Practice Exams II
... current loop, the torque on the loop will be zero. C) When a charge particle moves through a magnetic field, its kinetic energy does not change. D) The drift velocity of electrons in a wire can be determined from the Hall effect. E) The time constant = RC is the time needed to discharge a capacito ...
... current loop, the torque on the loop will be zero. C) When a charge particle moves through a magnetic field, its kinetic energy does not change. D) The drift velocity of electrons in a wire can be determined from the Hall effect. E) The time constant = RC is the time needed to discharge a capacito ...
Magnetic Flux and Inductance
... This has the units of henrys (H), equal to a weber per amp. Inductors are devices used to store energy in the magnetic field, analogous to the storage of energy in the electric field by capacitors. ...
... This has the units of henrys (H), equal to a weber per amp. Inductors are devices used to store energy in the magnetic field, analogous to the storage of energy in the electric field by capacitors. ...
Physics 142
... often very surprising to students, because it goes against their intuition that EM waves propagate through space like waves on a string (which would produce the opposite effect). Even more surprising is to rotate the horn to 90 degrees, such that there is no reception, and place the grill in between ...
... often very surprising to students, because it goes against their intuition that EM waves propagate through space like waves on a string (which would produce the opposite effect). Even more surprising is to rotate the horn to 90 degrees, such that there is no reception, and place the grill in between ...
Physics 1 Qs - L7+8
... A family, who did not understand electricity very well, always made sure there was a bulb in each of the light fittings in their house. They were afraid that electricity would escape from an empty light socket when the switch was turned on. (c) ...
... A family, who did not understand electricity very well, always made sure there was a bulb in each of the light fittings in their house. They were afraid that electricity would escape from an empty light socket when the switch was turned on. (c) ...
TITLE: Principles of Physics II PREFIX/NO: PHYS 111B
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: right hand rule for a magnetic field, right hand rule for a force, magnetic field strength, induction, magnetic field flux density, the unit the tesla, the unit the weber/m, the unit the gauss, a velocity selector, a solenoid, the Hall e ...
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: right hand rule for a magnetic field, right hand rule for a force, magnetic field strength, induction, magnetic field flux density, the unit the tesla, the unit the weber/m, the unit the gauss, a velocity selector, a solenoid, the Hall e ...
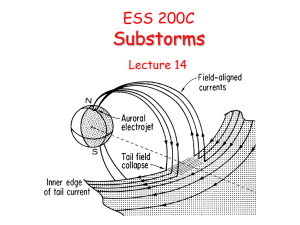
expansion phase
... • The reconnection of open field lines also forms closed field lines earthward of the X-line. • Eventually the balance of forces in the plasma sheet changes and the X-line begins to move tailward. • Earthward of the X-line the plasma sheet thickens and strong earthward flows are observed. • As the ...
... • The reconnection of open field lines also forms closed field lines earthward of the X-line. • Eventually the balance of forces in the plasma sheet changes and the X-line begins to move tailward. • Earthward of the X-line the plasma sheet thickens and strong earthward flows are observed. • As the ...
Magnetism PowerPoint Template
... magnets depends on how the poles of the magnets line up. Like poles repel, and opposite poles attract ...
... magnets depends on how the poles of the magnets line up. Like poles repel, and opposite poles attract ...
Kerala Board Class - X 2010 science Time: 4½ Hrs Score 120
... relatively cold. This difference in temperature is utilized to produce electrical energy. The warm surface water is used to boil a volatile liquid like ammoia. The vapours of the liquid are then used to run the turbine of generator and electricity is produced. 11. H=I2 RT = 25 x 20 x 30 H = 15000 J ...
... relatively cold. This difference in temperature is utilized to produce electrical energy. The warm surface water is used to boil a volatile liquid like ammoia. The vapours of the liquid are then used to run the turbine of generator and electricity is produced. 11. H=I2 RT = 25 x 20 x 30 H = 15000 J ...
Penn State-Developed Heart Pump Sees Successful Human Testing
... they incorporate nonlinearity, through saturation effects in the BH core response curve, but they do not calculate secondary effects, such as intracoil eddy currents and intra-core hysteresis losses. This model differs from the ecore transformer model, in that the two multi-turn coils are physically ...
... they incorporate nonlinearity, through saturation effects in the BH core response curve, but they do not calculate secondary effects, such as intracoil eddy currents and intra-core hysteresis losses. This model differs from the ecore transformer model, in that the two multi-turn coils are physically ...
step-up transformer N2>N1
... valve. The solid line of the current versus time graph at left would be the output of the transformer with only a diode (no capacitor). The capacitor essentially smooths out the signal. In the figure at left R represents the ...
... valve. The solid line of the current versus time graph at left would be the output of the transformer with only a diode (no capacitor). The capacitor essentially smooths out the signal. In the figure at left R represents the ...