Forces & Motion ()
... force of the same magnitude, but in the opposite direction Contact forces can be usefully decomposed into normal contact (perpendicular to a surface) and friction (parallel to the surface), which always opposes motion. The normal contact force ‘acts’ at the point of intersection of a vertical ‘plumb ...
... force of the same magnitude, but in the opposite direction Contact forces can be usefully decomposed into normal contact (perpendicular to a surface) and friction (parallel to the surface), which always opposes motion. The normal contact force ‘acts’ at the point of intersection of a vertical ‘plumb ...
Noninertial Frames
... As was pointed out earlier, the last term on the right hand side of equation (8.30) is responsible for the Coriolis effect. This effect is the source for some well-known motions of the air masses. To see how this happens, let’s consider the xyz coordinate system to be located at some latitude ! wher ...
... As was pointed out earlier, the last term on the right hand side of equation (8.30) is responsible for the Coriolis effect. This effect is the source for some well-known motions of the air masses. To see how this happens, let’s consider the xyz coordinate system to be located at some latitude ! wher ...
Calculating Velocity
... when there is no wind. His bike has a rolling resistance of 0.80 N*s/m. Joe and his bike’s drag area is CdA = 0.422m^2. We will assume that the density of air is 1.2 kg/m^3. The mass of Joe and the bike is constant in this problem; therefore it is negligible. ...
... when there is no wind. His bike has a rolling resistance of 0.80 N*s/m. Joe and his bike’s drag area is CdA = 0.422m^2. We will assume that the density of air is 1.2 kg/m^3. The mass of Joe and the bike is constant in this problem; therefore it is negligible. ...
Newtonian Physics
... A change in velocity could mean a change in speed or direction (or both). A racing car, going around a circular track at constant speed, actually has a changing velocity. (It is because its direction is changing!) ...
... A change in velocity could mean a change in speed or direction (or both). A racing car, going around a circular track at constant speed, actually has a changing velocity. (It is because its direction is changing!) ...
Slides from Review Session
... Concept of average speed and velocity Concept of average speed and velocity Concept of average acceleration The nature of VECTORS ...
... Concept of average speed and velocity Concept of average speed and velocity Concept of average acceleration The nature of VECTORS ...
PreLecture 07
... A box of mass 3 kg is pulled on a smooth (frictionless) surface by a second block of mass 2 kg hanging over a pulley. What is the acceleration of each block and tension in the string connecting them? Box 1 F=ma ...
... A box of mass 3 kg is pulled on a smooth (frictionless) surface by a second block of mass 2 kg hanging over a pulley. What is the acceleration of each block and tension in the string connecting them? Box 1 F=ma ...
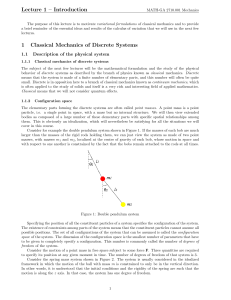
Lecture 1 – Introduction 1 Classical Mechanics of Discrete Systems
... The parameters that are used to describe the configuration of a system are called the generalized coordinates. For a complete description of a system, one needs at least as many generalized coordinates as there are degrees of freedom in the system. Depending on how one chooses to describe the system ...
... The parameters that are used to describe the configuration of a system are called the generalized coordinates. For a complete description of a system, one needs at least as many generalized coordinates as there are degrees of freedom in the system. Depending on how one chooses to describe the system ...
Particle Physics on Noncommutative Spaces
... that’s the central result: relation between coord. gauge fields and Yang-Mills fields! That’s not trivial: problem with direct product! ...
... that’s the central result: relation between coord. gauge fields and Yang-Mills fields! That’s not trivial: problem with direct product! ...