Document
... Student’s t distribution a distribution based on sample standard deviation s similar to the way the standard normal distribution is based on population standard deviation The t distributions (1) depend on degrees of freedom df (= n –1 for the one sample t test statistic); (2) are symmetric and be ...
... Student’s t distribution a distribution based on sample standard deviation s similar to the way the standard normal distribution is based on population standard deviation The t distributions (1) depend on degrees of freedom df (= n –1 for the one sample t test statistic); (2) are symmetric and be ...
Bootstrapping: described and illustrated Comparing
... The essence of bootstrapping: We begin by assuming a quantitative variable, for which we want to characterize or describe using numerous different statistics (means, medians, trimmed means, variances, sds, skewness, etc.). Our goal is to make inferences about ‘parent population’ parameters using con ...
... The essence of bootstrapping: We begin by assuming a quantitative variable, for which we want to characterize or describe using numerous different statistics (means, medians, trimmed means, variances, sds, skewness, etc.). Our goal is to make inferences about ‘parent population’ parameters using con ...
Independent Samples T
... Comparing Two Groups Independent Samples t-tests: Earlier, our focus was on the mean. We used the mean of the sample (statistic) to infer a range for what our population mean (parameter) might be (confidence interval) or whether it was like some guess or not (significance test). Now, our focus is o ...
... Comparing Two Groups Independent Samples t-tests: Earlier, our focus was on the mean. We used the mean of the sample (statistic) to infer a range for what our population mean (parameter) might be (confidence interval) or whether it was like some guess or not (significance test). Now, our focus is o ...
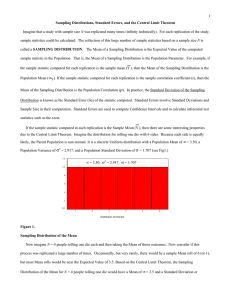
1 N SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION
... has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampled from a non-normal distribution, the sampling distribution of the mean (or sum) is normal as N becomes large (Hays, 1994). Thus, “normal theory” test statistics regarding means (or sums) can be applied if sample sizes are “suf ...
... has particular importance because it implies that even if data are sampled from a non-normal distribution, the sampling distribution of the mean (or sum) is normal as N becomes large (Hays, 1994). Thus, “normal theory” test statistics regarding means (or sums) can be applied if sample sizes are “suf ...
7-2D: Sample Size required to estimate a population mean Examples
... Chapter 7 – 2C: Determining the Sample Size required to Estimate A Population Mean µ The Sample Size required to estimate a Population Mean µ is found by the following formula ⎡ zα 2 • estimated σ x ⎤ n=⎢ ...
... Chapter 7 – 2C: Determining the Sample Size required to Estimate A Population Mean µ The Sample Size required to estimate a Population Mean µ is found by the following formula ⎡ zα 2 • estimated σ x ⎤ n=⎢ ...
1342Lecture8.pdf
... that the difference between 5 and µ X is zero, i.e., the difference is null). Let the alternative hypothesis be H A : µ X > 5 . Now we assign some level of significance denoted α . In practice, it is good statistical practice to select the level of significance before any samples have been taken. Th ...
... that the difference between 5 and µ X is zero, i.e., the difference is null). Let the alternative hypothesis be H A : µ X > 5 . Now we assign some level of significance denoted α . In practice, it is good statistical practice to select the level of significance before any samples have been taken. Th ...
Sample Size versus Detection Probabilities of Off-Aim Drifts in Support or Quality Improvement: A SAS/GRAPH Application
... chara.cteristics·of the processes or products. A key question upfront is that of the monitoring goals and the corresponding sampling frequency dictated by such goals. This quantitative evidence may be as fundamental as t.hat reflected in a quality control chart on the meant ra.nge, variance, or some ...
... chara.cteristics·of the processes or products. A key question upfront is that of the monitoring goals and the corresponding sampling frequency dictated by such goals. This quantitative evidence may be as fundamental as t.hat reflected in a quality control chart on the meant ra.nge, variance, or some ...
ClassicalTestTheory
... •A test is a measurement. Two parallel tests are two independent measurements. A student’s scores on two parallel tests are likely to be different. •Roughly speaking, the degree to which such differences are minimized is Reliability. •The greater the consistency of test scores between a test and its ...
... •A test is a measurement. Two parallel tests are two independent measurements. A student’s scores on two parallel tests are likely to be different. •Roughly speaking, the degree to which such differences are minimized is Reliability. •The greater the consistency of test scores between a test and its ...
TestOfHypothesis - Asia University, Taiwan
... • Now, considered two samples from this population. • These two different samples could have means very different from each other and also very different from the true population mean. • What happen if we considered, not only two samples, but all possible samples of the same size ? • The answer to t ...
... • Now, considered two samples from this population. • These two different samples could have means very different from each other and also very different from the true population mean. • What happen if we considered, not only two samples, but all possible samples of the same size ? • The answer to t ...