Chapter 5: Regression
... sample mean will “capture” µ in about 95% of all samples of size 16. If we estimate that µ lies somewhere in the interval 230.79 to 250.79, we’d be calculating an interval using a method that captures the true µ in about 95% of all possible samples of this size. ...
... sample mean will “capture” µ in about 95% of all samples of size 16. If we estimate that µ lies somewhere in the interval 230.79 to 250.79, we’d be calculating an interval using a method that captures the true µ in about 95% of all possible samples of this size. ...
Lecture notes - The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
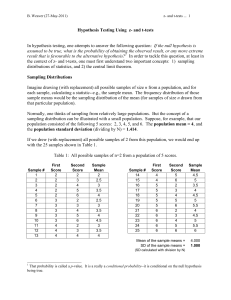
... Problem 2. Given that Z is the standard normal random variable, give the probabilities associated with the following: a. ...
... Problem 2. Given that Z is the standard normal random variable, give the probabilities associated with the following: a. ...
Basic statistics using R
... ¾ Asks whether to save workspace image or not. Answering yes would save all objects on disk in a file .RData. Simultaneously all the commands given in this session are saved in a file ...
... ¾ Asks whether to save workspace image or not. Answering yes would save all objects on disk in a file .RData. Simultaneously all the commands given in this session are saved in a file ...
Slide 1
... salary of Psychology majors who graduated from college in 2004, you select (randomly or non-randomly) some of these graduates and derive a mean from their salaries. Any value derived from the sample, such as the mean, is a statistic. ...
... salary of Psychology majors who graduated from college in 2004, you select (randomly or non-randomly) some of these graduates and derive a mean from their salaries. Any value derived from the sample, such as the mean, is a statistic. ...
The shifting boxplot. A boxplot based on essential
... Psychology, rely on results of parametric tests, like ANOVA and t-test. Parametric tests depend on two major assumptions in order to give unbiased results: homogeneity of variance and normality of data. It has been demonstrated that even small violations of those assumptions can cause the tests to g ...
... Psychology, rely on results of parametric tests, like ANOVA and t-test. Parametric tests depend on two major assumptions in order to give unbiased results: homogeneity of variance and normality of data. It has been demonstrated that even small violations of those assumptions can cause the tests to g ...
8 Two-Sample Inferences for Means Comparing Two Sets of Measurements
... contain a p-value for a two-sided tests of equal population means and a CI for the difference in population means. If you check the box for assuming equal variances you will get the pooled method, otherwise the output is for Satterthwaite’s method. An important point to note: You can request individ ...
... contain a p-value for a two-sided tests of equal population means and a CI for the difference in population means. If you check the box for assuming equal variances you will get the pooled method, otherwise the output is for Satterthwaite’s method. An important point to note: You can request individ ...
doc - Wayne Smith
... Statistics exam. No questions have been added, changed or deleted. I simply expanded the answer key by providing the “missing logic” (the why?) to help understand the correct answer for each question. For use before of after the review workshop, I recommend that the sample exam be administered in a ...
... Statistics exam. No questions have been added, changed or deleted. I simply expanded the answer key by providing the “missing logic” (the why?) to help understand the correct answer for each question. For use before of after the review workshop, I recommend that the sample exam be administered in a ...