Chapter 23 Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy
... • Avoiding unanticipated fluctuations in the price level is an important objective of monetary policy, thus providing a rationale for price stability as the primary long-run goal for monetary policy ...
... • Avoiding unanticipated fluctuations in the price level is an important objective of monetary policy, thus providing a rationale for price stability as the primary long-run goal for monetary policy ...
20160118_Transcript_Debt, Demographics and the Distribution of Income new challenges for monetary policy
... ways. First, longevity has risen and is expected to continue rising for the foreseeable future (Figure 4). We are living longer. Second, fertility has declined (Figure 5). We are making fewer babies. This leads to persistent changes in key demographic variables. First, population growth is slowing. ...
... ways. First, longevity has risen and is expected to continue rising for the foreseeable future (Figure 4). We are living longer. Second, fertility has declined (Figure 5). We are making fewer babies. This leads to persistent changes in key demographic variables. First, population growth is slowing. ...
There is little doubt that when central banks,
... Federal Reserve has a set of goals and objectives in mind that are not necessarily of equal priority, and that it sets monetary policy to meet these goals and objectives, given the economic environment it faces. The solution to this optimization problem—best meeting its goals subject to the economic ...
... Federal Reserve has a set of goals and objectives in mind that are not necessarily of equal priority, and that it sets monetary policy to meet these goals and objectives, given the economic environment it faces. The solution to this optimization problem—best meeting its goals subject to the economic ...
Chapter 15
... Stabilizers are changes in fiscal policy that stimulate aggregate demand when the economy goes into a recession without policy-makers having to take any deliberate action. Automatic stabilizers include: The Tax System: Y↓ >>T ↓ – Government Spending---EI especially – Flexible X rate. ...
... Stabilizers are changes in fiscal policy that stimulate aggregate demand when the economy goes into a recession without policy-makers having to take any deliberate action. Automatic stabilizers include: The Tax System: Y↓ >>T ↓ – Government Spending---EI especially – Flexible X rate. ...
Ready - Personal.psu.edu
... 2. (30 points total) We talked a lot about the Fed's balance sheet, quantitative easing, and the fact that since October 2008, they (the Fed) now pay interest on reserves. 2.a) (15 points) In 2008, the Fed pleaded and pleaded with Congress trying to convince them that the economic situation was det ...
... 2. (30 points total) We talked a lot about the Fed's balance sheet, quantitative easing, and the fact that since October 2008, they (the Fed) now pay interest on reserves. 2.a) (15 points) In 2008, the Fed pleaded and pleaded with Congress trying to convince them that the economic situation was det ...
Introduction to Money and the Financial System
... In real world, portfolios cannot be perfectly diversified because borrowers do not earn money and pay returns by flipping coins. Borrowers typically pay returns by earning money producing and selling goods, but since economies move up and down jointly through business cycles, returns have a common c ...
... In real world, portfolios cannot be perfectly diversified because borrowers do not earn money and pay returns by flipping coins. Borrowers typically pay returns by earning money producing and selling goods, but since economies move up and down jointly through business cycles, returns have a common c ...
Macro 4.1- Intro to Money
... In a personal finance class you learn about checking and savings accounts, credit cards, loans, the stock market, retirement plans, and how to ...
... In a personal finance class you learn about checking and savings accounts, credit cards, loans, the stock market, retirement plans, and how to ...
Chapter 15 Monetary Policy
... 61. When the Fed lends to commercial banks [ ], this is called the (Fed Funds Rate/discount rate) and when commercial banks make loans to one another, this is the (Fed Funds Rate/ Discount Rate). 62. The Keynesian cause-effect chain of an easy money policy would be to (buy/sell) bonds; which would ( ...
... 61. When the Fed lends to commercial banks [ ], this is called the (Fed Funds Rate/discount rate) and when commercial banks make loans to one another, this is the (Fed Funds Rate/ Discount Rate). 62. The Keynesian cause-effect chain of an easy money policy would be to (buy/sell) bonds; which would ( ...
U.S. Economy: Profit Surge May Help Broaden Expansion (Update1
... Payrolls probably increased this month, according to the median estimate of economists surveyed before a Labor Department report due April 2. Bernanke on Labor Market Federal Reserve Chairman Ben S. Bernanke said yesterday in testimony to the House Financial Services Committee that the “unemployment ...
... Payrolls probably increased this month, according to the median estimate of economists surveyed before a Labor Department report due April 2. Bernanke on Labor Market Federal Reserve Chairman Ben S. Bernanke said yesterday in testimony to the House Financial Services Committee that the “unemployment ...
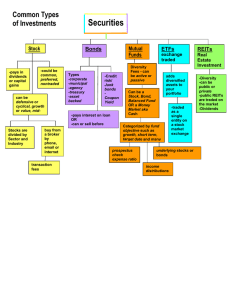
Securities
... Types of stock include Market Capitalization (indicates the size of a company, small-cap is less than one billion, mid-cap is one to 5 billion, large-cap-over is over 5 billion), Defensive (stocks with a stable demand such as groceries, health care or electricity), Cyclical (less stable, often fluct ...
... Types of stock include Market Capitalization (indicates the size of a company, small-cap is less than one billion, mid-cap is one to 5 billion, large-cap-over is over 5 billion), Defensive (stocks with a stable demand such as groceries, health care or electricity), Cyclical (less stable, often fluct ...
Microsoft Word - Money banking and Financial markets Assignment
... groups together funds from many investors and invests the money in a variety of stocks. Consequently, a mutual fund diversifies stocks, and it lowers investors’ risk. For example, youstart your own mutual fund and offer investors a chance to invest in this fund. You take themoney and buy 30 differen ...
... groups together funds from many investors and invests the money in a variety of stocks. Consequently, a mutual fund diversifies stocks, and it lowers investors’ risk. For example, youstart your own mutual fund and offer investors a chance to invest in this fund. You take themoney and buy 30 differen ...
The Development of Capital Markets
... • If behavior of price level or inflation were certain, then there would be less risk for business and individuals. They would know the real rates of interest. • Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate - Rate of Inflation • But the more uncertain people are about the price level or inflation, the ...
... • If behavior of price level or inflation were certain, then there would be less risk for business and individuals. They would know the real rates of interest. • Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate - Rate of Inflation • But the more uncertain people are about the price level or inflation, the ...
And Don`t Forget Your Final Project (worth 25 points)!
... What is the demand –pull inflation theory? What is the cost-push inflation theory? What impact can high inflation have on purchasing power? ...
... What is the demand –pull inflation theory? What is the cost-push inflation theory? What impact can high inflation have on purchasing power? ...
War, Money, and Inflation in the United States from the Revolution to
... be paid in cash to join; but they can also be given land grants, which were an important means of enlisting soldiers before the Civil War. And, of course, conscription has been used in most of America’s major wars. If conscripts are paid less than a competitive wage, the difference between a competi ...
... be paid in cash to join; but they can also be given land grants, which were an important means of enlisting soldiers before the Civil War. And, of course, conscription has been used in most of America’s major wars. If conscripts are paid less than a competitive wage, the difference between a competi ...
Money, functions and creation
... And make them available as long term loans to other economic agents (which earn interest) This funds economic activity (investment ...
... And make them available as long term loans to other economic agents (which earn interest) This funds economic activity (investment ...
Lecture 11: Inflation: Its Causes and Costs
... redistributed between net monetary debtors and creditors. This may result in wealth transfers that would not otherwise be acceptable. ...
... redistributed between net monetary debtors and creditors. This may result in wealth transfers that would not otherwise be acceptable. ...
Money, functions and creation
... And make them available as long term loans to other economic agents (which earn interest) This funds economic activity (investment ...
... And make them available as long term loans to other economic agents (which earn interest) This funds economic activity (investment ...
Multiple Choice Quiz 1. The labor force consists of A) the entire adult
... A) is an advisory group consisting of 7 state governors who represent the views of individual states in monetary policy. B) consists of seven members appointed by the President of the United States who together act as the key decisionmaking entity for monetary policy. C) is an advisory group consist ...
... A) is an advisory group consisting of 7 state governors who represent the views of individual states in monetary policy. B) consists of seven members appointed by the President of the United States who together act as the key decisionmaking entity for monetary policy. C) is an advisory group consist ...
aggregate demand-aggregate supply model
... For example, external balance for the U.S. implies that “THE” US BOP = CAB + KAB = 0, where CAB = Autonomous US XGS – Autonomous US IMPGS And KAB = Autonomous US XA – Autonomous US IMPA. If “THE” US BOP =0, the current foreign exchange rate between the US dollar and foreign currencies (say, the Swis ...
... For example, external balance for the U.S. implies that “THE” US BOP = CAB + KAB = 0, where CAB = Autonomous US XGS – Autonomous US IMPGS And KAB = Autonomous US XA – Autonomous US IMPA. If “THE” US BOP =0, the current foreign exchange rate between the US dollar and foreign currencies (say, the Swis ...
February 2012 Aftershock Newsletter Inflation or Deflation? As
... that when debts cannot be repaid, the resulting write-offs and bankruptcies will effectively decrease the money supply, causing deflation. This argument seems to come from the idea that money is created as debt, and that therefore when debt is destroyed, so is the money. But that is not the case. If ...
... that when debts cannot be repaid, the resulting write-offs and bankruptcies will effectively decrease the money supply, causing deflation. This argument seems to come from the idea that money is created as debt, and that therefore when debt is destroyed, so is the money. But that is not the case. If ...
Savings, Investment Spending, and the Financial System
... A mutual fund is a financial intermediary that creates a stock portfolio and then resells shares of this portfolio to individual investors. A pension fund is a type of mutual fund that holds assets in order to provide retirement income to its members. Life insurance companies sell policies which gua ...
... A mutual fund is a financial intermediary that creates a stock portfolio and then resells shares of this portfolio to individual investors. A pension fund is a type of mutual fund that holds assets in order to provide retirement income to its members. Life insurance companies sell policies which gua ...
Lecture 1: Introduction to Financial Markets
... However beginning in December 2008 the target has actually been a range (upper and lower limit). In addition to the Fed Funds target, another important overnight interbank rate is the “effective federal funds rate.” This is the actual rate at which banks are lending excess reserves to one anot ...
... However beginning in December 2008 the target has actually been a range (upper and lower limit). In addition to the Fed Funds target, another important overnight interbank rate is the “effective federal funds rate.” This is the actual rate at which banks are lending excess reserves to one anot ...
Avoiding some costs of inflation and crawling toward hyperinflation
... inflation tax - played a decisive role in explaining why Brazil has not undergone a serious anti-inflationary program for so long. In order to sustain this provision of the domestic currency substitute, the central bank had no other option but to follow a highly passive monetary policy. Given a very ...
... inflation tax - played a decisive role in explaining why Brazil has not undergone a serious anti-inflationary program for so long. In order to sustain this provision of the domestic currency substitute, the central bank had no other option but to follow a highly passive monetary policy. Given a very ...
Chapter 15
... Activists argue that monetary policy should be deliberately used to smooth out the business cycle. They are in favor of economic finetuning, which is the (usually frequent) use of monetary policy to counteract even small undesirable movements in economic activity. Sometimes, the monetary policy th ...
... Activists argue that monetary policy should be deliberately used to smooth out the business cycle. They are in favor of economic finetuning, which is the (usually frequent) use of monetary policy to counteract even small undesirable movements in economic activity. Sometimes, the monetary policy th ...
Chapter30
... upward. For actual inflation to remain above expected inflation, the actual rate of inflation must therefore be ever increasing, which means ever-increasing rates of money growth. Question 7 a) If the Bank of Canada does not respond to the negative AS shock, then the economy’s natural adjustment pr ...
... upward. For actual inflation to remain above expected inflation, the actual rate of inflation must therefore be ever increasing, which means ever-increasing rates of money growth. Question 7 a) If the Bank of Canada does not respond to the negative AS shock, then the economy’s natural adjustment pr ...