Lectures for January 18 and 20 -- review
... -- if p-value is less than or equal to a, then we reject null at the a significance level -- the p-value is the smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis would be rejected ...
... -- if p-value is less than or equal to a, then we reject null at the a significance level -- the p-value is the smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis would be rejected ...
two-tailed test - Bakersfield College
... When we fail to reject H0 we say the results are nonsignificant. Nonsignificant indicates that the results are likely to occur if the predicted relationship does not exist in the population. ...
... When we fail to reject H0 we say the results are nonsignificant. Nonsignificant indicates that the results are likely to occur if the predicted relationship does not exist in the population. ...
Statistics - WordPress.com
... The means(/medians/modes) may show you a difference, but we can’t be sure that it’s a ...
... The means(/medians/modes) may show you a difference, but we can’t be sure that it’s a ...
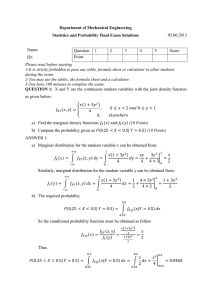
#1 Typing speeds (in words per minute) of 20 applicants for a
... (c) For a false is the decision a Type II error? ...
... (c) For a false is the decision a Type II error? ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Obtain the regression equation of Y on X. b) Five hundred employees of a firm that manufactures a product suspected of being associated with respiratory disorders were cross-classified by level of exposure to the product and whether or not they exhibited symptoms of respiratory disorders. The result ...
... Obtain the regression equation of Y on X. b) Five hundred employees of a firm that manufactures a product suspected of being associated with respiratory disorders were cross-classified by level of exposure to the product and whether or not they exhibited symptoms of respiratory disorders. The result ...
Lect 1 Medical Statistics as a science
... H1 =Levels are too different to have occurred purely by chance Statistical test: T test P < 0.0001 (extremely significant) Reject null hypothesis (Ho) and accept alternate hypothesis (H1) ie. 1 in 10 000 chance that these samples are both from the same overall group therefore we can say they are v ...
... H1 =Levels are too different to have occurred purely by chance Statistical test: T test P < 0.0001 (extremely significant) Reject null hypothesis (Ho) and accept alternate hypothesis (H1) ie. 1 in 10 000 chance that these samples are both from the same overall group therefore we can say they are v ...
Unit 4 Data Analysis
... » accept risk that out of 100 samples, a true null hypothesis would be rejected 5 times (5%) » Accept that in 95 of 100 cases (95%), a true null hypothesis would be correctly accepted – .01 level » Accept that 1 out of 100 samples, a true null hypothesis would be rejected (1%) » Accept that in 99 of ...
... » accept risk that out of 100 samples, a true null hypothesis would be rejected 5 times (5%) » Accept that in 95 of 100 cases (95%), a true null hypothesis would be correctly accepted – .01 level » Accept that 1 out of 100 samples, a true null hypothesis would be rejected (1%) » Accept that in 99 of ...
ppt
... It describes the variability of sample means that could occur just by chance and thereby serves as a frame of reference for generalizing from a single sample mean to a population mean. It allows us to determine whether, given the variability among all possible sample means, the one observed sample m ...
... It describes the variability of sample means that could occur just by chance and thereby serves as a frame of reference for generalizing from a single sample mean to a population mean. It allows us to determine whether, given the variability among all possible sample means, the one observed sample m ...