
Fever - Stony Brook University School of Medicine
... Fever frequently prompts the medical evaluation of neonates (younger than 28 days) and young infants (aged 29 to 90 days). In this age group, fever is generally defined as a temperature greater than 38.0°C (100.5°F). Up to 15% of neonates and young infants with fever have a serious bacterial infecti ...
... Fever frequently prompts the medical evaluation of neonates (younger than 28 days) and young infants (aged 29 to 90 days). In this age group, fever is generally defined as a temperature greater than 38.0°C (100.5°F). Up to 15% of neonates and young infants with fever have a serious bacterial infecti ...
vaccine
... excess of the expected level for a given time period • Pandemic: epidemic spread over several countries or continents, affecting a large number of people ...
... excess of the expected level for a given time period • Pandemic: epidemic spread over several countries or continents, affecting a large number of people ...
تحميل المحاضرة
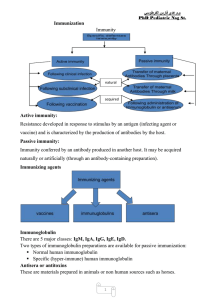
... Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. Passive immunity: Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-co ...
... Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. Passive immunity: Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-co ...
Resources: - Real Science
... The bacteriophage approach should bbee eessppeecciiaallllyy uusseeffuull ffoorr ttrreeaattiinngg ffoooodd ppooiissoonniinngg.. This is because the lower doses of antibiotic needed would not destroy friendly bacteria in the gut. This is a big problem with the usual levels of antibiotics that have to ...
... The bacteriophage approach should bbee eessppeecciiaallllyy uusseeffuull ffoorr ttrreeaattiinngg ffoooodd ppooiissoonniinngg.. This is because the lower doses of antibiotic needed would not destroy friendly bacteria in the gut. This is a big problem with the usual levels of antibiotics that have to ...
Canine superficial bacterial folliculitis: Current understanding of its
... pathogen in dogs with SBF (Cox et. al., 1984; Medleau et. al., 1986). More recently, microbiologists have shown that all the organisms identified in the past as S. intermedius were really S. pseudintermedius (Devriese et al., 2005). This has been modified further, such that there is now a Staphyloco ...
... pathogen in dogs with SBF (Cox et. al., 1984; Medleau et. al., 1986). More recently, microbiologists have shown that all the organisms identified in the past as S. intermedius were really S. pseudintermedius (Devriese et al., 2005). This has been modified further, such that there is now a Staphyloco ...
INFECTIOUS ORGANISMS OF OPHTHALMIC
... Corynebacteria have been recovered from corneal ulcers in domestic animals, usually as part of a mixed infection. In those cases, the specific etiologic role of corynebacterial organisms is not clear. Following periocular trauma, Corynebacterium may cause blepharitis, orbital cellulitis, or abscesse ...
... Corynebacteria have been recovered from corneal ulcers in domestic animals, usually as part of a mixed infection. In those cases, the specific etiologic role of corynebacterial organisms is not clear. Following periocular trauma, Corynebacterium may cause blepharitis, orbital cellulitis, or abscesse ...
Water Borne Disease
... Diseases Water borne diseases are among one of the major public health problems in developing countries like Ethiopia. They are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in all age groups particularly in children under 5 years of age. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) 3 million de ...
... Diseases Water borne diseases are among one of the major public health problems in developing countries like Ethiopia. They are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in all age groups particularly in children under 5 years of age. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) 3 million de ...
Cholangitis/ Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome
... Antibiotics that kill bacteria (known as “bactericidal antibiotics”)—against intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the animal’s body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); amoxicillin-cla ...
... Antibiotics that kill bacteria (known as “bactericidal antibiotics”)—against intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the animal’s body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); amoxicillin-cla ...
enterobacteria isolation in broiler carcasses from commercial
... concern worldwide. It is estimated that each year in the United States there are approximately 76 million food-borne illnesses (MEAD et al., 1999). Broiler meat consumption is known as one of the main sources of food-borne infections in humans ( FITZGERALDet al., 2001). Processing of poultry product ...
... concern worldwide. It is estimated that each year in the United States there are approximately 76 million food-borne illnesses (MEAD et al., 1999). Broiler meat consumption is known as one of the main sources of food-borne infections in humans ( FITZGERALDet al., 2001). Processing of poultry product ...
cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome
... Antibiotics that kill bacteria (known as “bactericidal antibiotics”)—against intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the animal’s body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); amoxicillin-cla ...
... Antibiotics that kill bacteria (known as “bactericidal antibiotics”)—against intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the animal’s body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); amoxicillin-cla ...
How To Treat Infections Without Using Antibiotics
... Do not over value non sterile site cultures Make the diagnosis Taper to or use narrow spectrum Abx Shorter duration Non bias education/CME ...
... Do not over value non sterile site cultures Make the diagnosis Taper to or use narrow spectrum Abx Shorter duration Non bias education/CME ...
Acute Inflammatory Upper Airway Obstruction
... Laryngitis is a common illness. Viruses cause most cases; diphtheria is an exception . The onset is usually characterized by an upper respiratory tract infection during which sore throat, cough, and hoarseness appear. The illness is generally mild; respiratory distress is unusual except in the ...
... Laryngitis is a common illness. Viruses cause most cases; diphtheria is an exception . The onset is usually characterized by an upper respiratory tract infection during which sore throat, cough, and hoarseness appear. The illness is generally mild; respiratory distress is unusual except in the ...
K4.Chronic renal failure for doctors
... is severe so that eGFR is <30ml/h. Fat soluble beta blockers like propranolol and calcium channel blockers are first line drugs in those without diabetes or who have advanced CRF. Diuretics should be added if there is fluid overload, but must not allow dehydration to occur. Explain to family when di ...
... is severe so that eGFR is <30ml/h. Fat soluble beta blockers like propranolol and calcium channel blockers are first line drugs in those without diabetes or who have advanced CRF. Diuretics should be added if there is fluid overload, but must not allow dehydration to occur. Explain to family when di ...
VACCINOLOGY
... protection • between 1955 and 1961, 300 million does were administered and incidence of polio declined ...
... protection • between 1955 and 1961, 300 million does were administered and incidence of polio declined ...
Streptococcus and enterococcus
... Despite the significant symptoms and clinical signs, differentiating streptococcal pharyngitis (‘strep throat’) from viral pharyngitis is impossible without microbiological or serological examination. Culture studies have demonstrated that 20–30% of cases of pharyngitis are associated with Str. pyog ...
... Despite the significant symptoms and clinical signs, differentiating streptococcal pharyngitis (‘strep throat’) from viral pharyngitis is impossible without microbiological or serological examination. Culture studies have demonstrated that 20–30% of cases of pharyngitis are associated with Str. pyog ...
Nontherapeutic Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Animal Agriculture
... that there are 1.3 million Campylobacter infections per year, of which 310 000 are drug resistant. Of all Campylobacter samples tested, 23% were resistant to ciprofloxacin, and 2% were resistant to erythromycin. In children, azithromycin and erythromycin are the preferred treatment of Campylobacter g ...
... that there are 1.3 million Campylobacter infections per year, of which 310 000 are drug resistant. Of all Campylobacter samples tested, 23% were resistant to ciprofloxacin, and 2% were resistant to erythromycin. In children, azithromycin and erythromycin are the preferred treatment of Campylobacter g ...
Herpes
... No. Either of you could have acquired the infection in the past but was unaware of mild symptoms. IgM and IgG antibodies could possibly show recent versus an old infection. I have herpes. My partner has been tested and has never had herpes. How can we prevent infection? Transmission risk can be redu ...
... No. Either of you could have acquired the infection in the past but was unaware of mild symptoms. IgM and IgG antibodies could possibly show recent versus an old infection. I have herpes. My partner has been tested and has never had herpes. How can we prevent infection? Transmission risk can be redu ...
[1] Incidence of invasive group B streptococcal disease and
... National charity Group B Strep Support campaigns for much greater awareness of this potentially devastating infection among mums-to-be. Group B Strep Support wants to see every pregnant woman given accurate information about group B Strep as a routine part of her antenatal care, coupled with the off ...
... National charity Group B Strep Support campaigns for much greater awareness of this potentially devastating infection among mums-to-be. Group B Strep Support wants to see every pregnant woman given accurate information about group B Strep as a routine part of her antenatal care, coupled with the off ...
Is strep causing that sore throat?
... grow. Many doctors have the ability to perform a rapid test in the office to determine if the sore throat is caused by the strep bacteria (and needs treatment with antibiotics) or if it is a viral infection (which cannot—and should not— be treated with antibiotics). Many doctors also recommend an ov ...
... grow. Many doctors have the ability to perform a rapid test in the office to determine if the sore throat is caused by the strep bacteria (and needs treatment with antibiotics) or if it is a viral infection (which cannot—and should not— be treated with antibiotics). Many doctors also recommend an ov ...
Is It Strep Throat
... The strep test results will help the doctor decide if you need antibiotics. Antibiotics reduce the length of time you’re sick and reduce your symptoms. Antibiotic treatment may also prevent the spread of infection to friends and family members. They can also prevent complications such as tonsil and ...
... The strep test results will help the doctor decide if you need antibiotics. Antibiotics reduce the length of time you’re sick and reduce your symptoms. Antibiotic treatment may also prevent the spread of infection to friends and family members. They can also prevent complications such as tonsil and ...
Understanding Mid-Life and Older Age Mortality Declines: Evidence from Union Army Veterans.
... This paper examines a past population, veterans of the Union Army, to establish the role of infectious disease at early, young adult ages, and later ages and of occupation at young and mid-life ages on older age mortality. It also decomposes the twentieth century increase in older age survival rate ...
... This paper examines a past population, veterans of the Union Army, to establish the role of infectious disease at early, young adult ages, and later ages and of occupation at young and mid-life ages on older age mortality. It also decomposes the twentieth century increase in older age survival rate ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... be quite efficacious in vaginal infections. In contrast gentamicin showed significant higher activity (50.3%) against vaginal isolates as that against urinary isolates (40.8%) hence may be more indicated in treatment of vaginal infection than UTIs. Generally, amoxicillin and tetracycline showed very ...
... be quite efficacious in vaginal infections. In contrast gentamicin showed significant higher activity (50.3%) against vaginal isolates as that against urinary isolates (40.8%) hence may be more indicated in treatment of vaginal infection than UTIs. Generally, amoxicillin and tetracycline showed very ...
Expected Questions 1
... 1. It is more commonly due to trabecular dysgenesis 2. Is usually managed initially by trabeculectomy 3. Rarely cause Amblyopia 4. Inheritance is usually autosomal dominant 5. It is associated with rupture of the bowman's layer Parasympathetic agent for glaucoma all are true EXCEPT: 1. The maximum u ...
... 1. It is more commonly due to trabecular dysgenesis 2. Is usually managed initially by trabeculectomy 3. Rarely cause Amblyopia 4. Inheritance is usually autosomal dominant 5. It is associated with rupture of the bowman's layer Parasympathetic agent for glaucoma all are true EXCEPT: 1. The maximum u ...
GBS - 4Drs
... Formation of solid crystals from bile saturated with cholesterol. Nidus (Ca bilirubinate) is another mechanism by which solid crystals ...
... Formation of solid crystals from bile saturated with cholesterol. Nidus (Ca bilirubinate) is another mechanism by which solid crystals ...
Gastroenteritis

Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea is a medical condition from inflammation (""-itis"") of the gastrointestinal tract that involves both the stomach (""gastro""-) and the small intestine (""entero""-). It causes some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and cramping. Dehydration may occur as a result. Gastroenteritis has been referred to as gastro, stomach bug, and stomach virus. Although unrelated to influenza, it has also been called stomach flu and gastric flu.Globally, most cases in children are caused by rotavirus. In adults, norovirus and Campylobacter are more common. Less common causes include other bacteria (or their toxins) and parasites. Transmission may occur due to consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water or via close contact with individuals who are infectious. Prevention includes drinking clean water, hand washing with soap, and breast feeding babies instead of using formula. This applies particularly where sanitation and hygiene are lacking. The rotavirus vaccine is recommended for all children.The key treatment is enough fluids. For mild or moderate cases, this can typically be achieved via oral rehydration solution (a combination of water, salts, and sugar). In those who are breast fed, continued breast feeding is recommended. For more severe cases, intravenous fluids from a healthcare centre may be needed. Antibiotics are generally not recommended. Gastroenteritis primarily affects children and those in the developing world. It results in about three to five billion cases and causes 1.4 million deaths a year.














![[1] Incidence of invasive group B streptococcal disease and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001144448_1-920b1dd5bff6cd6d41f47c259f486e9e-300x300.png)





