Arts and Sciences Program Chemistry Department Chemistry Placement Test
... Calculate the mass of the air contained in a room that measures 2.50 m 5.50 m 3.00 m (density of air = 1.29 g/dm3 at 25C). ...
... Calculate the mass of the air contained in a room that measures 2.50 m 5.50 m 3.00 m (density of air = 1.29 g/dm3 at 25C). ...
Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide
... 25. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision and give an example of each. ...
... 25. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision and give an example of each. ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... Fill in the blank with the most appropriate term from the chapter, unit, or course. To summarize what happens to substances during a chemical reaction, scientists use a chemical _______________________. Arsenic has a total of 33 electrons. It has _______________________ electron shells around its nu ...
... Fill in the blank with the most appropriate term from the chapter, unit, or course. To summarize what happens to substances during a chemical reaction, scientists use a chemical _______________________. Arsenic has a total of 33 electrons. It has _______________________ electron shells around its nu ...
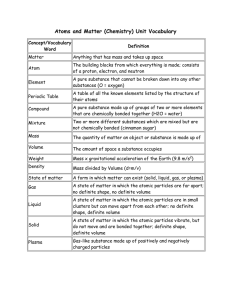
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... may boil not from being heated, but when the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere is sufficiently reduced, such as the use of a vacuum pump or at high altitudes. boiling point – The temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid. A li ...
... may boil not from being heated, but when the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere is sufficiently reduced, such as the use of a vacuum pump or at high altitudes. boiling point – The temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid. A li ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... B) a single element C) a mixture of compounds D) a single compound Based on the Selected Radioisotopes chemistry reference table, which radioisotope is best represented by the graph? A) 32P C) 222Rn B) 131I ...
... B) a single element C) a mixture of compounds D) a single compound Based on the Selected Radioisotopes chemistry reference table, which radioisotope is best represented by the graph? A) 32P C) 222Rn B) 131I ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... separated. A mixture may be homogeneous (uniform – a solution), or heterogeneous (uneven). Substances in a mixture retain their original properties. Substances in a mixture may be separated by their size, polarity, density, boiling and freezing points, and solubility (among others). Filtrati ...
... separated. A mixture may be homogeneous (uniform – a solution), or heterogeneous (uneven). Substances in a mixture retain their original properties. Substances in a mixture may be separated by their size, polarity, density, boiling and freezing points, and solubility (among others). Filtrati ...
document
... A. Fellow students - meet others in the class. Even though you and the other student may be perplexed about a subject, you will find that talking together in the language of chemistry may help you out of a trouble. B. Your instructor(s) - I am especially willing to answer questions in class, and I a ...
... A. Fellow students - meet others in the class. Even though you and the other student may be perplexed about a subject, you will find that talking together in the language of chemistry may help you out of a trouble. B. Your instructor(s) - I am especially willing to answer questions in class, and I a ...
Jeopardy
... What property of metal best describes why an ice cube will melt faster in a metal pan than on a plastic cutting board---even if both items are at room temperature ...
... What property of metal best describes why an ice cube will melt faster in a metal pan than on a plastic cutting board---even if both items are at room temperature ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
Periodic Table
... (Lathanides and Actinides) 1. Lanthanides – 3+ ions; soft, silvery metals; fairly reactive; fairly common in nature 2.Actinides – most are radioactive; most are synthetic produced from bombarding uranium with protons ...
... (Lathanides and Actinides) 1. Lanthanides – 3+ ions; soft, silvery metals; fairly reactive; fairly common in nature 2.Actinides – most are radioactive; most are synthetic produced from bombarding uranium with protons ...
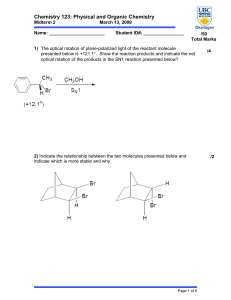
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
CVB101 – Lecture 3 Chemical Bonding • Chemical bonding
... The maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent (at a specific temperature) Some compounds are very soluble e.g. NaCl o It is possible to make very concentrated solutions on NaCl Other compounds are not very soluble e.g. AgCl o If AgCl solid is placed in water, o ...
... The maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent (at a specific temperature) Some compounds are very soluble e.g. NaCl o It is possible to make very concentrated solutions on NaCl Other compounds are not very soluble e.g. AgCl o If AgCl solid is placed in water, o ...
Define:
... d. evaporation e. rusting f. fermenting g. boiling h. burning 32. Which of the following is a heterogeneous(he) mixture and which is homogeneous (ho)? a. Air b. salt water c. steel d. soil e. vinegar in water d. oil in vinegar e. milk f. beef stew g. sand in water 33. What are the five indicators th ...
... d. evaporation e. rusting f. fermenting g. boiling h. burning 32. Which of the following is a heterogeneous(he) mixture and which is homogeneous (ho)? a. Air b. salt water c. steel d. soil e. vinegar in water d. oil in vinegar e. milk f. beef stew g. sand in water 33. What are the five indicators th ...
C1 Revision Fundamental ideas adapted CS
... Sodium has formed a p........................ charged ion and chlorine has formed a n......................... charged ion. The opposite charges a................ to form a very s................... ionic b............. ...
... Sodium has formed a p........................ charged ion and chlorine has formed a n......................... charged ion. The opposite charges a................ to form a very s................... ionic b............. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.