RTF Version
... The Westminster system is defined by its distinctive accountability features: the twin tenets of parliamentary sovereignty and responsible government. Under this constitutional system, Parliament can make any law it wishes within the limits of the constitution—for example, the division of jurisdicti ...
... The Westminster system is defined by its distinctive accountability features: the twin tenets of parliamentary sovereignty and responsible government. Under this constitutional system, Parliament can make any law it wishes within the limits of the constitution—for example, the division of jurisdicti ...
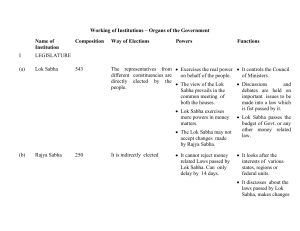
Second chamber in Indian parliament: Role and
... The Union Constitution Committee, set up by the Constituent Assembly under the chairmanship of Shri Jawaharlal Nehru, in its report presented to the Assembly on 21 July 1947, made certain proposals in respect of the Second Chamber at the Centre. The Report of the Committee was also discussed in the ...
... The Union Constitution Committee, set up by the Constituent Assembly under the chairmanship of Shri Jawaharlal Nehru, in its report presented to the Assembly on 21 July 1947, made certain proposals in respect of the Second Chamber at the Centre. The Report of the Committee was also discussed in the ...
Research Report on "Process of Appointment of Senior Members of
... to becoming the Lord Chancellor. However, this has not been the case since then. See Diana Woodhouse, The Office of Lord Chancellor, Portland, Oregon: Hart Publishing, 2001, p.11. The disqualifications for the House of Commons are (1) (a) minority (being aged under 21); (b) severe mental illness; (c ...
... to becoming the Lord Chancellor. However, this has not been the case since then. See Diana Woodhouse, The Office of Lord Chancellor, Portland, Oregon: Hart Publishing, 2001, p.11. The disqualifications for the House of Commons are (1) (a) minority (being aged under 21); (b) severe mental illness; (c ...
parliamentary democracy in indian political environment
... any time, the lack of a definite election calendar can be abused. Previously under some systems, such as the British, a ruling party could schedule elections when it felt that it was likely to retain power, and so avoid elections at times of unpopularity. (Election timing in the UK, however, is now ...
... any time, the lack of a definite election calendar can be abused. Previously under some systems, such as the British, a ruling party could schedule elections when it felt that it was likely to retain power, and so avoid elections at times of unpopularity. (Election timing in the UK, however, is now ...
Indian Constitution - Secretariat Assistant
... Fifthly, it contains procedures for its own change which is generally quite different from the procedure for the enactment of ordinary laws. Sixthly, the constitution generally contains a statement of its objectives. Finally, the constitution not only lays down the rights of the citizens, but also s ...
... Fifthly, it contains procedures for its own change which is generally quite different from the procedure for the enactment of ordinary laws. Sixthly, the constitution generally contains a statement of its objectives. Finally, the constitution not only lays down the rights of the citizens, but also s ...
the executive - GEOCITIES.ws
... Prime Ministerial Government The theory that the office of the Prime Minister is now so powerful that it forms the political executive, that effectively makes the decisions. In practice, this is characterised by the dominance of the Prime Minister; the existence of an unelected ‘inner cabinet’ of a ...
... Prime Ministerial Government The theory that the office of the Prime Minister is now so powerful that it forms the political executive, that effectively makes the decisions. In practice, this is characterised by the dominance of the Prime Minister; the existence of an unelected ‘inner cabinet’ of a ...
South Asia`s Governments
... • Communist government overturned – becomes an Islamic republic • Taliban (fundamentalist Muslims) take over ...
... • Communist government overturned – becomes an Islamic republic • Taliban (fundamentalist Muslims) take over ...
Government of India

The Government of India (GoI), officially known as the Union Government and also known as the Central Government, was established by the Constitution of India, and is the governing authority of the union of 29 states and seven union territories, collectively called the Republic of India. It is located in New Delhi, the capital of India.The basic civil and criminal laws governing the citizens of India are set down in major parliamentary legislation, such as the Civil Procedure Code, the Indian Penal Code, and the Criminal Procedure Code. The union and individual state governments all each consist of executive, legislative and judicial branches. The legal system as applicable to the federal and individual state governments is based on the English Common and Statutory Law. Because the seat of government is in New Delhi, ""New Delhi"" is commonly used as a metonym for the Central Government.ABCD