stars - acpsd
... for new stars begins in the Main Sequence. These mature stars undergo a remarkable transformation after they consume all the hydrogen in their core. With the hydrogen consumed, stars leave the main sequence and expand to form red giants. With this new stage, the fusion of helium begins to form heavi ...
... for new stars begins in the Main Sequence. These mature stars undergo a remarkable transformation after they consume all the hydrogen in their core. With the hydrogen consumed, stars leave the main sequence and expand to form red giants. With this new stage, the fusion of helium begins to form heavi ...
Stellar Classification - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... B 10,000 - 30,000 K Blue-white stars A 7,500 - 10,000 K White stars F 6,000 - 7,500 K Yellow-white stars G 5,000 - 6,000 K Yellow stars (like the Sun) K 3,500 - 5,000K Yellow-orange stars M < 3,500 K Red stars ...
... B 10,000 - 30,000 K Blue-white stars A 7,500 - 10,000 K White stars F 6,000 - 7,500 K Yellow-white stars G 5,000 - 6,000 K Yellow stars (like the Sun) K 3,500 - 5,000K Yellow-orange stars M < 3,500 K Red stars ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
CHAPTER 12—STELLAR EVOLUTION
... ____ 27. Stars support their weight by generating energy in their centers. ____ 28. Stars swell into giants when hydrogen is exhausted in their centers. ____ 29. The helium flash is the cause of some supernovae. ____ 30. Helium fusion does not begin until the star has entered the giant region of the ...
... ____ 27. Stars support their weight by generating energy in their centers. ____ 28. Stars swell into giants when hydrogen is exhausted in their centers. ____ 29. The helium flash is the cause of some supernovae. ____ 30. Helium fusion does not begin until the star has entered the giant region of the ...
Answers for the HST Scavenger Hunt
... Give a definition of these kinds of stars. Hot, dense remains of a low-mass star like our Sun that has exhausted its sources of fuel for thermonuclear fusion. What is a Wolf-Rayet Star? Massive stars, which are usually are surrounded by outflowing gas clouds. How is this star type different from whi ...
... Give a definition of these kinds of stars. Hot, dense remains of a low-mass star like our Sun that has exhausted its sources of fuel for thermonuclear fusion. What is a Wolf-Rayet Star? Massive stars, which are usually are surrounded by outflowing gas clouds. How is this star type different from whi ...
Where Do Chemical Elements Come From?
... emission spectrum specific that emits the light. For example, the hydrogen’s emission spectrum only to hydrogen. consists of four lines: purple, blue, green, and red, located at positions that correspond to their wavelengths. The emission spectrum of helium consists of six lines that are purple, cya ...
... emission spectrum specific that emits the light. For example, the hydrogen’s emission spectrum only to hydrogen. consists of four lines: purple, blue, green, and red, located at positions that correspond to their wavelengths. The emission spectrum of helium consists of six lines that are purple, cya ...
Stars Part 1
... between height and weight for humans. - now add to your plot the population of basketball players who are very tall and very thin. - now add the population of obese children •The plot would show a cluster of people that would have similar “middle-of-the-road” height/weight ratios •It would also show ...
... between height and weight for humans. - now add to your plot the population of basketball players who are very tall and very thin. - now add the population of obese children •The plot would show a cluster of people that would have similar “middle-of-the-road” height/weight ratios •It would also show ...
ncam-program-2016 - Cline Observatory
... built for this very purpose. I report on the constraints on the planetary compositions, and address the transition from terrestrial planets, composed of rock and iron, to Neptune-like worlds, which have accreted an envelope of primordial H/He gas. I will explain the essential role of the NASA Transi ...
... built for this very purpose. I report on the constraints on the planetary compositions, and address the transition from terrestrial planets, composed of rock and iron, to Neptune-like worlds, which have accreted an envelope of primordial H/He gas. I will explain the essential role of the NASA Transi ...
Astronomy Report Southern Cross Authors Maria Constanza Pavez
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Distances to Stars
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
LESSON 8: STARS
... shockwave of material that explodes into space. This explosion is called a supernova, and will increase the luminosity of the star by a factor of millions. A supernova is much more powerful than a nova and will be extremely bright for a few weeks or months, until it gradually subsides and dims. What ...
... shockwave of material that explodes into space. This explosion is called a supernova, and will increase the luminosity of the star by a factor of millions. A supernova is much more powerful than a nova and will be extremely bright for a few weeks or months, until it gradually subsides and dims. What ...
January 2015 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... about 21:00 on 15th January. West is to the right and east to the left. The curved line across the sky is the ecliptic. This is the imaginary line along which the Sun, Moon and planets appear to move across the sky. The constellations through which the ecliptic passes are known as the constellations ...
... about 21:00 on 15th January. West is to the right and east to the left. The curved line across the sky is the ecliptic. This is the imaginary line along which the Sun, Moon and planets appear to move across the sky. The constellations through which the ecliptic passes are known as the constellations ...
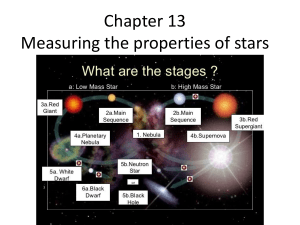
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... the star to heat and cool, expand and contract. The very most massive stars are so luminous they blow off their outer layers. The remaining star, called a Wolf-Rayet star, is recognizable by its strange spectrum. Once the material at the core is burned to iron, the star faces the ultimate energy cri ...
... the star to heat and cool, expand and contract. The very most massive stars are so luminous they blow off their outer layers. The remaining star, called a Wolf-Rayet star, is recognizable by its strange spectrum. Once the material at the core is burned to iron, the star faces the ultimate energy cri ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
star pattern identification : application to the precise attitude
... thus the attitude determination went inaccurate in the region of scientific interest. All these problems which were left aside in a first intensive attitude production were recently reassessed and the present status of their solution is described in this work. Of particular interest was the possibil ...
... thus the attitude determination went inaccurate in the region of scientific interest. All these problems which were left aside in a first intensive attitude production were recently reassessed and the present status of their solution is described in this work. Of particular interest was the possibil ...
Project 2. CCD Photometry
... Standard stars are required so that different observers are able to compare results with each other. The reason this is true is because every observational setup is likely to have different response functions, so the same stars will not be observed to have the same brightness (even relative ...
... Standard stars are required so that different observers are able to compare results with each other. The reason this is true is because every observational setup is likely to have different response functions, so the same stars will not be observed to have the same brightness (even relative ...
Eyes to the Sky
... Venus is the crescent Moon's most noticeable companion, but look for other planets near the moon too. ...
... Venus is the crescent Moon's most noticeable companion, but look for other planets near the moon too. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.