Exam 3 Review Decision Trees Cluster Analysis SAS
... Clustering • What statistics do we care about in cluster analysis? What do they represent? • What happens to these statistics as the number of clusters is increased? • Why do we standardize data? Why do we eliminate outliers? ...
... Clustering • What statistics do we care about in cluster analysis? What do they represent? • What happens to these statistics as the number of clusters is increased? • Why do we standardize data? Why do we eliminate outliers? ...
Chapter 8 Estimating with Confidence Notes Power Point Monday
... that affect the response, and then one member is randomly assigned to treatment 1 and the other to treatment 2. Recall that twin studies provide a natural pairing. Before and after studies are examples of matched pairs designs, but they require careful interpretation because random assignment is not ...
... that affect the response, and then one member is randomly assigned to treatment 1 and the other to treatment 2. Recall that twin studies provide a natural pairing. Before and after studies are examples of matched pairs designs, but they require careful interpretation because random assignment is not ...
Oct 18
... The t-distribution is a family of distributions: Bell-shaped and symmetric Greater area in the tails than the normal. Defined by its degrees of freedom. The t-distribution approaches the normal distribution as the degrees of freedom increase. ...
... The t-distribution is a family of distributions: Bell-shaped and symmetric Greater area in the tails than the normal. Defined by its degrees of freedom. The t-distribution approaches the normal distribution as the degrees of freedom increase. ...
File - Coach Parker`s Classes
... A distribution is skewed if one of its tails is longer than the other. ▪ The first distribution shown has a positive skew. This means that it has a long tail in the ...
... A distribution is skewed if one of its tails is longer than the other. ▪ The first distribution shown has a positive skew. This means that it has a long tail in the ...
Finding Statistics for Quantitative Data Using the TI-83 or TI
... Note: You can type data in any order. You can then go back to the EDIT menu and choose options 2: SORTA( or 3: SORTD(. These options will sort the data in ascending or descending order. You would have to specify a list if you use one other than L1. To specify a list you would simply type in the name ...
... Note: You can type data in any order. You can then go back to the EDIT menu and choose options 2: SORTA( or 3: SORTD(. These options will sort the data in ascending or descending order. You would have to specify a list if you use one other than L1. To specify a list you would simply type in the name ...
Repeated Measures ANOVA
... What is it? • Used when testing more than 2 experimental groups. • In dependent groups ANOVA, all groups are dependent: each score in one group is associated with a score in every other group. This may be because the same subjects served in every group or because subjects have been matched. • Withi ...
... What is it? • Used when testing more than 2 experimental groups. • In dependent groups ANOVA, all groups are dependent: each score in one group is associated with a score in every other group. This may be because the same subjects served in every group or because subjects have been matched. • Withi ...
Lab 5
... where statistical testing comes in. In statistical tests, we set up a null hypothesis and test whether our data fit that null hypothesis. Actually, what we get from a statistical test is a probability value (or P-Value). What this P-value tells us is this: The P-value is the probability that we coul ...
... where statistical testing comes in. In statistical tests, we set up a null hypothesis and test whether our data fit that null hypothesis. Actually, what we get from a statistical test is a probability value (or P-Value). What this P-value tells us is this: The P-value is the probability that we coul ...
Estimated - Illinois State University Department of Psychology
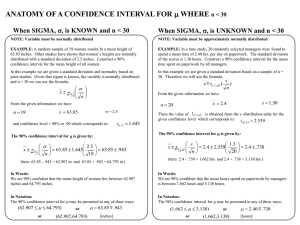
... » 90% confidence means that 90% of confidence interval estimates of this sample size will include the actual population mean ...
... » 90% confidence means that 90% of confidence interval estimates of this sample size will include the actual population mean ...
10.27 STUDENT ATTITUDE The Survey of Study of Study Habits
... in your sketch. Then suppose that the study result is ̅ . Mark this point on your sketch. Referring to your sketch, explain in simple language why one result is good evidence that average Cleveland spending on housing is less than 31%, whereas the other result is not. (c) Shade the area under the cu ...
... in your sketch. Then suppose that the study result is ̅ . Mark this point on your sketch. Referring to your sketch, explain in simple language why one result is good evidence that average Cleveland spending on housing is less than 31%, whereas the other result is not. (c) Shade the area under the cu ...