
Mathematical statistics Week 2/b: Finite sample
... • Consider θb1 and θb2 , which are two unbiased estimators of a population parameter θ. • Estimator θb1 is said to be relatively more efficient than θb2 (to estimate θ) if V ar(θb1 ) ≤ V ar(θb2 ) for all θ, with strict inequality for at least one value of θ. – i.e. the variance of its sampling distr ...
... • Consider θb1 and θb2 , which are two unbiased estimators of a population parameter θ. • Estimator θb1 is said to be relatively more efficient than θb2 (to estimate θ) if V ar(θb1 ) ≤ V ar(θb2 ) for all θ, with strict inequality for at least one value of θ. – i.e. the variance of its sampling distr ...
Section 8.3 PowerPoint
... has unknown shape and n < 30, use a graph of the sample data to assess the Normality of the population. Do not use t procedures if the graph shows strong skewness or outliers. ...
... has unknown shape and n < 30, use a graph of the sample data to assess the Normality of the population. Do not use t procedures if the graph shows strong skewness or outliers. ...
Chapter 7 Estimation:Single Population
... • Note the actual value we calculate for the sample mean (like 4.2) is a realization of a random variable and is called the estimate • The estimator, ̄ is a random variable (i.e. it has a distribution). ...
... • Note the actual value we calculate for the sample mean (like 4.2) is a realization of a random variable and is called the estimate • The estimator, ̄ is a random variable (i.e. it has a distribution). ...
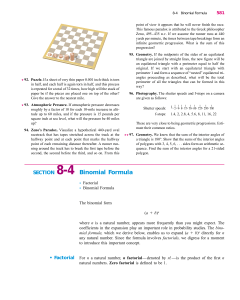
SECTION 8-4 Binomial Formula
... 4. In each term, the sum of the powers of a and b always adds up to n. 5. Starting with a given term, we can get the coefficient of the next term by multiplying the coefficient of the given term by the exponent of a and dividing by the number that represents the position of the term in the series of ...
... 4. In each term, the sum of the powers of a and b always adds up to n. 5. Starting with a given term, we can get the coefficient of the next term by multiplying the coefficient of the given term by the exponent of a and dividing by the number that represents the position of the term in the series of ...
Chapter 9
... A tire company investigates the tread life of its tires. A sample of 10 tires driven 50,000 miles revealed a sample mean of 0.32 inch of tread remaining with a standard deviation of 0.09 inch. Construct a 95 percent confidence interval for the population mean. Would it be reasonable for the company ...
... A tire company investigates the tread life of its tires. A sample of 10 tires driven 50,000 miles revealed a sample mean of 0.32 inch of tread remaining with a standard deviation of 0.09 inch. Construct a 95 percent confidence interval for the population mean. Would it be reasonable for the company ...
Seventh homework
... (a ) Find the total number of suicides reported over the 5-year period and the sample monthly mean rate of suicides. (b ) Find the estimated standard error of the sample monthly mean rate. (c ) Construct and interpret a 90% con dence interval for the population monthly mean rate. (PG). One of the go ...
... (a ) Find the total number of suicides reported over the 5-year period and the sample monthly mean rate of suicides. (b ) Find the estimated standard error of the sample monthly mean rate. (c ) Construct and interpret a 90% con dence interval for the population monthly mean rate. (PG). One of the go ...
Confidence intervals for difference of means of two independent
... 4. As mentioned in the previous note, the samples size is affected by the number of observations in a sample (or samples). It is possible to determine the minimum sample size required to estimate a population parameter with a specified precision at a given confidence level. 5. The consequence of not ...
... 4. As mentioned in the previous note, the samples size is affected by the number of observations in a sample (or samples). It is possible to determine the minimum sample size required to estimate a population parameter with a specified precision at a given confidence level. 5. The consequence of not ...
Document
... population standard deviation of 2.5 minutes. Click on a cell and then type =CONFIDENCE(0.05,2.5,50) in the Excel input box and click on ok. We only use the sample size and standard deviation in this command. You will get the value of 0.692951. 30 - 0.7 = 29.3 and 30 + 0.7 = 30.7 So, the expression ...
... population standard deviation of 2.5 minutes. Click on a cell and then type =CONFIDENCE(0.05,2.5,50) in the Excel input box and click on ok. We only use the sample size and standard deviation in this command. You will get the value of 0.692951. 30 - 0.7 = 29.3 and 30 + 0.7 = 30.7 So, the expression ...
German tank problem

In the statistical theory of estimation, the problem of estimating the maximum of a discrete uniform distribution from sampling without replacement is known in English as the German tank problem, due to its application in World War II to the estimation of the number of German tanks.The analyses illustrate the difference between frequentist inference and Bayesian inference.Estimating the population maximum based on a single sample yields divergent results, while the estimation based on multiple samples is an instructive practical estimation question whose answer is simple but not obvious.











![AP-Test-Prep---Flashcards[2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/023264297_1-3b04ac15176c964f2860805ab458892d-300x300.png)










