Hypothesis Testing Methods to test
... standard normal, Table Z in the text and Excel normal distribution functions use cumulative probability, hence Z1- denotes a table value with 1- area below it and in the upper tail and Z1-/2 denotes the value with 1- area below and in the upper tail. For the t distribution, Table T in th ...
... standard normal, Table Z in the text and Excel normal distribution functions use cumulative probability, hence Z1- denotes a table value with 1- area below it and in the upper tail and Z1-/2 denotes the value with 1- area below and in the upper tail. For the t distribution, Table T in th ...
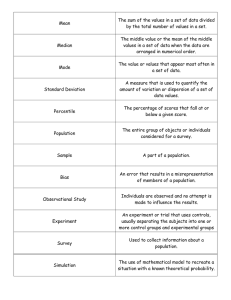
inferential stat
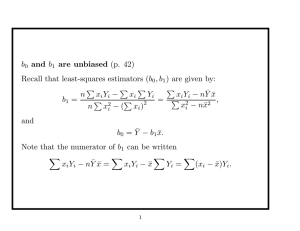
... point estimate - a single value/number that can be regarded as a sensible value for the population parameter. Interval estimate- an interval of possible values of an unknown population parameter ...
... point estimate - a single value/number that can be regarded as a sensible value for the population parameter. Interval estimate- an interval of possible values of an unknown population parameter ...
department of - Faculty of Arts and Sciences - EMU
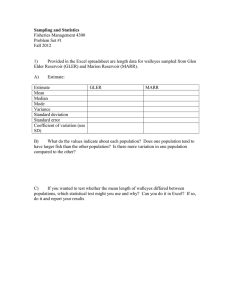
... sampling theory; small samples, chi-square distributions, t-distribution, degree of freedom, confidence intervals, chi-square test, analysis of tables. Estimation of parameters; point and interval estimations. Curve fitting; method of least squares, linear regression, correlation, approximating curv ...
... sampling theory; small samples, chi-square distributions, t-distribution, degree of freedom, confidence intervals, chi-square test, analysis of tables. Estimation of parameters; point and interval estimations. Curve fitting; method of least squares, linear regression, correlation, approximating curv ...
2002_APSTATS_MC 26,27,28,29,30
... the null given that the null was one of the values within the confidence interval. Since, 40,000 is not included in the given confidence interval ($41,300, $58,630), you would reject the null hypothesis at this given confidence interval. ...
... the null given that the null was one of the values within the confidence interval. Since, 40,000 is not included in the given confidence interval ($41,300, $58,630), you would reject the null hypothesis at this given confidence interval. ...
#29 a) skewed right means there are a few instances where groups
... reject it more often you are more likely to reject a false null hypothesis which is good so that power must increase. f) since power is a good thing and it is good to get more data then only using 37 rather than 87 employees should result in the loss of power for the test. G) n=37 and p-hat=.19 and ...
... reject it more often you are more likely to reject a false null hypothesis which is good so that power must increase. f) since power is a good thing and it is good to get more data then only using 37 rather than 87 employees should result in the loss of power for the test. G) n=37 and p-hat=.19 and ...
1 Introduction
... value greater than the chosen percentile threshold (say, 0.025 and 0.975 for an empirical α level of 0.05), divided by B. This value is the empirical p-value. If B = n! then the test is called exact; if all of the permutations are not performed, then there is an inflated Type I error rate, as we are ...
... value greater than the chosen percentile threshold (say, 0.025 and 0.975 for an empirical α level of 0.05), divided by B. This value is the empirical p-value. If B = n! then the test is called exact; if all of the permutations are not performed, then there is an inflated Type I error rate, as we are ...