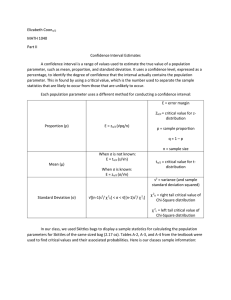
N = population size
... by the number of data items. Your text says to “round your means to one more decimal place than occurs in the raw data.” We will always take everything out to 4 decimal places as a rule, so ignore what your book says. x ...
... by the number of data items. Your text says to “round your means to one more decimal place than occurs in the raw data.” We will always take everything out to 4 decimal places as a rule, so ignore what your book says. x ...
252x0763
... the exam and might want to skip some questions. 2. A table identifying methods for comparing 2 samples is at the end of the exam. 3. If you answer ‘None of the above’ in any question, you should provide an alternative answer and explain why. You may receive credit for this even if you are wrong. 4. ...
... the exam and might want to skip some questions. 2. A table identifying methods for comparing 2 samples is at the end of the exam. 3. If you answer ‘None of the above’ in any question, you should provide an alternative answer and explain why. You may receive credit for this even if you are wrong. 4. ...
Statistics -- Exam I Review Note: This is only a sample of exercises
... Determine whether the given value is a statistic or a parameter. 1) A sample of 120 employees of a company is selected, and the average age is found to be 37 years. 2) After inspecting all of 55,000 kg of meat stored at the Wurst Sausage Company, it was found that 45,000 kg of the meat was spoiled. ...
... Determine whether the given value is a statistic or a parameter. 1) A sample of 120 employees of a company is selected, and the average age is found to be 37 years. 2) After inspecting all of 55,000 kg of meat stored at the Wurst Sausage Company, it was found that 45,000 kg of the meat was spoiled. ...
BUSA 5325 – Exam 1, Summer, 2007
... 23. You want to determine if sleep affects the passing of an exam and have divided thirty students into three groups of ten. The first group is required to stay up all night studying for the exam. The second group does not study at all. The third group studies the previous day and gets eight hours ...
... 23. You want to determine if sleep affects the passing of an exam and have divided thirty students into three groups of ten. The first group is required to stay up all night studying for the exam. The second group does not study at all. The third group studies the previous day and gets eight hours ...
Practice Final - Sean Ho, Computing Science / Math, Trinity Western
... Chi-sq = 3.92, one-tailed: 0.02 < p < 0.05 (p =~ 0.0477). Reject H0 (13) In a study of balloon angioplasty, patients with coronary artery disease were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups: placebo, probucol, multivitamins, or probucol together with multivitamins. Balloon angioplasty was ...
... Chi-sq = 3.92, one-tailed: 0.02 < p < 0.05 (p =~ 0.0477). Reject H0 (13) In a study of balloon angioplasty, patients with coronary artery disease were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups: placebo, probucol, multivitamins, or probucol together with multivitamins. Balloon angioplasty was ...
Exam 3A Fall 2002
... 1. A sample of 90 measurements was taken in order to test a claim that the population mean is less than 420. The sample mean and standard deviation were found to be 360 and 210, respectively. An hypothesis test will be performed at the 1% level of significance. a) (6 pts) Formulate the hypotheses. b ...
... 1. A sample of 90 measurements was taken in order to test a claim that the population mean is less than 420. The sample mean and standard deviation were found to be 360 and 210, respectively. An hypothesis test will be performed at the 1% level of significance. a) (6 pts) Formulate the hypotheses. b ...
Statistics: 1.2 Unpaired t
... ’meat‘ (mainly pork and beef but can contain up to 15% poultry) and poultry. The results below are the calorie content of the different brands of beef and poultry hotdogs. Beef hotdogs: ...
... ’meat‘ (mainly pork and beef but can contain up to 15% poultry) and poultry. The results below are the calorie content of the different brands of beef and poultry hotdogs. Beef hotdogs: ...
primer - University of St. Thomas
... designated group of people/places/things/events POPULATION - the collection of ALL objects that are of interest - must be carefully defined - must be able to determine under all circumstances whether something is in the population or not e.g. employees - current? fired? retired? part-time? Problem: ...
... designated group of people/places/things/events POPULATION - the collection of ALL objects that are of interest - must be carefully defined - must be able to determine under all circumstances whether something is in the population or not e.g. employees - current? fired? retired? part-time? Problem: ...
Central Limit Theorem Application Project
... μ and σ. These computed values may not necessarily be equal to the theoretical parametric values; however they should be reasonably close. 3. Calculate the 95% tolerance interval for the population (sample size n= 40). 4. Create 200 different random samples (sample size n= 40) from the population. T ...
... μ and σ. These computed values may not necessarily be equal to the theoretical parametric values; however they should be reasonably close. 3. Calculate the 95% tolerance interval for the population (sample size n= 40). 4. Create 200 different random samples (sample size n= 40) from the population. T ...
Collection Organization Pres and Description of Data
... identify the appropriate shape of distribution of data recognize the difference between qualitative and quantitative data recognize the difference between a discrete and continuous data organize data into frequency distributions graph data identify the position of data value in a data set using vari ...
... identify the appropriate shape of distribution of data recognize the difference between qualitative and quantitative data recognize the difference between a discrete and continuous data organize data into frequency distributions graph data identify the position of data value in a data set using vari ...
Chapter 1: Statistics
... dependent samples are used, is equivalent to the mean of the paired differences. 4. An inference about the mean of the paired differences is an inference about the difference of two means. 5. The mean of the sample paired differences is used as a point estimate for these inferences. ...
... dependent samples are used, is equivalent to the mean of the paired differences. 4. An inference about the mean of the paired differences is an inference about the difference of two means. 5. The mean of the sample paired differences is used as a point estimate for these inferences. ...