1 - JustAnswer
... Test : Because Ha contains “greater than 0. 35”, the hypothesis test is right-tailed. 2.Use the method specified to perform the hypothesis test for the population mean μ. WeatherBug say that the mean daily high for December in a large Florida city is 76(degrees) F. WFLA weather suspects that this te ...
... Test : Because Ha contains “greater than 0. 35”, the hypothesis test is right-tailed. 2.Use the method specified to perform the hypothesis test for the population mean μ. WeatherBug say that the mean daily high for December in a large Florida city is 76(degrees) F. WFLA weather suspects that this te ...
Using SAS® to Create an Effect Size Resampling Distribution for a Statistical Test
... That is, the sample mean differs from the hypothesized mean by more than ½ an observed standard deviation for a medium effect size. For assessing clinical/operational significance the effect size is more meaningful than the p-value which is strongly influenced by the sample size. Note that in the on ...
... That is, the sample mean differs from the hypothesized mean by more than ½ an observed standard deviation for a medium effect size. For assessing clinical/operational significance the effect size is more meaningful than the p-value which is strongly influenced by the sample size. Note that in the on ...
marking scheme
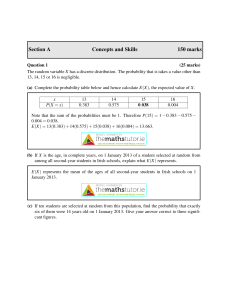
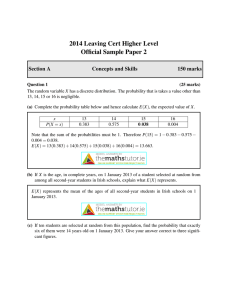
... random sampling within each of the strata. We usually ensure that the size of the sample from each strata is proportional to the size of the strata relative to the overall population. One reason why this method might be chosen is to ensure that each strata of the population is represented proportion ...
... random sampling within each of the strata. We usually ensure that the size of the sample from each strata is proportional to the size of the strata relative to the overall population. One reason why this method might be chosen is to ensure that each strata of the population is represented proportion ...
power point - personal.stevens.edu
... The Bonferroni procedure is the simplest possible approach to the problem of performing many pair-wise tests simultaneously. It multiplies each p-value by the number of comparisons made. ...
... The Bonferroni procedure is the simplest possible approach to the problem of performing many pair-wise tests simultaneously. It multiplies each p-value by the number of comparisons made. ...
statistics_exam
... Accepted characters: numbers, decimal point markers (period or comma), sign indicators (-), spaces (e.g., as thousands separator, 5 000), "E" or "e" (used in scientific notation). NOTE: For scientific notation, a period MUST be used as the decimal point marker. Complex numbers should be in the form ...
... Accepted characters: numbers, decimal point markers (period or comma), sign indicators (-), spaces (e.g., as thousands separator, 5 000), "E" or "e" (used in scientific notation). NOTE: For scientific notation, a period MUST be used as the decimal point marker. Complex numbers should be in the form ...
Data Analysis for a Random Process I. Introduction A. Radioactive
... is again a binomial coefficient which gives the number of combinations of N things (nuclei) taken n at a time (n being the number that decayed during the time interval of length t). N ...
... is again a binomial coefficient which gives the number of combinations of N things (nuclei) taken n at a time (n being the number that decayed during the time interval of length t). N ...
Analysis and Presentation of Student Evaluations of Faculty Data Using SAS
... Another condition which impacted with the problem of implementing SEF data using a co~ puterized system was the affinity the academic com.unity has for committees. Early in the process of defi ni ng the sys tems and methods of SEF implementation, faculty committees were appointed to address segment ...
... Another condition which impacted with the problem of implementing SEF data using a co~ puterized system was the affinity the academic com.unity has for committees. Early in the process of defi ni ng the sys tems and methods of SEF implementation, faculty committees were appointed to address segment ...