Infection Control - Respiratory Therapy Files
... to drain back into reservoir. Sterilize or high-level disinfect large-volume nebulizers between patients and after every 24 hours of use on the same patient. ...
... to drain back into reservoir. Sterilize or high-level disinfect large-volume nebulizers between patients and after every 24 hours of use on the same patient. ...
Additional risk factors for infection by multidrug
... In 2002, Deborah Friedman and colleagues [3] proposed a definition of HCAI including the above subgroups of patients, but despite being widely used in clinical studies [4-9], there is a lack of consensus regarding risk factors, and more recent studies have included additional risk factors such as an ...
... In 2002, Deborah Friedman and colleagues [3] proposed a definition of HCAI including the above subgroups of patients, but despite being widely used in clinical studies [4-9], there is a lack of consensus regarding risk factors, and more recent studies have included additional risk factors such as an ...
Disease challenges facing the livestock industry in - IFAH
... Vector-borne zoonotic diseases: West Nile fever (WNF) ...
... Vector-borne zoonotic diseases: West Nile fever (WNF) ...
May Phylogenetic Analysis Support Epidemiological Investigation in
... Indian strains, two clustered together and were statistically supported, whereas one clustered with a strain infection affecting an Italian citizen along with three cases from India. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the viral from ...
... Indian strains, two clustered together and were statistically supported, whereas one clustered with a strain infection affecting an Italian citizen along with three cases from India. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the viral from ...
Infectious Diseases and Human Population History
... came large enough to sustain direct life cycle bacterial and viral infec5. The age-dependent mortality rate due to an outbreak of measles in the tions. It is in these first cities that the Figure population of the Faeroe Islands in 1846 (after Panum 1940). now common diseases of humans started to ap ...
... came large enough to sustain direct life cycle bacterial and viral infec5. The age-dependent mortality rate due to an outbreak of measles in the tions. It is in these first cities that the Figure population of the Faeroe Islands in 1846 (after Panum 1940). now common diseases of humans started to ap ...
VA Bacterial Diseases
... – Properties of the Genus Neiserria • Gram-negative cocci in pairs • Several species; some of which are normal colon flora • Fastidious nutritional requirements Grow best on chocolate agar ...
... – Properties of the Genus Neiserria • Gram-negative cocci in pairs • Several species; some of which are normal colon flora • Fastidious nutritional requirements Grow best on chocolate agar ...
PDF
... dormitory, collected by leveraging the residents’ use of cellular phones. The data are based on daily symptom surveys taken over a period of four months and proximity tracking through cellular phones. We demonstrate that using a Bayesian, discrete-time multi-agent model of infection to model real-wo ...
... dormitory, collected by leveraging the residents’ use of cellular phones. The data are based on daily symptom surveys taken over a period of four months and proximity tracking through cellular phones. We demonstrate that using a Bayesian, discrete-time multi-agent model of infection to model real-wo ...
ASYMPTOMATIC INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS FOR
... through contact with water or soil contaminated with urine or other body fluids from infected wild or domestic animals. Exposure of skin or mucous membranes to leptospires can lead to infection.1–3 Clinical signs and symptoms are variable and range from subclinical to potentially fatal manifestation ...
... through contact with water or soil contaminated with urine or other body fluids from infected wild or domestic animals. Exposure of skin or mucous membranes to leptospires can lead to infection.1–3 Clinical signs and symptoms are variable and range from subclinical to potentially fatal manifestation ...
Reparatory tract infection
... community. In some communities, up to 50% of Staph aureus infections are due to organisms resistant to the antibiotic methicillin. This organism is referred to as MRSA (methicillinresistant Staph aureus) and requires special antibiotics when it causes infection. It can cause pneumonia but also frequ ...
... community. In some communities, up to 50% of Staph aureus infections are due to organisms resistant to the antibiotic methicillin. This organism is referred to as MRSA (methicillinresistant Staph aureus) and requires special antibiotics when it causes infection. It can cause pneumonia but also frequ ...
Análisis mediante espectroscopia infrarroja FT
... efficient vaccination, in the last two decades there has been a worldwide resurgence of pertussis [2, 3]. The resurgence of the disease has been associated to various factors including suboptimal vaccines, waning immunity and pathogen adaptation to persist in vaccinated populations. Although traditi ...
... efficient vaccination, in the last two decades there has been a worldwide resurgence of pertussis [2, 3]. The resurgence of the disease has been associated to various factors including suboptimal vaccines, waning immunity and pathogen adaptation to persist in vaccinated populations. Although traditi ...
Microsporidia Affecting Forest Lepidoptera
... produce two types of environmental spores. In addition to the Nosema-type life cycle described above, microsporidia in this genus produce an additional type of spore which contains one nucleus and is enclosed in an envelope containing 8 spores. These mononucleated octospores are probably haploid and ...
... produce two types of environmental spores. In addition to the Nosema-type life cycle described above, microsporidia in this genus produce an additional type of spore which contains one nucleus and is enclosed in an envelope containing 8 spores. These mononucleated octospores are probably haploid and ...
Frogeye Leaf Spot - Purdue Extension
... the disease is a more chronic problem in the southern United States, resistance is more commonly available in varieties of maturity group V and higher. Resistance is available in some, perhaps many, varieties adapted to Indiana. However, some varieties were clearly very susceptible to frogeye leaf s ...
... the disease is a more chronic problem in the southern United States, resistance is more commonly available in varieties of maturity group V and higher. Resistance is available in some, perhaps many, varieties adapted to Indiana. However, some varieties were clearly very susceptible to frogeye leaf s ...
Serological investigation of chlamydial infection among ruminants in
... Abstract: Chlamydiae are gram negative, obligatory intracellular pathogens, which are responsible abortions in animals, birds and humans. Infection occurs by ingestion of elementary bodies from aborted fetus, uterine discharge and placenta from infected animals or via contaminated feed and water. La ...
... Abstract: Chlamydiae are gram negative, obligatory intracellular pathogens, which are responsible abortions in animals, birds and humans. Infection occurs by ingestion of elementary bodies from aborted fetus, uterine discharge and placenta from infected animals or via contaminated feed and water. La ...
acute diarrhoea
... • Distributed throughout the animal kingdom • Contaminated food or water – poultry, eggs, fast foods – may persist for months in cheese, frozen meat, or ice cream ...
... • Distributed throughout the animal kingdom • Contaminated food or water – poultry, eggs, fast foods – may persist for months in cheese, frozen meat, or ice cream ...
Infectious Disease Models 4
... • This is the key form of the equation in many infectious disease models • Total # of susceptibles infected per unit time # of Susceptibles * “Likelihood” a given susceptible will be infected per unit time = S*(“Force of Infection”) =S(c(I/N)) – Note that this is a term that multiplies both S and I ...
... • This is the key form of the equation in many infectious disease models • Total # of susceptibles infected per unit time # of Susceptibles * “Likelihood” a given susceptible will be infected per unit time = S*(“Force of Infection”) =S(c(I/N)) – Note that this is a term that multiplies both S and I ...
International Standards for Tuberculosis Care, 2009
... May take weeks to get results Requires ongoing quality assurance ...
... May take weeks to get results Requires ongoing quality assurance ...
Infection Prevention in the Classroom Setting
... Materials provided by the USA Center for Rural Public Health Preparedness at the Texas A&M Health Science Center School of Rural Public Health supported by Grant/Cooperative Agreement Number 5U90TP624250-04. Contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the o ...
... Materials provided by the USA Center for Rural Public Health Preparedness at the Texas A&M Health Science Center School of Rural Public Health supported by Grant/Cooperative Agreement Number 5U90TP624250-04. Contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the o ...
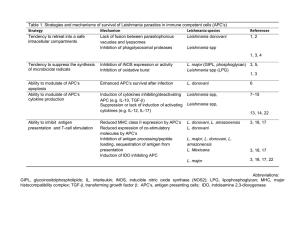
Table 1. Strategies and mechanisms of survival of Leishmania
... GIPL, glycoinositolphospholipids; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2); LPG, lipophosphoglycan; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TGF-, transforming growth factor ; APC’s, antigen presenting cells; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase ...
... GIPL, glycoinositolphospholipids; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2); LPG, lipophosphoglycan; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TGF-, transforming growth factor ; APC’s, antigen presenting cells; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase ...
Sarcocystis
Sarcocystis is a genus of protozoa. Species in this genus are parasites, the majority infecting mammals, and some infecting reptiles and birds.The life-cycle of a typical member of this genus involves two host species, a definitive host and an intermediate host. Often the definitive host is a predator and the intermediate host is its prey. The parasite reproduces sexually in the gut of the definitive host, is passed with the feces and ingested by the intermediate host. There it eventually enters muscle tissue. When the intermediate host is eaten by the definitive host, the cycle is completed. The definitive host usually does not show any symptoms of infection, but the intermediate host does.There are about 130 recognised species in this genus. Revision of the taxonomy of the genus is ongoing, and it is possible that all the currently recognised species may in fact be a much smaller number of species that can infect multiple hosts.The name Sarcocystis is dervived from Greek: sarx = flesh and kystis = bladder.