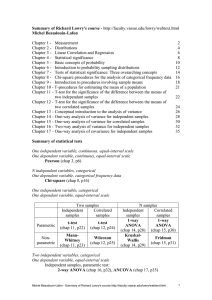
11.2
... Set up the hypotheses Select the level of significance α Compute the test statistic Compare the test statistic with the appropriate critical values Reach a do not reject or reject the null hypothesis conclusion ...
... Set up the hypotheses Select the level of significance α Compute the test statistic Compare the test statistic with the appropriate critical values Reach a do not reject or reject the null hypothesis conclusion ...
Slides 2-5 Hypothesis Testing
... spent by all executives reading and sending e-mail is different from 60 minutes? Assume 5% significance level. Calculate the p-value. ...
... spent by all executives reading and sending e-mail is different from 60 minutes? Assume 5% significance level. Calculate the p-value. ...
MAT 220 Class Notes
... Example. A set of grades has x = 75, s = 6. Then (i) (k = 1): at least 0% of all grades lie in [69, 81] (ii) (k = 2): at least 75% of all grades lie in [63, 87] (iii) (k = 3): at least 88% of all grades lie in [57, 93] (iv) (k = 4): at least ?% of all grades lie in [?, ?] (v) (k = 5): at least ?% of ...
... Example. A set of grades has x = 75, s = 6. Then (i) (k = 1): at least 0% of all grades lie in [69, 81] (ii) (k = 2): at least 75% of all grades lie in [63, 87] (iii) (k = 3): at least 88% of all grades lie in [57, 93] (iv) (k = 4): at least ?% of all grades lie in [?, ?] (v) (k = 5): at least ?% of ...
Interpreting Confidence Intervals
... mean µ,you would probably use x. If you were estimating a population proportion p, you might use pˆ . In both cases, you would be providing a point estimate of the parameter of interest. A point estimator is a statistic that provides an estimate of a population parameter. The value of that statistic ...
... mean µ,you would probably use x. If you were estimating a population proportion p, you might use pˆ . In both cases, you would be providing a point estimate of the parameter of interest. A point estimator is a statistic that provides an estimate of a population parameter. The value of that statistic ...