Part - Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering
... 2. Derive an expression for the electric field due to a straight uniformly charged wire of length ‘L’ in meters and with a charge density of +λ c/m at the point p which lies along the perpendicular bisector of wire. (10) 3. State and prove Gauss’s law. Describe any two applications of Gauss’s law?(1 ...
... 2. Derive an expression for the electric field due to a straight uniformly charged wire of length ‘L’ in meters and with a charge density of +λ c/m at the point p which lies along the perpendicular bisector of wire. (10) 3. State and prove Gauss’s law. Describe any two applications of Gauss’s law?(1 ...
Physics 203 Sample Exam 1
... (a) constant electric and magnetic fields. (b) oscillating electric and magnetic fields in the same direction. (c) electric and magnetic fields at various angles. (d) oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles. [8] Magnetic fields can be produced by (a) electric currents (b) changing e ...
... (a) constant electric and magnetic fields. (b) oscillating electric and magnetic fields in the same direction. (c) electric and magnetic fields at various angles. (d) oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles. [8] Magnetic fields can be produced by (a) electric currents (b) changing e ...
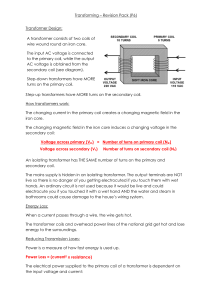
Transforming – Revision Pack (P6) Transformer Design: Step
... An isolating transformer has THE SAME number of turns on the primary and secondary coil. The mains supply is hidden in an isolating transformer. The output terminals are NOT live so there is no danger of you getting electrocuted if you touch them with wet hands. An ordinary circuit is not used becau ...
... An isolating transformer has THE SAME number of turns on the primary and secondary coil. The mains supply is hidden in an isolating transformer. The output terminals are NOT live so there is no danger of you getting electrocuted if you touch them with wet hands. An ordinary circuit is not used becau ...
phy_1304 - WordPress.com
... 12)Draw magnetic field lines when a diamagnetic and paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field and write one difference between its in terms of magnetic susceptibility. 13) Two long straight parallel conductors X and Y , carrying steady currents I1 and I2 in the same direction a ...
... 12)Draw magnetic field lines when a diamagnetic and paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field and write one difference between its in terms of magnetic susceptibility. 13) Two long straight parallel conductors X and Y , carrying steady currents I1 and I2 in the same direction a ...
Functional Ecology (Boreal Ecosystems)
... – 100 x – doping conc – 10 x thinner device – 500-1000 better conductivity (reduced by carrier mobility) ...
... – 100 x – doping conc – 10 x thinner device – 500-1000 better conductivity (reduced by carrier mobility) ...
MAGNETS AND MAGNETISM. - Sydney Open Journals online
... magnets were permanent "horseshoe" magnets similar to those sold in toy shops-now very strong electro-magnets are used, the electricity generated being passed through coils wound on, but insulated from, soft iron, so as to produce magnets of much greater strength than would otherwise exist. Apart fr ...
... magnets were permanent "horseshoe" magnets similar to those sold in toy shops-now very strong electro-magnets are used, the electricity generated being passed through coils wound on, but insulated from, soft iron, so as to produce magnets of much greater strength than would otherwise exist. Apart fr ...
W10D1_Presentation_answers_jwb
... 1. House=Left, Line=Right 2. Line=Left, House=Right 3. I don’t know ...
... 1. House=Left, Line=Right 2. Line=Left, House=Right 3. I don’t know ...
Magnetism - a magnet has polarity. It has 2 ends. A north seeking
... switch constantly produce current in second coil. ⇒vary the magnetic field. To do this, we need an alternating current. The current produced by an AC generator provides a means for the current to be turned on and off without manually operating a switch. Faraday’s iron ring is a TRANSFORMER. • The vo ...
... switch constantly produce current in second coil. ⇒vary the magnetic field. To do this, we need an alternating current. The current produced by an AC generator provides a means for the current to be turned on and off without manually operating a switch. Faraday’s iron ring is a TRANSFORMER. • The vo ...
Today • Questions re: Magnetism problems 2 • HW: Magnetism
... field strength will increase by some number that is associated with iron (for Iron, k = 200). In essence, by filling the space with a magnetic material, you effectively increase the strength of the Electromagnet. ...
... field strength will increase by some number that is associated with iron (for Iron, k = 200). In essence, by filling the space with a magnetic material, you effectively increase the strength of the Electromagnet. ...