Physics 20 Lesson 23 Orbits and Satellites
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
Document
... runs month after month through all other zodiacal line before returning on the line of Aries... ...
... runs month after month through all other zodiacal line before returning on the line of Aries... ...
Astronomy Unit BM study guide
... Because the Moon’s period of rotation on its axis and period of revolution around the Earth are nearly the same, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Changes in the Moon’s position as it revolves around the Earth results in more or less of the sunlight reflected form the Moon being visible ...
... Because the Moon’s period of rotation on its axis and period of revolution around the Earth are nearly the same, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Changes in the Moon’s position as it revolves around the Earth results in more or less of the sunlight reflected form the Moon being visible ...
The Orrery - Eli Whitney Museum
... Earth. As those two planets travel around the Sun, the furthest they can appear away from the Sun is when their position in their orbit is perpendicular to Earth. In this position Venus has a maximum angle of 35 degrees from the Sun and Mercury has a maximum angle of 21 degrees. If the Sun was just ...
... Earth. As those two planets travel around the Sun, the furthest they can appear away from the Sun is when their position in their orbit is perpendicular to Earth. In this position Venus has a maximum angle of 35 degrees from the Sun and Mercury has a maximum angle of 21 degrees. If the Sun was just ...
Study Guide 2 - Otterbein University
... system, and describe why his model cannot reproduce this pattern in the sky. Warm-up #14: based on Section 1.3. “The Laws of Planetary Motion” 1. In what way is an ellipse the generalization of a circle? 2. Did Kepler succeed in finding the distance to the Sun? Why or why not? Warm-up #15: based on ...
... system, and describe why his model cannot reproduce this pattern in the sky. Warm-up #14: based on Section 1.3. “The Laws of Planetary Motion” 1. In what way is an ellipse the generalization of a circle? 2. Did Kepler succeed in finding the distance to the Sun? Why or why not? Warm-up #15: based on ...
Solar System Formation
... • 2nd largest planet in solar system. • A “day” on Saturn is a little over 10 hours long! • It takes 29 years to orbit the sun. • Almost 10 times larger than Earth. • Most visible rings of any planet. • Density is 0.69 g/cm3. • If a large enough ocean could be found, Saturn would float in it! ...
... • 2nd largest planet in solar system. • A “day” on Saturn is a little over 10 hours long! • It takes 29 years to orbit the sun. • Almost 10 times larger than Earth. • Most visible rings of any planet. • Density is 0.69 g/cm3. • If a large enough ocean could be found, Saturn would float in it! ...
Solar System - eNetLearning
... • 2nd largest planet in solar system. • A “day” on Saturn is a little over 10 hours long! • It takes 29 years to orbit the sun. • Almost 10 times larger than Earth. • Most visible rings of any planet. • Density is 0.69 g/cm3. • If a large enough ocean could be found, Saturn would float in it! ...
... • 2nd largest planet in solar system. • A “day” on Saturn is a little over 10 hours long! • It takes 29 years to orbit the sun. • Almost 10 times larger than Earth. • Most visible rings of any planet. • Density is 0.69 g/cm3. • If a large enough ocean could be found, Saturn would float in it! ...
December 2007 Clear Skies Newsletter PDF
... gamma-ray/X-ray spectrometer, a microwave radiometer, a high-energy particle 5 detector, and a solar wind particle detector. Named after the Chinese goddess of the Moon, Chang'e-1 represents the first phase in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP). This program is expected to last until arou ...
... gamma-ray/X-ray spectrometer, a microwave radiometer, a high-energy particle 5 detector, and a solar wind particle detector. Named after the Chinese goddess of the Moon, Chang'e-1 represents the first phase in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP). This program is expected to last until arou ...
Seasons
... Pointed at sun = warm = summer Pointed away from sun = cold = winter Not pointed at = neither = fall and spring Summer solstice = longest day of year Winter solstice = shortest day of year Equinoxes = equal day and night N & S hemispheres are opposites ...
... Pointed at sun = warm = summer Pointed away from sun = cold = winter Not pointed at = neither = fall and spring Summer solstice = longest day of year Winter solstice = shortest day of year Equinoxes = equal day and night N & S hemispheres are opposites ...
Earth Moon Sun System PPT
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
Earth Moon Sun System PPT
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
or view
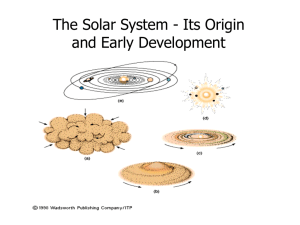
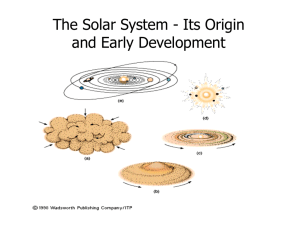
... to less than 50K at the outer regions. The heat in the inner Solar System only allowed materials with high condensation temperatures to remain solid. These particles eventually gathered to form the four terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. A similar process formed the outer planets o ...
... to less than 50K at the outer regions. The heat in the inner Solar System only allowed materials with high condensation temperatures to remain solid. These particles eventually gathered to form the four terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. A similar process formed the outer planets o ...
THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... D. Other Vagabonds of the Solar System In addition to the planets and their moons, there are also a collection of smaller orbiting bodies in the solar system. These are: ...
... D. Other Vagabonds of the Solar System In addition to the planets and their moons, there are also a collection of smaller orbiting bodies in the solar system. These are: ...
The Ultimate Tool of Astronomy: Telescopes
... Two identical stars are observed from the Earth. Star A’s emission lines (that are at visible wavelengths in the rest frame) are observed to be at ultraviolet wavelengths. The same emission lines for Star B are observed to be at X-ray wavelengths. From these ...
... Two identical stars are observed from the Earth. Star A’s emission lines (that are at visible wavelengths in the rest frame) are observed to be at ultraviolet wavelengths. The same emission lines for Star B are observed to be at X-ray wavelengths. From these ...
Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS
... community. Which of the following statements is best supported by the diagram? A. The water level will decrease by added chemicals to the ground. B. Pollutants from different sources can contaminate the groundwater. C. The rock fragments will protect the groundwater from the pollutants. D. Toxic was ...
... community. Which of the following statements is best supported by the diagram? A. The water level will decrease by added chemicals to the ground. B. Pollutants from different sources can contaminate the groundwater. C. The rock fragments will protect the groundwater from the pollutants. D. Toxic was ...
CP CircularGravityReview
... A) Becausethe moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth B) Becausethe moon movesin a curved path C) Becausethere is no air on the moon D) Becausethe moon is moving 7. Newton had the insight to seethat the A) moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth. B) moon orbits the earth. C) moon is moving. D) f ...
... A) Becausethe moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth B) Becausethe moon movesin a curved path C) Becausethere is no air on the moon D) Becausethe moon is moving 7. Newton had the insight to seethat the A) moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth. B) moon orbits the earth. C) moon is moving. D) f ...
Unit 6: Space
... SC.8.E.5.In.11: Identify technology used by scientists to locate, view, and study objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Su.8: Recognize that scientists use special tools to examine objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Pa.4: Recognize a technology tool created for space exploration and adapted for personal use, such as c ...
... SC.8.E.5.In.11: Identify technology used by scientists to locate, view, and study objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Su.8: Recognize that scientists use special tools to examine objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Pa.4: Recognize a technology tool created for space exploration and adapted for personal use, such as c ...
About Uranus - COSTA VERDE production
... When Uranus didn't travel exactly as astronomers expected it to, a French mathematician proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus' orbit, which finally lead to the discovery of Neptune. ...
... When Uranus didn't travel exactly as astronomers expected it to, a French mathematician proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus' orbit, which finally lead to the discovery of Neptune. ...
1. The Sun has a surface temperature of about 6000 K.
... The inner planets are made of rocks and metals. The outer planets also have ices and gasses. Only rocks and metals were solids near the Sun, so the planetesimals were made of rocks and metals. Out farther, ices could freeze onto the dust grains, so they got included in the planetesimals. In addition ...
... The inner planets are made of rocks and metals. The outer planets also have ices and gasses. Only rocks and metals were solids near the Sun, so the planetesimals were made of rocks and metals. Out farther, ices could freeze onto the dust grains, so they got included in the planetesimals. In addition ...
The Ancient Heavens: Exploring the History of Astronomy
... these activities help participants appreciate not only what we know, but how we know it. ...
... these activities help participants appreciate not only what we know, but how we know it. ...
Document
... looking at earth through telescopes at the same time, which aliens would be last to receive current information? A W ...
... looking at earth through telescopes at the same time, which aliens would be last to receive current information? A W ...
Educator`s Guide
... Ahead of time: Write the names of the Sun and each planet on index cards. Utilizing the information from the Toilet Paper Distance Table, have the students create their toilet paper solar system model. (Note: the number of squares of toilet paper listed by each planet is the distance from the Sun no ...
... Ahead of time: Write the names of the Sun and each planet on index cards. Utilizing the information from the Toilet Paper Distance Table, have the students create their toilet paper solar system model. (Note: the number of squares of toilet paper listed by each planet is the distance from the Sun no ...
Astronomy 101 Course Review and Summary
... Earth’s rotation axis relative to its orbit around the Sun. The day is based on the time between one noon and the next. The year is based on the time between one vernal equinox and the next. The moon (month) is based on the time between one new moon and the next. ...
... Earth’s rotation axis relative to its orbit around the Sun. The day is based on the time between one noon and the next. The year is based on the time between one vernal equinox and the next. The moon (month) is based on the time between one new moon and the next. ...
January SKY Newsletter 2012
... southern horizon below Canis Major between 10:00 and 11:00 p.m. The Winter Hexagon will move across the southern sky over the course of the night. Other constellations in the south at this time are very large and fairly dim, but if you are in a dark site you may want to check for observing details ...
... southern horizon below Canis Major between 10:00 and 11:00 p.m. The Winter Hexagon will move across the southern sky over the course of the night. Other constellations in the south at this time are very large and fairly dim, but if you are in a dark site you may want to check for observing details ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.