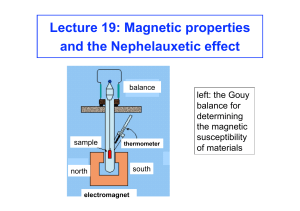
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... electrons are magnetically dilute, and so the unpaired electrons in one atom are not aligned with those in other atoms. However, in ferromagnetic materials, such as metallic iron, or iron oxides such as magnetite (Fe3O4), where the paramagnetic iron atoms are very close together, they can create an ...
... electrons are magnetically dilute, and so the unpaired electrons in one atom are not aligned with those in other atoms. However, in ferromagnetic materials, such as metallic iron, or iron oxides such as magnetite (Fe3O4), where the paramagnetic iron atoms are very close together, they can create an ...
Temas Selectos de Física
... coil of the electric motor rotates an unlimited number of turns. __________ The electrical resistance of an electrical circuit with three resistors connected in parallel is greater than the resistance of an electrical circuit with the same three resistors connected in series. ...
... coil of the electric motor rotates an unlimited number of turns. __________ The electrical resistance of an electrical circuit with three resistors connected in parallel is greater than the resistance of an electrical circuit with the same three resistors connected in series. ...
Magnetic field of the earth OBJEctiVE gEnEral
... plane in such a way that its needle points to 0° when parallel to the horizontal component 0°. An additional horizontal magnetic field BHH, which is perpendicular to Bh, is generated by a pair of Helmholtz coils and this field causes the compass needle to turn by an angle β. According to Fig. 1 the ...
... plane in such a way that its needle points to 0° when parallel to the horizontal component 0°. An additional horizontal magnetic field BHH, which is perpendicular to Bh, is generated by a pair of Helmholtz coils and this field causes the compass needle to turn by an angle β. According to Fig. 1 the ...
Magnetic Effects due to Electric Currents Result:
... • Force is proportional to product of both currents. • Force is inversely proportional to distance (r) between wires. • Force is proportional to length (l) of wires. • Force is attractive when currents in same direction and repulsive if current in opposite direction. • Example: Determine force betwe ...
... • Force is proportional to product of both currents. • Force is inversely proportional to distance (r) between wires. • Force is proportional to length (l) of wires. • Force is attractive when currents in same direction and repulsive if current in opposite direction. • Example: Determine force betwe ...
Experiment - TerpConnect
... surface. Electrical currents generate magnetic fields, similar to the way that electrical charges generate electric fields. The magnitude of the magnetic field generated depends of the specific geometry of the wire in which the current is flowing, and sometimes in a complicated way, but for a given ...
... surface. Electrical currents generate magnetic fields, similar to the way that electrical charges generate electric fields. The magnitude of the magnetic field generated depends of the specific geometry of the wire in which the current is flowing, and sometimes in a complicated way, but for a given ...
February 2011
... – More mechanically robust – Magnet losses can be an issue (not shielded by rotor iron); reduce by segmenting magnets axially or radially or increasing magnet resistivity ...
... – More mechanically robust – Magnet losses can be an issue (not shielded by rotor iron); reduce by segmenting magnets axially or radially or increasing magnet resistivity ...
5. Capacitance & Inductor
... •When the potential different is same as the voltage of the battery, the entering of charges stop. •Charges are stored in the capacitor plates after the connection to the battery is disconnected. •Ratio of Q:V is constant and is called as capacitance, thus ...
... •When the potential different is same as the voltage of the battery, the entering of charges stop. •Charges are stored in the capacitor plates after the connection to the battery is disconnected. •Ratio of Q:V is constant and is called as capacitance, thus ...
magnetic field
... current-carrying wire loop. Electric motors use a commutator to change the direction of the current in the loop. Alternating current electric motors do not use commutators. ...
... current-carrying wire loop. Electric motors use a commutator to change the direction of the current in the loop. Alternating current electric motors do not use commutators. ...
Electromagnetism: Home
... way? The magnetic field increased because you increased the number of coils, and thus, the ...
... way? The magnetic field increased because you increased the number of coils, and thus, the ...
ER Week17, Magnetism
... o Electromagnet: An electromagnet is a coil wound around typically an iron or steel core. When current flows through it, the core becomes magnetized. o Demonstration running current through a conductor in one direction then in the ...
... o Electromagnet: An electromagnet is a coil wound around typically an iron or steel core. When current flows through it, the core becomes magnetized. o Demonstration running current through a conductor in one direction then in the ...
A 100-turn coil of area 0.1 m 2 rotates at half a revolution per second
... Q.20. Explain, why high frequency carrier waves are needed for effective transmission of signals. A message signal of 12 kHz and peak voltage 30 V. calculate the (i) modulation index (ii) side-band frequencies. Q.21. Distinguish between unpolarised and plane polarized light. An unpolarised light is ...
... Q.20. Explain, why high frequency carrier waves are needed for effective transmission of signals. A message signal of 12 kHz and peak voltage 30 V. calculate the (i) modulation index (ii) side-band frequencies. Q.21. Distinguish between unpolarised and plane polarized light. An unpolarised light is ...