KERNEL REGRESSION ESTIMATION FOR INCOMPLETE DATA
... Statisticians working in any field are often interested in the relationship between a response variable Y and a vector of covariates Z = (Z1 , · · · , Zd ). This relationship can best be described by the regression function m(z) = E[Y |Z = z]. The regression function is estimated utilizing data whic ...
... Statisticians working in any field are often interested in the relationship between a response variable Y and a vector of covariates Z = (Z1 , · · · , Zd ). This relationship can best be described by the regression function m(z) = E[Y |Z = z]. The regression function is estimated utilizing data whic ...
Sampling theory
... It is important to note that the sampling fraction is often very small in practice, i.e. f ≈ 0 . In fact, this is then equivalent to random sampling with replacement. It is also intuitively clear that replacement or non replacement no longer has an effect on the value of the estimator when the popul ...
... It is important to note that the sampling fraction is often very small in practice, i.e. f ≈ 0 . In fact, this is then equivalent to random sampling with replacement. It is also intuitively clear that replacement or non replacement no longer has an effect on the value of the estimator when the popul ...
Inferential Statistics Unit
... asked how many phone calls they made today, their responses would be whole numbers like 0, 4 or 12. They would not respond with something like 7.8 phone calls. Since they can only report isolated points, then we end up with discrete numerical data. Numerical data is continuous if the set of possible ...
... asked how many phone calls they made today, their responses would be whole numbers like 0, 4 or 12. They would not respond with something like 7.8 phone calls. Since they can only report isolated points, then we end up with discrete numerical data. Numerical data is continuous if the set of possible ...
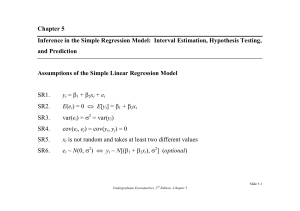
Chapter 5 Inference in the Simple Regression Model: Interval
... In the interval endpoint, b2 – tcse(b2) and b2 + tcse(b2), both b2 and se(b2) are random variables, since their value are not known until a sample of data is drawn. • The probability endpoints of the interval define an interval estimator of β2. The probability statement in Equation (5.1.13) says th ...
... In the interval endpoint, b2 – tcse(b2) and b2 + tcse(b2), both b2 and se(b2) are random variables, since their value are not known until a sample of data is drawn. • The probability endpoints of the interval define an interval estimator of β2. The probability statement in Equation (5.1.13) says th ...
Unconditional Quantile Regressions
... of RIF (Y ; µ) on X is the same as the standard regression of Y on X. This explains why, in our framework, OLS estimates are valid estimates of the effect of X on the unconditional mean of Y . More importantly, we show that this property extends to any other distributional statistic. For the τ -quan ...
... of RIF (Y ; µ) on X is the same as the standard regression of Y on X. This explains why, in our framework, OLS estimates are valid estimates of the effect of X on the unconditional mean of Y . More importantly, we show that this property extends to any other distributional statistic. For the τ -quan ...
Teeter, Rebecca Ann; (1982)Effects of Measurement Error in Piecewise Regression Models."
... consistent join point estimates and the numerical estimate of the variance is close to the variance from the empirical distribution. A less comprehensive study is made of estimation procedurel as proposed by Tultey (1951) which can be used when the data are replicated. In this cale it is possible t ...
... consistent join point estimates and the numerical estimate of the variance is close to the variance from the empirical distribution. A less comprehensive study is made of estimation procedurel as proposed by Tultey (1951) which can be used when the data are replicated. In this cale it is possible t ...
No Slide Title
... ASYMPTOTIC PROPERTIES OF ESTIMATORS: PLIMS AND CONSISTENCY n = 100000 probability density function of Z ...
... ASYMPTOTIC PROPERTIES OF ESTIMATORS: PLIMS AND CONSISTENCY n = 100000 probability density function of Z ...
Derivative Estimation Based on Difference Sequence via Locally
... There are three main approaches of nonparametric derivative estimation in the literature: smoothing spline, local polynomial regression (LPR), and difference-based method. As for smoothing spline, the usual way of estimating derivatives is to take derivatives of spline estimate. Stone (1985) showed ...
... There are three main approaches of nonparametric derivative estimation in the literature: smoothing spline, local polynomial regression (LPR), and difference-based method. As for smoothing spline, the usual way of estimating derivatives is to take derivatives of spline estimate. Stone (1985) showed ...
S1 Past Paper Booklet - The Grange School Blogs
... (ii) The values of y in the table were in fact obtained from measurements in inches and converted into centimetres by multiplying by 2.54. State what effect it would have had on the value of the product moment correlation coefficient if it had been calculated using inches instead of centimetres. [1] ...
... (ii) The values of y in the table were in fact obtained from measurements in inches and converted into centimetres by multiplying by 2.54. State what effect it would have had on the value of the product moment correlation coefficient if it had been calculated using inches instead of centimetres. [1] ...
Distance Methods - Publicera vid SLU
... plant population can be considered grouped or random. To make clear what is meant by a random distribution, the author would like to quote CLARK& EVA% (1954): "In a random distribution of a set of points on a given area i t is assumed t h a t any point has had the same chance of occurring on any sub ...
... plant population can be considered grouped or random. To make clear what is meant by a random distribution, the author would like to quote CLARK& EVA% (1954): "In a random distribution of a set of points on a given area i t is assumed t h a t any point has had the same chance of occurring on any sub ...
Application of loglinear models to claims triangle
... An insurance company must ensure as first order of business that there are suitable reserves available to meet the demand by outstanding claims. Insurance companies make promises to policyholders to pay out monetary amounts if certain events (claims) occur. Events may be, for example, due to a car a ...
... An insurance company must ensure as first order of business that there are suitable reserves available to meet the demand by outstanding claims. Insurance companies make promises to policyholders to pay out monetary amounts if certain events (claims) occur. Events may be, for example, due to a car a ...
German tank problem

In the statistical theory of estimation, the problem of estimating the maximum of a discrete uniform distribution from sampling without replacement is known in English as the German tank problem, due to its application in World War II to the estimation of the number of German tanks.The analyses illustrate the difference between frequentist inference and Bayesian inference.Estimating the population maximum based on a single sample yields divergent results, while the estimation based on multiple samples is an instructive practical estimation question whose answer is simple but not obvious.