Preliminary Practice Exam for BST621
... how many statistically significant t-tests would be expected if Ho is true in each of the 20 situations? ________ 65) Which of the following does not belong with the others? a) An observed t-ratio is less than the critical t-ratio. b) The null hypothesis is rejected. c) The null hypothesis is tenabl ...
... how many statistically significant t-tests would be expected if Ho is true in each of the 20 situations? ________ 65) Which of the following does not belong with the others? a) An observed t-ratio is less than the critical t-ratio. b) The null hypothesis is rejected. c) The null hypothesis is tenabl ...
H 1 : µ 1 - SI-35-02
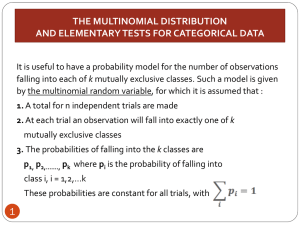
... In the special case of k=2, there are two-possible outcomes at each trial, which can be called success and failure. A test of is a test of the same null hypothesis ...
... In the special case of k=2, there are two-possible outcomes at each trial, which can be called success and failure. A test of is a test of the same null hypothesis ...
251y0212
... 3. All my family doctor's patient files are coded as follows: FS (Adult females who currently smoke); FN (Adult females who do not currently smoke); MS (Adult males who currently smoke) and MN (Adult males who do not currently smoke). Are these categories mutually exclusive and collectively exhausti ...
... 3. All my family doctor's patient files are coded as follows: FS (Adult females who currently smoke); FN (Adult females who do not currently smoke); MS (Adult males who currently smoke) and MN (Adult males who do not currently smoke). Are these categories mutually exclusive and collectively exhausti ...
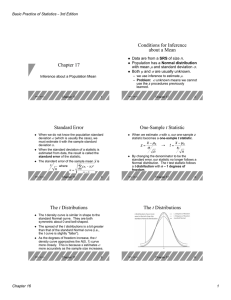
Chapter 17 Conditions for Inference about a Mean Standard Error
... also calls for using matched pairs. To compare the responses to the two treatments in a matched pairs design, apply the one-sample t procedures to the observed differences (one treatment observation minus the other). The parameter µ is the mean difference in the responses to the two treatments withi ...
... also calls for using matched pairs. To compare the responses to the two treatments in a matched pairs design, apply the one-sample t procedures to the observed differences (one treatment observation minus the other). The parameter µ is the mean difference in the responses to the two treatments withi ...
Chapter 9
... Confidence Interval for Population Proportion A poll conducted found that 944 of 1748 adults do not believe that people with tattoos are more rebellious. If appropriate construct a 90% confidence interval. Is it appropriate? Yes, it satisfies both conditions. ...
... Confidence Interval for Population Proportion A poll conducted found that 944 of 1748 adults do not believe that people with tattoos are more rebellious. If appropriate construct a 90% confidence interval. Is it appropriate? Yes, it satisfies both conditions. ...
Using the SAS® System for Analysis of Means
... limits are plotted to statistically and visually test the hypothesis of differences in means. Consequently, ANOM graphically provides a measure of statistical significance as well as a graphical measure of quantitative differences. ...
... limits are plotted to statistically and visually test the hypothesis of differences in means. Consequently, ANOM graphically provides a measure of statistical significance as well as a graphical measure of quantitative differences. ...
Lecture 11
... For vectors, STD(X) returns the standard deviation. For matrices, STD(X) is a row vector containing the standard deviation of each column. For N-D arrays, STD(X) is the standard deviation of the elements along the first non-singleton dimension of X. STD(X) normalizes by (N-1) where N is the sequence ...
... For vectors, STD(X) returns the standard deviation. For matrices, STD(X) is a row vector containing the standard deviation of each column. For N-D arrays, STD(X) is the standard deviation of the elements along the first non-singleton dimension of X. STD(X) normalizes by (N-1) where N is the sequence ...