Practice Exam Final KEY - Department of Statistics, Purdue University
... they take the test? A random sample of four students who took the test twice received the following scores. Assume that the change in SAT-M score (second score – first score) for the population of all students taking the test twice is Normally distributed. Suppose we do not believe that students ten ...
... they take the test? A random sample of four students who took the test twice received the following scores. Assume that the change in SAT-M score (second score – first score) for the population of all students taking the test twice is Normally distributed. Suppose we do not believe that students ten ...
Math 131. Applied Optimization Problems Name
... Answer. Let the first number be x and the second number be y. Then x + 2y = 216. Thus x = 216 − 2y and the product function is P (y) = xy = (216 − 2y)y = 216y − 2y 2 . Then P 0 (y) = 216 − 4y and so the critical number is y = 216/4 = 54. The maximum product is then obtained when the first number is ...
... Answer. Let the first number be x and the second number be y. Then x + 2y = 216. Thus x = 216 − 2y and the product function is P (y) = xy = (216 − 2y)y = 216y − 2y 2 . Then P 0 (y) = 216 − 4y and so the critical number is y = 216/4 = 54. The maximum product is then obtained when the first number is ...
Name AP Statistics Multiple Choice Exam Directions: Solve each of
... (A) This confidence interval is valid because a sample size of more than 30 was used. (B) This confidence interval is valid because each area resident was asked the same question. (C) The confidence interval is valid because no conditions are required for constructing a large sample confidence inter ...
... (A) This confidence interval is valid because a sample size of more than 30 was used. (B) This confidence interval is valid because each area resident was asked the same question. (C) The confidence interval is valid because no conditions are required for constructing a large sample confidence inter ...
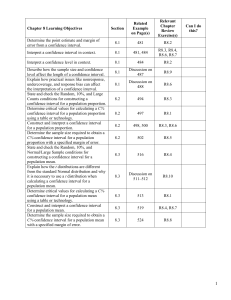
Chapter 7 Sampling and Sampling Distributions
... o All elements within each sampled (chosen) cluster form the sample. o Advantage: The close proximity of elements can be cost effective (I.e. many sample observations can be obtained in a short time). o Disadvantage: This method generally requires a larger total sample size than simple or stratified ...
... o All elements within each sampled (chosen) cluster form the sample. o Advantage: The close proximity of elements can be cost effective (I.e. many sample observations can be obtained in a short time). o Disadvantage: This method generally requires a larger total sample size than simple or stratified ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... body temperatures of n = 106 subjects. The sample mean of the data set is x 98.20 F and the standard deviation for the sample is s 0.62 F . ...
... body temperatures of n = 106 subjects. The sample mean of the data set is x 98.20 F and the standard deviation for the sample is s 0.62 F . ...
Estimation - User Web Pages
... • It is important that the sample is an unbiased representation of the population. This is achieved by: • Sampling randomly so each observation has an equal chance of being selected • Collecting a sufficiently large number (n) of observations (replicates) in your sample ...
... • It is important that the sample is an unbiased representation of the population. This is achieved by: • Sampling randomly so each observation has an equal chance of being selected • Collecting a sufficiently large number (n) of observations (replicates) in your sample ...
A Unified Maximum Likelihood Approach for Optimal
... rate falls short of the best-known property estimates. For example, suppose we sample the uniform distribution over k elements n = k/2 times. Since at most n distinct symbols will appear, the empirical distribution will have entropy at most log n ≤ log k − 1 bits. However from Table 1.3, for large k ...
... rate falls short of the best-known property estimates. For example, suppose we sample the uniform distribution over k elements n = k/2 times. Since at most n distinct symbols will appear, the empirical distribution will have entropy at most log n ≤ log k − 1 bits. However from Table 1.3, for large k ...
German tank problem

In the statistical theory of estimation, the problem of estimating the maximum of a discrete uniform distribution from sampling without replacement is known in English as the German tank problem, due to its application in World War II to the estimation of the number of German tanks.The analyses illustrate the difference between frequentist inference and Bayesian inference.Estimating the population maximum based on a single sample yields divergent results, while the estimation based on multiple samples is an instructive practical estimation question whose answer is simple but not obvious.