... 1. Why is Astronomy different that any other science in the way in which the scientific method is applied (especially when dealing with stars and galaxies)? ...
... 1. Why is Astronomy different that any other science in the way in which the scientific method is applied (especially when dealing with stars and galaxies)? ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.