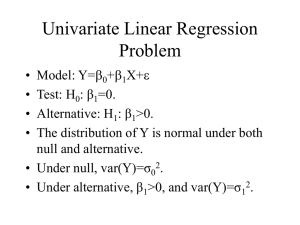
Statistical Analysis
... of your experimental group. Therefore any observed difference between the two sample means occurred by chance and is not statistically significant. If you can reject your null hypothesis then there is a significant difference between your control and experimental groups. Hence accept the alternative ...
... of your experimental group. Therefore any observed difference between the two sample means occurred by chance and is not statistically significant. If you can reject your null hypothesis then there is a significant difference between your control and experimental groups. Hence accept the alternative ...
Hwk 3
... that during the summer months on the average 4200 cars pass by the property each day. Being suspicious that this figure is might be a bit high, the management of the motel chain conducts its own study and obtains a mean of 4,038 cars per day and a standard deviation of 512 cars per day for observati ...
... that during the summer months on the average 4200 cars pass by the property each day. Being suspicious that this figure is might be a bit high, the management of the motel chain conducts its own study and obtains a mean of 4,038 cars per day and a standard deviation of 512 cars per day for observati ...
Statistics 11.1
... The t statistic is used when we don’t know the standard deviation of the population, and instead we use the standard deviation of the ...
... The t statistic is used when we don’t know the standard deviation of the population, and instead we use the standard deviation of the ...
Statistics Computer Lab 6
... hypotheses about a population mean. What do we do when we are dealing with small samples (i.e. n < 30) , and therefore the normality of the sampling distribution of the mean does not follow from the Central Limit Theorem ? In such cases we may still proceed providing that the underlying distribution ...
... hypotheses about a population mean. What do we do when we are dealing with small samples (i.e. n < 30) , and therefore the normality of the sampling distribution of the mean does not follow from the Central Limit Theorem ? In such cases we may still proceed providing that the underlying distribution ...
6 - uf statistics
... 12. During the Million Minutes of Reading campaign elementary school students are encouraged to record how many minutes they read every day for a month. A random sample of 5th grade students was selected, and their total number of minutes for the month was recorded: 454, 617, 1785, 545, 583. Constr ...
... 12. During the Million Minutes of Reading campaign elementary school students are encouraged to record how many minutes they read every day for a month. A random sample of 5th grade students was selected, and their total number of minutes for the month was recorded: 454, 617, 1785, 545, 583. Constr ...