printer-friendly version of benchmark
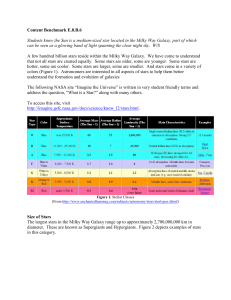
... Brightness of Stars The brightness of stars, including our Sun, is measured in terms of magnitude and luminosity. This measurement is somewhat complicated by the fact that nearby dimmer stars might appear brighter than really bright distant stars. The further a star is below a magnitude of zero, th ...
... Brightness of Stars The brightness of stars, including our Sun, is measured in terms of magnitude and luminosity. This measurement is somewhat complicated by the fact that nearby dimmer stars might appear brighter than really bright distant stars. The further a star is below a magnitude of zero, th ...
Curiosities of the Sky
... diffuse a state can be incandescent through heat, and phosphorescent light is in itself a mystery. The supposition is also in accord with what we know of the existence of dark solid bodies in space. Many bright stars are accompanied by obscure companions, sometimes as massive as themselves; the plan ...
... diffuse a state can be incandescent through heat, and phosphorescent light is in itself a mystery. The supposition is also in accord with what we know of the existence of dark solid bodies in space. Many bright stars are accompanied by obscure companions, sometimes as massive as themselves; the plan ...
Downloadable Full Text
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
Chapter 26.2 notes
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
Light and shadow from distant worlds
... The nearness of the hot Jupiters to their stars means that they have a significant probability (typically about 0.1) of transiting their star as seen from Earth. During the transit, our Earth falls within the shadow of the exoplanet, and the light we receive from the parent star is diminished by a s ...
... The nearness of the hot Jupiters to their stars means that they have a significant probability (typically about 0.1) of transiting their star as seen from Earth. During the transit, our Earth falls within the shadow of the exoplanet, and the light we receive from the parent star is diminished by a s ...
Direct Imaging Searches Around White Dwarfs - X
... • cadence: 8min for WASP v transit times of 1-few mins • unknown frequency of close planetary companions • Survivors of common envelope evolution? • 2nd generation planets? Faedi, West, Burleigh, Goad, & Hebb, (2011), MNRAS, 410, 899 and various conference proceedings since 2007 ...
... • cadence: 8min for WASP v transit times of 1-few mins • unknown frequency of close planetary companions • Survivors of common envelope evolution? • 2nd generation planets? Faedi, West, Burleigh, Goad, & Hebb, (2011), MNRAS, 410, 899 and various conference proceedings since 2007 ...
A brief history of extra-solar planets - X
... Searching for Earths by transit method Launched last year by NASA Aims to find an Earth around a Sun-like star in a one year orbit Need three transits to confirm So mission lasts at least three years… ...
... Searching for Earths by transit method Launched last year by NASA Aims to find an Earth around a Sun-like star in a one year orbit Need three transits to confirm So mission lasts at least three years… ...
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd)
... outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the period of a low-mass star's life when it can no longer fuse carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in its core • the ...
... outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the period of a low-mass star's life when it can no longer fuse carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in its core • the ...
A Hero`s Little Horse: Discovery of a Dissolving Star Cluster in
... best-fit Plummer profile (Plummer 1911) to parametrise the underlying stellar distribution. We obtain a half-light radius of 1.2 ± 0.1 arcmin or rh = 6.9 ± 0.6 pc, adopting the distance modulus of 16.48 mag. In analogy to Walsh et al. (2008) we estimate the total luminosity of Kim 1 by integrating t ...
... best-fit Plummer profile (Plummer 1911) to parametrise the underlying stellar distribution. We obtain a half-light radius of 1.2 ± 0.1 arcmin or rh = 6.9 ± 0.6 pc, adopting the distance modulus of 16.48 mag. In analogy to Walsh et al. (2008) we estimate the total luminosity of Kim 1 by integrating t ...
The Next 2-3 Weeks
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... studies on the wide double stars are also in progress. The importance of visual double stars to astronomy needs to be emphasized. A study of their orbit permits the calculation of the sum of the masses of the components if we also have the parallax of the system. The first stage of orbit computation ...
... studies on the wide double stars are also in progress. The importance of visual double stars to astronomy needs to be emphasized. A study of their orbit permits the calculation of the sum of the masses of the components if we also have the parallax of the system. The first stage of orbit computation ...
Stars - Emera Astronomy Center
... or wood. Stars are different colors because they are different temperatures. They are all “hot” compared to most things on Earth; they range in surface temperature from less then 3000 K to over 50,000 K. Explain to students that when we heat things that don’t easily melt (like metal), they first loo ...
... or wood. Stars are different colors because they are different temperatures. They are all “hot” compared to most things on Earth; they range in surface temperature from less then 3000 K to over 50,000 K. Explain to students that when we heat things that don’t easily melt (like metal), they first loo ...
che
... eclipse is extremely variable (presumably due to gaseous streams from ther star and stellar wind from the disk) Ingress to the primary eclipse is much more stable Interpretation of the primary eclipse by geometrical model should be based on the upper envelope of the eclipse ingress ...
... eclipse is extremely variable (presumably due to gaseous streams from ther star and stellar wind from the disk) Ingress to the primary eclipse is much more stable Interpretation of the primary eclipse by geometrical model should be based on the upper envelope of the eclipse ingress ...
File - Mr. Gray`s Class
... million miles an hour, take a little over four years to make the journey between these two systems. Other stars are even farther than Alpha Centauri, separated from us by increasingly larger gulfs of space and time. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are hundreds of light years away. If we could ...
... million miles an hour, take a little over four years to make the journey between these two systems. Other stars are even farther than Alpha Centauri, separated from us by increasingly larger gulfs of space and time. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are hundreds of light years away. If we could ...
Review 3 (11-18-10)
... I. Death of Stars • White Dawrfs: very dense, about mass of Sun in size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be ...
... I. Death of Stars • White Dawrfs: very dense, about mass of Sun in size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be ...
Astronomy 114 - Department of Astronomy
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.