CYPRUS
... 1. Atom (Hydrogen atom, atomic orbitals, polyelectronic atoms, electronic configuration, periodic table, atom size, ionization energy, electron affinity, oxidation state, charge). 2. Chemical Bonds and Molecular Structure (Ionic and Covalent bonds, electron coupling, electronegativity, molecular str ...
... 1. Atom (Hydrogen atom, atomic orbitals, polyelectronic atoms, electronic configuration, periodic table, atom size, ionization energy, electron affinity, oxidation state, charge). 2. Chemical Bonds and Molecular Structure (Ionic and Covalent bonds, electron coupling, electronegativity, molecular str ...
Under Choice Based Credit System Proposed syllabus and Scheme of Examination
... Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding. Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calcu ...
... Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding: General characteristics of ionic bonding. Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Statement of Born-Landé equation for calcu ...
A Classification of AP Chemistry Reactions
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
... There are four types of redox with oxygen compounds, classified by the oxidizing agent: oxidizing acids (HNO3 and H2SO4), manganese compounds (MnO4- and MnO2), chromium compounds (Cr2O72-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Oxidizing acids Oxidizing acids are strong acids with anions that can be reduced ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Example - Write the molecular, ionic, and netionic equation for the reaction of aqueous nitric acid with aqueous calcium hydroxide 6. Dissociate all aqueous strong electrolytes to get complete ionic equation not H2O 2 H+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + Ca+2(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Ca+2(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + H2O(l) ...
... Example - Write the molecular, ionic, and netionic equation for the reaction of aqueous nitric acid with aqueous calcium hydroxide 6. Dissociate all aqueous strong electrolytes to get complete ionic equation not H2O 2 H+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + Ca+2(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Ca+2(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + H2O(l) ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... NB: C4H- would be very interesting because C4H is massively abundant in IRC+10216. The cyanopolyynyl radicals like C5N are also very promising because they have EA values of 4 eV or more, so attachment is very favourable, but these radicals aren't as abundant as CnH radicals. ...
... NB: C4H- would be very interesting because C4H is massively abundant in IRC+10216. The cyanopolyynyl radicals like C5N are also very promising because they have EA values of 4 eV or more, so attachment is very favourable, but these radicals aren't as abundant as CnH radicals. ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution
... You will be expected to be able to write complete (molecular) and net ionic chemical equations. This will require you to be disciplined, committing yourself to memorizing certain information and doing much practice. To be successful you must develop the ability to recognize an acid, a base and an io ...
... You will be expected to be able to write complete (molecular) and net ionic chemical equations. This will require you to be disciplined, committing yourself to memorizing certain information and doing much practice. To be successful you must develop the ability to recognize an acid, a base and an io ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... monitoring the decrease of the Me resonance in the 1H NMR spectrum relative to an internal reference of maleic anhydride flame-sealed in a glass capillary. Decomposition of 2 displayed first-order kinetics and was independent of the concentration of 2 and the addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in ...
... monitoring the decrease of the Me resonance in the 1H NMR spectrum relative to an internal reference of maleic anhydride flame-sealed in a glass capillary. Decomposition of 2 displayed first-order kinetics and was independent of the concentration of 2 and the addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in ...
Document
... Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ionizes into H+ and anions. H2SO4(aq) 2 H+(aq) + SO42−(aq) ...
... Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ionizes into H+ and anions. H2SO4(aq) 2 H+(aq) + SO42−(aq) ...
Chapter 4 Solution Chemistry
... • When a solid is put into a liquid solvent such as water, there is a competition between the forces of attraction among the particles of the solute (solutesolute interactions) and the forces of attraction between the solvent molecules and the particles in the solute (solvent-solute interactions). W ...
... • When a solid is put into a liquid solvent such as water, there is a competition between the forces of attraction among the particles of the solute (solutesolute interactions) and the forces of attraction between the solvent molecules and the particles in the solute (solvent-solute interactions). W ...
Topic 5 Reacting masses and chemical equations notes
... The chemical formula is made up using the symbol on the periodic table. Make sure you get the correct symbol. For simple molecules the formula shows the actual number of each type of atom present. However for ionic substances and macromolecules, which have giant structures, the formula shows the rat ...
... The chemical formula is made up using the symbol on the periodic table. Make sure you get the correct symbol. For simple molecules the formula shows the actual number of each type of atom present. However for ionic substances and macromolecules, which have giant structures, the formula shows the rat ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
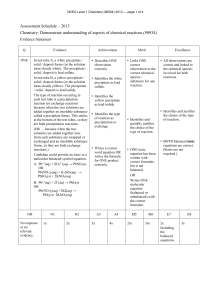
82KB - NZQA
... solid, CaCO3, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, carbon dioxide, CO2, and forms another white solid calcium oxide, CaO. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) When white calcium hydroxide solid, Ca(OH)2, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, water, H2O, and also forms the white solid ca ...
... solid, CaCO3, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, carbon dioxide, CO2, and forms another white solid calcium oxide, CaO. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) When white calcium hydroxide solid, Ca(OH)2, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, water, H2O, and also forms the white solid ca ...
Solution Stoichiometry - Angelo State University
... they were intact molecules (e.g., NaCl) – Complete (or overall) ionic equation: soluble strong electrolytes (soluble ionic compounds and strong acids) are written as ions (e.g., Na+, Cl-) • Insoluble precipitates, weak electrolytes, and molecules are left intact. • Ions that are not involved in the ...
... they were intact molecules (e.g., NaCl) – Complete (or overall) ionic equation: soluble strong electrolytes (soluble ionic compounds and strong acids) are written as ions (e.g., Na+, Cl-) • Insoluble precipitates, weak electrolytes, and molecules are left intact. • Ions that are not involved in the ...
File
... 21. What type of bonding is associated with compounds that have the following characteristics? • high melting points • conduct electricity in the molten state • solutions conduct electricity • normally crystalline solids at room temperature. A. covalent B. ionic C. hydrogen D. metallic 22. Which pai ...
... 21. What type of bonding is associated with compounds that have the following characteristics? • high melting points • conduct electricity in the molten state • solutions conduct electricity • normally crystalline solids at room temperature. A. covalent B. ionic C. hydrogen D. metallic 22. Which pai ...
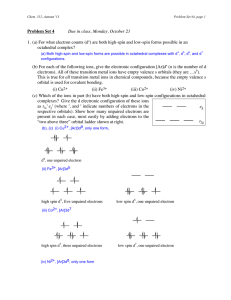
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... electrons). All of these transition metal ions have empty valence s orbitals (they are …s0). This is true for all transition metal ions in chemical compounds, because the empty valence s orbital is used for covalent bonding. (i) Cu2+ (ii) Fe3+ (iii) Co2+ (iv) Ni2+ (c) Which of the ions in part (b) h ...
... electrons). All of these transition metal ions have empty valence s orbitals (they are …s0). This is true for all transition metal ions in chemical compounds, because the empty valence s orbital is used for covalent bonding. (i) Cu2+ (ii) Fe3+ (iii) Co2+ (iv) Ni2+ (c) Which of the ions in part (b) h ...
The Coordination Chemistry of Solvated Metal Ions in DMPU
... exist independently, but prefers to join together in a structurally well-defined manner. A metal complex consists of a metal ion, often referred to as the central atom (or ion), which binds a number of ions and/or molecules, called ligands. Usually coordination chemistry is regarded as a branch of i ...
... exist independently, but prefers to join together in a structurally well-defined manner. A metal complex consists of a metal ion, often referred to as the central atom (or ion), which binds a number of ions and/or molecules, called ligands. Usually coordination chemistry is regarded as a branch of i ...
practical identification of organic compounds.docx
... soluble in dilute sodium hydroxide. It should be recalled that some of the compounds belonging to this group are sufficiently strong acids to release carbon dioxide from sodium hydrogen carbonate (e,g. carboxylic acids, sulphonic and sulphuric acids, and certain substituted phenols ) Compounds insol ...
... soluble in dilute sodium hydroxide. It should be recalled that some of the compounds belonging to this group are sufficiently strong acids to release carbon dioxide from sodium hydrogen carbonate (e,g. carboxylic acids, sulphonic and sulphuric acids, and certain substituted phenols ) Compounds insol ...
The Representative Elements: Group 5A Through 8A
... Oxo-acids and Oxo-anions of Nitrogen Nitric acid (HNO3) and nitrous acid (HNO2) are the two common oxo-acids of nitrogen. Nitric acid is a strong acid and a very powerful oxidizing agent. It oxidizes almost all metals it comes in contact with, except gold and platinum. Unlike the reactions of metal ...
... Oxo-acids and Oxo-anions of Nitrogen Nitric acid (HNO3) and nitrous acid (HNO2) are the two common oxo-acids of nitrogen. Nitric acid is a strong acid and a very powerful oxidizing agent. It oxidizes almost all metals it comes in contact with, except gold and platinum. Unlike the reactions of metal ...
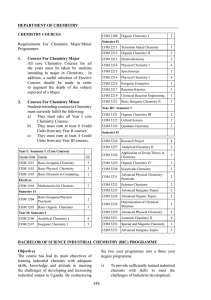
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Requirements For Chemistry Major
... All core Chemistry Courses for all the years must be taken by students intending to major in Chemistry. In addition, a useful selection of Elective Courses should be made in order to augment the depth of the subject expected of a Major. ...
... All core Chemistry Courses for all the years must be taken by students intending to major in Chemistry. In addition, a useful selection of Elective Courses should be made in order to augment the depth of the subject expected of a Major. ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.