Foodborne disease outbreaks in United States schools
... cause) were caused by enterotoxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus. Overall staphylococcal food poisoning resulted in 6591 illnesses and 319 hospitalizations. Meat or poultry was implicated in 32 (87%) of the 37 staphylococcal outbreaks in which a single vehicle was identified. Enterotoxin made by ...
... cause) were caused by enterotoxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus. Overall staphylococcal food poisoning resulted in 6591 illnesses and 319 hospitalizations. Meat or poultry was implicated in 32 (87%) of the 37 staphylococcal outbreaks in which a single vehicle was identified. Enterotoxin made by ...
Lymphadenopathy in African Children
... or with extensive skin necrosis, curettage can be performed as an alternative to total excision as the initial procedure. This is usually part of a staged process followed by subsequent excision and wound closure. Immunocompetent patients with nontuberculous cervical lymphadenitis do, however, appea ...
... or with extensive skin necrosis, curettage can be performed as an alternative to total excision as the initial procedure. This is usually part of a staged process followed by subsequent excision and wound closure. Immunocompetent patients with nontuberculous cervical lymphadenitis do, however, appea ...
Chapter 243 – Measles
... extremities that become petechial and purpuric and progressed in a centripetal direction. The illness was frequently complicated by pneumonia and pleural effusions. It is thought that atypical measles was caused by development of circulating immune complexes that formed due to an abnormal immune res ...
... extremities that become petechial and purpuric and progressed in a centripetal direction. The illness was frequently complicated by pneumonia and pleural effusions. It is thought that atypical measles was caused by development of circulating immune complexes that formed due to an abnormal immune res ...
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) - Boston Public Health Commission
... (CDC), nearly one out of three people in the United States will develop shingles. Skin rash caused by shingles ...
... (CDC), nearly one out of three people in the United States will develop shingles. Skin rash caused by shingles ...
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria®
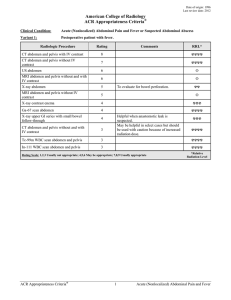
... those with fever. Several studies have shown that CT improves the final diagnosis and management of patients who present with abdominal pain [2,36-41]. Two reports have found CT to be superior to clinical evaluation for finding the cause of abdominal pain. CT interpretation was correct in 90%-96% of ...
... those with fever. Several studies have shown that CT improves the final diagnosis and management of patients who present with abdominal pain [2,36-41]. Two reports have found CT to be superior to clinical evaluation for finding the cause of abdominal pain. CT interpretation was correct in 90%-96% of ...
case report measles-mumps-rubella vaccination induced
... 12 studies from 10 countries showing the incidence of ITP after MMR vaccination ranges from 0.087 to 4 cases per 100,000 vaccine doses (Mantadakis et al, 2010). This variation may be due to different surveillance methods rather than a difference in the incidence, since the incidence was higher in co ...
... 12 studies from 10 countries showing the incidence of ITP after MMR vaccination ranges from 0.087 to 4 cases per 100,000 vaccine doses (Mantadakis et al, 2010). This variation may be due to different surveillance methods rather than a difference in the incidence, since the incidence was higher in co ...
Document
... feces and soil. As soon as it enters the human body through a major or minor wound and the conditions are anaerobic, the spores germinate and release the toxins. Tetanus may follow burns, deep puncture wounds, ear or dental infections, animal bites, ...
... feces and soil. As soon as it enters the human body through a major or minor wound and the conditions are anaerobic, the spores germinate and release the toxins. Tetanus may follow burns, deep puncture wounds, ear or dental infections, animal bites, ...
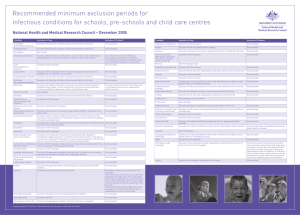
Recommended minimum exclusion periods for infectious conditions
... maintaining hygiene practices to minimise the risk of transmission. If the person is unable to comply with these practices they should be excluded until the sores are dry. Sores should be covered by a dressing where possible. ...
... maintaining hygiene practices to minimise the risk of transmission. If the person is unable to comply with these practices they should be excluded until the sores are dry. Sores should be covered by a dressing where possible. ...
pertussis cdna national guidelines for public health units
... Follow up any case in a woman known to be in the last month of pregnancy Follow up where the case is already known to be in contact with infants <6 months of age or women in the last month of pregnancy Follow up where the case is known to attend or work in a setting where there is likely to be ...
... Follow up any case in a woman known to be in the last month of pregnancy Follow up where the case is already known to be in contact with infants <6 months of age or women in the last month of pregnancy Follow up where the case is known to attend or work in a setting where there is likely to be ...
Salmonella - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... colonisation of the gastrointestinal tract without symptoms of illness (asymptomatic infection), or colonisation with the typical symptoms of acute gastroenteritis. Gastroenteritis symptoms are generally mild and may include abdominal cramps, nausea, diarrhoea, mild fever, vomiting, dehydration, hea ...
... colonisation of the gastrointestinal tract without symptoms of illness (asymptomatic infection), or colonisation with the typical symptoms of acute gastroenteritis. Gastroenteritis symptoms are generally mild and may include abdominal cramps, nausea, diarrhoea, mild fever, vomiting, dehydration, hea ...
History Repeating? Avoiding a Return to the Pre
... Selman Waksman proposed the term “antibiotic” to refer to a “compound produced by one microorganism which is capable of killing or inhibiting another.”40 This name derived from the word “antibiosis,” which the Frenchman Vuillemin had coined in 1889 to refer to the antagonistic effects of microorgan ...
... Selman Waksman proposed the term “antibiotic” to refer to a “compound produced by one microorganism which is capable of killing or inhibiting another.”40 This name derived from the word “antibiosis,” which the Frenchman Vuillemin had coined in 1889 to refer to the antagonistic effects of microorgan ...
avances
... The anaerobic setting within the large intestine of warmblooded animals is considered the primary habitat of Escherichia coli; here E. coli populations readily replicate. However, a crucial part of E. coli’s life cycle is fecaloral transmission between animal hosts. Large numbers of E. coli cells ar ...
... The anaerobic setting within the large intestine of warmblooded animals is considered the primary habitat of Escherichia coli; here E. coli populations readily replicate. However, a crucial part of E. coli’s life cycle is fecaloral transmission between animal hosts. Large numbers of E. coli cells ar ...
Maternal infectious diseases, antimicrobial therapy or immunizations
... man milk, continuing to breastfeed while on TB therapy is not a problem. TB medications appear to be safe to use while breastfeeding.[10]-[12] The breastfed neonates of women on isoniazid therapy do not need pyridoxine supplementation, unless they are receiving isoniazid themselves.[11] If mother an ...
... man milk, continuing to breastfeed while on TB therapy is not a problem. TB medications appear to be safe to use while breastfeeding.[10]-[12] The breastfed neonates of women on isoniazid therapy do not need pyridoxine supplementation, unless they are receiving isoniazid themselves.[11] If mother an ...
Lung Health: What You Should Know
... Germs* (pathogens), like bacteria and viruses that cause lung infections, can spread between people in many ways. These are known as routes of transmission. The 3 main ways are (1) by contact, (2) in a droplet or (3) through tiny remains of droplets floating in air (airborne). The most common way ge ...
... Germs* (pathogens), like bacteria and viruses that cause lung infections, can spread between people in many ways. These are known as routes of transmission. The 3 main ways are (1) by contact, (2) in a droplet or (3) through tiny remains of droplets floating in air (airborne). The most common way ge ...
Bacterial translocation: Overview of mechanisms and clinical impact
... Epithelial cell hypoxic injury and subsequent reperfusion have been postulated as major mechanisms involved in BT occurring in several conditions, such as trauma, shock of any origin and thermal injury. Oxygen tension at the tip of the intestinal villus is lower than it is in arterial blood even und ...
... Epithelial cell hypoxic injury and subsequent reperfusion have been postulated as major mechanisms involved in BT occurring in several conditions, such as trauma, shock of any origin and thermal injury. Oxygen tension at the tip of the intestinal villus is lower than it is in arterial blood even und ...
Bacterial Meningitis
... It can be caused by bacteria, fungi or a virus Bacterial Meningitis is the most common, accounting for nearly “80% of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis” People with viral meningitis are much less likely to have permanent brain damage after the infection resolves ...
... It can be caused by bacteria, fungi or a virus Bacterial Meningitis is the most common, accounting for nearly “80% of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis” People with viral meningitis are much less likely to have permanent brain damage after the infection resolves ...
- InfezMed
... ogenic E. coli strains 34 (97%) were fimbriated in children with pyelonephritis, and of 26 E. coli strains five (19%) were fimbriated in patients with cystitis. Väisänen-Rhen et al [26], reported that of 35 uropathogenic E. coli strains, 33 (94%) with P fimbriae occurred in children with clinical p ...
... ogenic E. coli strains 34 (97%) were fimbriated in children with pyelonephritis, and of 26 E. coli strains five (19%) were fimbriated in patients with cystitis. Väisänen-Rhen et al [26], reported that of 35 uropathogenic E. coli strains, 33 (94%) with P fimbriae occurred in children with clinical p ...
Strep Throat - Sun Prairie Area School District
... be permanently damaged by rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever develops 2-5 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis. Rheumatic fever became quite rare in the United States during the 1970's but, for unknown reasons, an increasing number of cases have been recognized since the mid-1980's. Post-streptococca ...
... be permanently damaged by rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever develops 2-5 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis. Rheumatic fever became quite rare in the United States during the 1970's but, for unknown reasons, an increasing number of cases have been recognized since the mid-1980's. Post-streptococca ...
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)—paradigm of an
... syndrome (SARS) came to an end in July 2003, it had caused over 8000 probable cases worldwide and more than 700 deaths. Starting in March 2003, the World Health Organization (WHO) organised an unprecedented international effort by leading laboratories working together to find the causative agent. Li ...
... syndrome (SARS) came to an end in July 2003, it had caused over 8000 probable cases worldwide and more than 700 deaths. Starting in March 2003, the World Health Organization (WHO) organised an unprecedented international effort by leading laboratories working together to find the causative agent. Li ...
Epidemiology, Treatment, and Prevention of Community
... Methicillin-resistant S aureus infections in the community are composed of escaped nosocomial isolates (particularly among people with traditional MRSA risk factors) and novel community isolates of MRSA,the latter of which we deem to be true CA-MRSA. Regardless of origin, the growing community reser ...
... Methicillin-resistant S aureus infections in the community are composed of escaped nosocomial isolates (particularly among people with traditional MRSA risk factors) and novel community isolates of MRSA,the latter of which we deem to be true CA-MRSA. Regardless of origin, the growing community reser ...
Diaper rash - Home | Learn Pediatrics
... INCIDENCE OF THE CONDITION: Diaper rash is the most common dermatitis found in infancy. Prevalence has been variably reported from 4-35% in the first 2 years of life; incidence triples in babies with diarrhea. It is not unusual for infants to have at least 1 episode of diaper rash by the time he or ...
... INCIDENCE OF THE CONDITION: Diaper rash is the most common dermatitis found in infancy. Prevalence has been variably reported from 4-35% in the first 2 years of life; incidence triples in babies with diarrhea. It is not unusual for infants to have at least 1 episode of diaper rash by the time he or ...
F441 §483.65 Infection Control §483.65(a) Infection Control
... • “Transmission-based precautions” (a.k.a. “Isolation Precautions”) refers to the actions (precautions) implemented, in addition to standard precautions, that are based upon the means of transmission (airborne, contact, and droplet) in order to prevent or control infections. • “Vancomycin resistant ...
... • “Transmission-based precautions” (a.k.a. “Isolation Precautions”) refers to the actions (precautions) implemented, in addition to standard precautions, that are based upon the means of transmission (airborne, contact, and droplet) in order to prevent or control infections. • “Vancomycin resistant ...
Gastroenteritis

Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea is a medical condition from inflammation (""-itis"") of the gastrointestinal tract that involves both the stomach (""gastro""-) and the small intestine (""entero""-). It causes some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and cramping. Dehydration may occur as a result. Gastroenteritis has been referred to as gastro, stomach bug, and stomach virus. Although unrelated to influenza, it has also been called stomach flu and gastric flu.Globally, most cases in children are caused by rotavirus. In adults, norovirus and Campylobacter are more common. Less common causes include other bacteria (or their toxins) and parasites. Transmission may occur due to consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water or via close contact with individuals who are infectious. Prevention includes drinking clean water, hand washing with soap, and breast feeding babies instead of using formula. This applies particularly where sanitation and hygiene are lacking. The rotavirus vaccine is recommended for all children.The key treatment is enough fluids. For mild or moderate cases, this can typically be achieved via oral rehydration solution (a combination of water, salts, and sugar). In those who are breast fed, continued breast feeding is recommended. For more severe cases, intravenous fluids from a healthcare centre may be needed. Antibiotics are generally not recommended. Gastroenteritis primarily affects children and those in the developing world. It results in about three to five billion cases and causes 1.4 million deaths a year.