Statistical Inference in Education
... a hypothesis and then use a logical argument to prove that the conclusion follows. Example: If a quadrilateral is a rectangle, then its diagonals are congruent. (This can be proven through an a priori logical argument – not by just examining a bunch of rectangles and measuring their diagonals to see ...
... a hypothesis and then use a logical argument to prove that the conclusion follows. Example: If a quadrilateral is a rectangle, then its diagonals are congruent. (This can be proven through an a priori logical argument – not by just examining a bunch of rectangles and measuring their diagonals to see ...
Chapter 2
... • In calculating the variance, we squared all of the deviations, and in doing so changed the scale of the measurements. • To return this measure of variability to the original units of measure, we calculate the standard deviation, the positive square root of the variance. Population standard deviati ...
... • In calculating the variance, we squared all of the deviations, and in doing so changed the scale of the measurements. • To return this measure of variability to the original units of measure, we calculate the standard deviation, the positive square root of the variance. Population standard deviati ...
Outline - Benedictine University
... draw the appropriate hypothesis-test conclusion based on the given level of α, the table-z (critical value) and the calculated-z (test statistic) interpret the conclusion determine and interpret the p-value given appropriate data, conduct estimation and hypothesis testing on the population mea ...
... draw the appropriate hypothesis-test conclusion based on the given level of α, the table-z (critical value) and the calculated-z (test statistic) interpret the conclusion determine and interpret the p-value given appropriate data, conduct estimation and hypothesis testing on the population mea ...
Document
... 151. Define and discuss the differences between grammar, semantics, and syntax. 152. Who is Noam Chomsky? What significance does he have to language. Briefly discuss his findings. 153. Summarize the discussion about thought and language. 154. Summarize the discussion about animal thinking and langua ...
... 151. Define and discuss the differences between grammar, semantics, and syntax. 152. Who is Noam Chomsky? What significance does he have to language. Briefly discuss his findings. 153. Summarize the discussion about thought and language. 154. Summarize the discussion about animal thinking and langua ...
Chapter 12: Inference for Proportions
... 24. Of the 100 people who phoned in, 70 answered “yes.” Which of the following assumptions for inference about a proportion using a confidence interval are violated? A) The desired confidence level is not given. B) The population is at least 10 times as large as the sample. C) n is so large that bot ...
... 24. Of the 100 people who phoned in, 70 answered “yes.” Which of the following assumptions for inference about a proportion using a confidence interval are violated? A) The desired confidence level is not given. B) The population is at least 10 times as large as the sample. C) n is so large that bot ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint
... = the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation. ...
... = the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation. ...
Questions - Ms. Paras
... internal causes and to discount situational factors. FUNDAMENTAL ATTRIBUTION ERROR ...
... internal causes and to discount situational factors. FUNDAMENTAL ATTRIBUTION ERROR ...
here
... A further appreciation can be gained by approaching this issue from the opposite direction; that is, by examining what percentage of the population is estimated to exhibit a score as low as an individual’s score when the standard procedure estimates it at 5%. Again using the case of N = 10, the esti ...
... A further appreciation can be gained by approaching this issue from the opposite direction; that is, by examining what percentage of the population is estimated to exhibit a score as low as an individual’s score when the standard procedure estimates it at 5%. Again using the case of N = 10, the esti ...
Problem 4 (5 points)
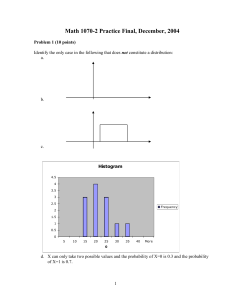
... The mean applicant score is a. 472.5 b. 480 c. 485 d. 497.5 The median applicant score is a. 472.5 b. 480 c. 485 d. 497.5 The first quartile for the applicant is a. 340 b. 390 c. 480 d. 605 The third quartile for the applicant is a. 340 b. 480 c. 605 d. 640 If 25 points were added to each other, the ...
... The mean applicant score is a. 472.5 b. 480 c. 485 d. 497.5 The median applicant score is a. 472.5 b. 480 c. 485 d. 497.5 The first quartile for the applicant is a. 340 b. 390 c. 480 d. 605 The third quartile for the applicant is a. 340 b. 480 c. 605 d. 640 If 25 points were added to each other, the ...
Chapter 2-98 Homework Problems
... The adjustment for the five comparisons was made separately for each parameter, which is the popular way to do it. One might consider if an adjustment needs to be made for all of the parameters simultaneously, so k parameters × 5 comparisons, which would be a large number. Alternatively, you could a ...
... The adjustment for the five comparisons was made separately for each parameter, which is the popular way to do it. One might consider if an adjustment needs to be made for all of the parameters simultaneously, so k parameters × 5 comparisons, which would be a large number. Alternatively, you could a ...
statistics - summary - Michigan State University
... the sample, not whether you can generalize this to the population. There is a test of whether a correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero that evaluates generalizability from the sample correlation to the population correlation. This tests the null hypothesis that the correlation ...
... the sample, not whether you can generalize this to the population. There is a test of whether a correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero that evaluates generalizability from the sample correlation to the population correlation. This tests the null hypothesis that the correlation ...