solartele
... The designs were a general method of shortening telescopes. Four years previously, in 1672, Hooke had engaged Isaac Newton in a dispute over priority of the reflecting telescope. An interesting aspect of the development of the reflecting telescope was that the early claims were not so much for a ful ...
... The designs were a general method of shortening telescopes. Four years previously, in 1672, Hooke had engaged Isaac Newton in a dispute over priority of the reflecting telescope. An interesting aspect of the development of the reflecting telescope was that the early claims were not so much for a ful ...
Stellar population models in the Near-Infrared Meneses
... longer possible to resolve individual stars within them. However, it is still possible to obtain valuable information about the different types of stars within these systems, by analysing their electromagnetic spectrum in detail. This thesis is focussed on the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range, w ...
... longer possible to resolve individual stars within them. However, it is still possible to obtain valuable information about the different types of stars within these systems, by analysing their electromagnetic spectrum in detail. This thesis is focussed on the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range, w ...
Gemini and the Virtual Observatory
... resources now being devoted to developing “fully processed” data pipelines; however, more FTEs needed and welcomed!! • Channel some Aus-VO resources into developing pipelines for instrument modes popular with Aus Gemini users?? Australian Virtual Observatory – 2003 Workshop ATNF, Marsfield, 17-18 No ...
... resources now being devoted to developing “fully processed” data pipelines; however, more FTEs needed and welcomed!! • Channel some Aus-VO resources into developing pipelines for instrument modes popular with Aus Gemini users?? Australian Virtual Observatory – 2003 Workshop ATNF, Marsfield, 17-18 No ...
Duncan Wright
... To be capable of detecting the <10 m s-1 Doppler amplitudes expected from habitable zone planets around M Dwarfs we need to be able to calibrate the UCLES spectrograph to < 2 m s-1. This is possible with CYCLOPS due to the tremendous amount of position information available when we take a calibratio ...
... To be capable of detecting the <10 m s-1 Doppler amplitudes expected from habitable zone planets around M Dwarfs we need to be able to calibrate the UCLES spectrograph to < 2 m s-1. This is possible with CYCLOPS due to the tremendous amount of position information available when we take a calibratio ...
Distance Ladder
... •Typically 300 km/s or so How to to determine distances: is moving away from us at •Measure v using Doppler shift 2100 km/s? A) 1 Mly D) 484 Mly •Deduce the distance from: B) 10 Mly E) 4,840 Mly v = H0d C) 100 Mly F) 48,400 Mly ...
... •Typically 300 km/s or so How to to determine distances: is moving away from us at •Measure v using Doppler shift 2100 km/s? A) 1 Mly D) 484 Mly •Deduce the distance from: B) 10 Mly E) 4,840 Mly v = H0d C) 100 Mly F) 48,400 Mly ...
Chapter 12
... 4. Modern measuring devices allow astronomers to determine magnitudes to an accuracy of 0.001 or better. 5. A few stars (e.g., Sirius) are so bright that they have negative magnitudes. Sirius’s apparent magnitude is –1.43 (it is about 10 times brighter than an average first-magnitude star). 6. Moder ...
... 4. Modern measuring devices allow astronomers to determine magnitudes to an accuracy of 0.001 or better. 5. A few stars (e.g., Sirius) are so bright that they have negative magnitudes. Sirius’s apparent magnitude is –1.43 (it is about 10 times brighter than an average first-magnitude star). 6. Moder ...
Filters and General Equipment for Astronomical Observing
... This filter has been used by the author for observing the ice caps of Mars during its close encounter in 2003 and found that despite the low altitude of Mars from the UK during that apparition the filter worked well in bringing out these features and even hinted at other rocky features on the planet ...
... This filter has been used by the author for observing the ice caps of Mars during its close encounter in 2003 and found that despite the low altitude of Mars from the UK during that apparition the filter worked well in bringing out these features and even hinted at other rocky features on the planet ...
In This Issue The Hottest Planet in the Solar System President`s Article
... Earth to complete exactly one full rotation on its axis (using a distant star … not our sun … as a way to measure when the rotation is completed.) But in that same amount of time, the Earth will have moved forward in its approximately 365¼ day orbit around the Sun — by just shy of 1º. This means the ...
... Earth to complete exactly one full rotation on its axis (using a distant star … not our sun … as a way to measure when the rotation is completed.) But in that same amount of time, the Earth will have moved forward in its approximately 365¼ day orbit around the Sun — by just shy of 1º. This means the ...
Spiral Galaxies - Astronomy Centre
... • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
... • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
An introduce of the spectrograph of the GALEX
... Astro 1 and 2: UV Intensified Telescope (UIT), Hopkins UV Telescope (HUT), Wisconsin UV Photo Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE). ...
... Astro 1 and 2: UV Intensified Telescope (UIT), Hopkins UV Telescope (HUT), Wisconsin UV Photo Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE). ...
Personal Digital Assistants
... planets up to 9000 starts Calculates twilight times, moon phases, magnitude, distance, rise and set times and much more. ...
... planets up to 9000 starts Calculates twilight times, moon phases, magnitude, distance, rise and set times and much more. ...
Autoguiding - Thrush Observatory
... camera with a built-in auto guider like the SBIG ST7, ST8 and ST9 cameras or a CCD which can download a part of the image without deleting all the pixels, like the StarlightXpress MX series. ...
... camera with a built-in auto guider like the SBIG ST7, ST8 and ST9 cameras or a CCD which can download a part of the image without deleting all the pixels, like the StarlightXpress MX series. ...
poster208
... consistent with envelope material recently heated by a central massive (proto)star (see Fig. 3). This suggests that the observed sources may have experienced a prestellar phase with gas temperature similar to those in the nearby low-mass cores (~10 K). ...
... consistent with envelope material recently heated by a central massive (proto)star (see Fig. 3). This suggests that the observed sources may have experienced a prestellar phase with gas temperature similar to those in the nearby low-mass cores (~10 K). ...
The Optical Design of the Background Emission Anisotropy Scanning Telescope
... 3. BEAM PATTERN Once we had a design that met our specification, we used GRASP8 software to calculate both the illumination on the ...
... 3. BEAM PATTERN Once we had a design that met our specification, we used GRASP8 software to calculate both the illumination on the ...
Motions in the Night Sky and the Celestial Sphere
... of the solar system may include an accurate representation of the planets’ sizes relative to one another, but not their distances from one another. Such a model would still be considered a scientific model. Several scientific models have been developed that mimic, with some accuracy, the motions of ...
... of the solar system may include an accurate representation of the planets’ sizes relative to one another, but not their distances from one another. Such a model would still be considered a scientific model. Several scientific models have been developed that mimic, with some accuracy, the motions of ...
Stellar Evolution
... Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
April 2015 - Southern Astronomical Society
... dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this invisible material might be. Dark matter does not reflect or absorb light. But its presence c ...
... dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this invisible material might be. Dark matter does not reflect or absorb light. But its presence c ...
Star Constellations
... Ancient Babylonian astronomers created the Zodiac. The Zodiac is a circle that divides the ecliptic into twelve 30-degree zones. Each zone contains a constellation, many of them animals. Horoscopes based on these astrological signs first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt in around 50 BC. These early peopl ...
... Ancient Babylonian astronomers created the Zodiac. The Zodiac is a circle that divides the ecliptic into twelve 30-degree zones. Each zone contains a constellation, many of them animals. Horoscopes based on these astrological signs first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt in around 50 BC. These early peopl ...
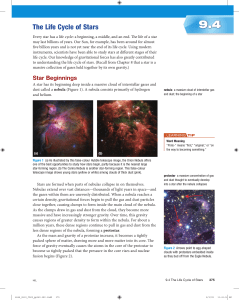
The Life Cycle of Stars
... stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area than the hotter, dim stars, resulting in more light being produced. The large, bright, cool stars are called red giants. The small, dim, hot stars are called white dwarfs. The hottest, most luminous stars are very large stars ...
... stars? It was reasoned that these cooler stars have a greater surface area than the hotter, dim stars, resulting in more light being produced. The large, bright, cool stars are called red giants. The small, dim, hot stars are called white dwarfs. The hottest, most luminous stars are very large stars ...
Manual - TUM
... 100 - 1000 solar masses and their diameters are 1 - 10 pc. A well known example for an open cluster is the Pleiades cluster (see Fig. 1). In our Galaxy more than 1100 open clusters are known. The estimated total number of Galactic open clusters is ∼ 2 · 104 . Globular clusters, on the other hand, ar ...
... 100 - 1000 solar masses and their diameters are 1 - 10 pc. A well known example for an open cluster is the Pleiades cluster (see Fig. 1). In our Galaxy more than 1100 open clusters are known. The estimated total number of Galactic open clusters is ∼ 2 · 104 . Globular clusters, on the other hand, ar ...
PULSE@Parkes science and technology overview
... necessary to plan and produce the final versions of the 1) observing system, 2) data monitoring, 3) data log, 4) data storage and archiving, 5) link between Epping and Parkes, 6) web access and 7) software for pulsar searching and timing. This work could be undertaken by existing group members (mai ...
... necessary to plan and produce the final versions of the 1) observing system, 2) data monitoring, 3) data log, 4) data storage and archiving, 5) link between Epping and Parkes, 6) web access and 7) software for pulsar searching and timing. This work could be undertaken by existing group members (mai ...
RTFS Test - 2017 BCS Cobra
... 75. Two stars are each observed in January and again in July. Star A has a parallax of 1.03 arcseconds, while the Star B has a parallax of 1.70 arcseconds. Which star is closer to earth? 76. What process is the main energy source of the star Aldebaran, a red ...
... 75. Two stars are each observed in January and again in July. Star A has a parallax of 1.03 arcseconds, while the Star B has a parallax of 1.70 arcseconds. Which star is closer to earth? 76. What process is the main energy source of the star Aldebaran, a red ...
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the same behavioral patterns as the distant quasars. Quasars are voracious consumers, greedily gobbling up the material around them at an enormous ra ...
... have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the same behavioral patterns as the distant quasars. Quasars are voracious consumers, greedily gobbling up the material around them at an enormous ra ...
Potential Meteorite Impact - Albert
... Where do they come from? They probably come from within our own solar system, rather than interstellar space. They may share a common origin with the asteroids. Some evidence indicates an origin from comets. Several "shooting stars" or meteors per hour can usually be seen on any given night. Sometim ...
... Where do they come from? They probably come from within our own solar system, rather than interstellar space. They may share a common origin with the asteroids. Some evidence indicates an origin from comets. Several "shooting stars" or meteors per hour can usually be seen on any given night. Sometim ...
Potential meteorite impact - Albert
... are heated to incandescence by the friction of the air. The bright trails that are coming through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are ter ...
... are heated to incandescence by the friction of the air. The bright trails that are coming through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are ter ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.