One-Sample T
... Building on the logic of hypothesis testing: T-tests ______________________________________________ 1) Introduce the t-test and explain when it should be used 2) Define Directional Hypotheses (one-tailed t-tests) and contrast them with ‘Non-Directional Hypotheses’ (two-tailed t-tests) that were desc ...
... Building on the logic of hypothesis testing: T-tests ______________________________________________ 1) Introduce the t-test and explain when it should be used 2) Define Directional Hypotheses (one-tailed t-tests) and contrast them with ‘Non-Directional Hypotheses’ (two-tailed t-tests) that were desc ...
Differences-in-Differences and A (Very) Brief Introduction
... maximum in that areas do this over and over across different grids Get an approximation of the underlying objective function If this converges to a single maximum—you’re done ...
... maximum in that areas do this over and over across different grids Get an approximation of the underlying objective function If this converges to a single maximum—you’re done ...
Describing Data: class 2
... Why n-1? Rather than simply n??? The normal procedure involves estimating variance for a population using data from a sample. ...
... Why n-1? Rather than simply n??? The normal procedure involves estimating variance for a population using data from a sample. ...
%ME: A SAS® Macro to Assess Measurement Equivalence for Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
... outcome variables; and class defines the class variable in the class statement of PROC TTEST. fix indicates whether the bound is a fixed number (1) or a coefficient (0)1. bound defines the upper and lower bounds for the TOST tests. Then, %tost uses SAS/ODS and SAS/DATA to read the results of TOST te ...
... outcome variables; and class defines the class variable in the class statement of PROC TTEST. fix indicates whether the bound is a fixed number (1) or a coefficient (0)1. bound defines the upper and lower bounds for the TOST tests. Then, %tost uses SAS/ODS and SAS/DATA to read the results of TOST te ...
Lecture #10
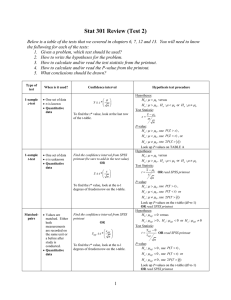
... The z or t tests can be used to compare two distribution means, or compare one distribution mean to a fixed value (interval or ratio data) Compare the actual z or t score to the critical z or t score If the actual z or t score is closer to zero than the critical value, accept the null hypothesis ...
... The z or t tests can be used to compare two distribution means, or compare one distribution mean to a fixed value (interval or ratio data) Compare the actual z or t score to the critical z or t score If the actual z or t score is closer to zero than the critical value, accept the null hypothesis ...
STAT 1220 Spring 2007 Common Final Exam May 3, 2007
... PART I. Consists of 30 multiple choice questions worth a total of 60 points. Read all questions carefully. You may do calculations on the test paper. Mark the number of the opscan sheet corresponding to the test question number with a Number 2 pencil or a mechanical pencil with HB lead. Mark only on ...
... PART I. Consists of 30 multiple choice questions worth a total of 60 points. Read all questions carefully. You may do calculations on the test paper. Mark the number of the opscan sheet corresponding to the test question number with a Number 2 pencil or a mechanical pencil with HB lead. Mark only on ...
File - McMurray VMC
... rewards. Compared to the children who failed the marshmallow test, the children who passed it demonstrated greater personal and social competence in adulthood. Consideration of the future consequences of one’s behaviour seems to be associated with better health, greater job success, and stonger inte ...
... rewards. Compared to the children who failed the marshmallow test, the children who passed it demonstrated greater personal and social competence in adulthood. Consideration of the future consequences of one’s behaviour seems to be associated with better health, greater job success, and stonger inte ...