Grade 5 CPSD Science Curriculum Guide
... The orbits of Earth around the sun and of the moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its North and South poles, cause observable patterns. These include day and night; daily changes in the length and direction of shadows; and different positions of the sun, moon ...
... The orbits of Earth around the sun and of the moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its North and South poles, cause observable patterns. These include day and night; daily changes in the length and direction of shadows; and different positions of the sun, moon ...
Clear Skies - Cowichan Valley Starfinders Society
... relatively unknown in the Cowichan Valley, any such displays can only help to promote our club and encourage new membership. Another such display is scheduled for Saturday July 14, one week before the ISP. Looking to the future year, I would like to promote two initiatives. The first is to impliment ...
... relatively unknown in the Cowichan Valley, any such displays can only help to promote our club and encourage new membership. Another such display is scheduled for Saturday July 14, one week before the ISP. Looking to the future year, I would like to promote two initiatives. The first is to impliment ...
Seeing Through the Clouds of Venus
... Hydrogen absorbs these wavelengths of light, so they cannot be seen in the spectrum ...
... Hydrogen absorbs these wavelengths of light, so they cannot be seen in the spectrum ...
2.1.1 Study: The Big Bang Theory
... Stars larger than our sun will either supernova and then form a neutron star, or, if they are very large, supernova and then form a black hole. Stars form when a solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity. Nuclear fusion takes place throughout the star's life cycle, and when it is over, it re ...
... Stars larger than our sun will either supernova and then form a neutron star, or, if they are very large, supernova and then form a black hole. Stars form when a solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity. Nuclear fusion takes place throughout the star's life cycle, and when it is over, it re ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4656 (10.4) pc. are a fine example of a pair of interacting galaxies, both edge-on to our view, located mid-way between Cor Coroli and the Coma star cluster. One end of NGC4656 has a distinct hook which may be glimpsed in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M9 ...
... NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4656 (10.4) pc. are a fine example of a pair of interacting galaxies, both edge-on to our view, located mid-way between Cor Coroli and the Coma star cluster. One end of NGC4656 has a distinct hook which may be glimpsed in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M9 ...
ISNS3371_020607_bw
... facing side - creates tide - and pulls the Earth away from the ocean water on the other side - reason for tides twice a day. Time of tides varies by 50 min per day - Moon at its highest point every 24 hrs 50 min because Moon orbits Earth while Earth rotates. ...
... facing side - creates tide - and pulls the Earth away from the ocean water on the other side - reason for tides twice a day. Time of tides varies by 50 min per day - Moon at its highest point every 24 hrs 50 min because Moon orbits Earth while Earth rotates. ...
Study Guide for Astronomy 10A Prologue What is the purpose of
... What star is at your zenith when standing at the North Pole? What is the distance from the Earth to the Sun called? How far is the distance form the Earth to the Sun in miles (km)? What is the difference between astrology and astronomy? Why do many astronomers hate astrology? Why doesn’t your belove ...
... What star is at your zenith when standing at the North Pole? What is the distance from the Earth to the Sun called? How far is the distance form the Earth to the Sun in miles (km)? What is the difference between astrology and astronomy? Why do many astronomers hate astrology? Why doesn’t your belove ...
Biological Adaptations - Hartsville Middle School
... considerably larger than terrestrial planets. • Planets may have rings. Some planets have a unique surface characteristic, for example color or an atmospheric storm. • Movement of planets is based on revolution around the Sun and rotation on the planet’s axis. Moons • Moons are studied in relation t ...
... considerably larger than terrestrial planets. • Planets may have rings. Some planets have a unique surface characteristic, for example color or an atmospheric storm. • Movement of planets is based on revolution around the Sun and rotation on the planet’s axis. Moons • Moons are studied in relation t ...
How to Use This Presentation
... • The path that a body follows as it travels around another body is called an orbit. • Earth’s orbit around the sun is an ellipse, a closed curve whose shape is determined by two points, or foci, within the ellipse. • In planetary orbits, one focus is located within the sun. No object is located at ...
... • The path that a body follows as it travels around another body is called an orbit. • Earth’s orbit around the sun is an ellipse, a closed curve whose shape is determined by two points, or foci, within the ellipse. • In planetary orbits, one focus is located within the sun. No object is located at ...
Uranus
... Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus has 21 moons and small, dusty rings. Voyager 2 acquired this view of the seventh planet while departing the Uranian system in late January 1986. This image looks at the planet approximately along its rotational pole. ...
... Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus has 21 moons and small, dusty rings. Voyager 2 acquired this view of the seventh planet while departing the Uranian system in late January 1986. This image looks at the planet approximately along its rotational pole. ...
uranus
... Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus has 21 moons and small, dusty rings. Voyager 2 acquired this view of the seventh planet while departing the Uranian system in late January 1986. This image looks at the planet approximately along its rotational pole. ...
... Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus has 21 moons and small, dusty rings. Voyager 2 acquired this view of the seventh planet while departing the Uranian system in late January 1986. This image looks at the planet approximately along its rotational pole. ...
PLANETARY MOTIONS
... planets, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto, have orbits farther from the Sun. As a planet orbits the Sun, there are many arrangements possible between the Earth, the planet, and the Sun. Astronomers have identified some particular geometric arrangements of a planet’s position relative ...
... planets, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto, have orbits farther from the Sun. As a planet orbits the Sun, there are many arrangements possible between the Earth, the planet, and the Sun. Astronomers have identified some particular geometric arrangements of a planet’s position relative ...
Designing Curriculum and Instruction in Elementary School
... witness it. Our own evolution is tied closely to the evolution of the Solar System. Thus, without understanding from where the Solar System came from, it is difficult to comprehend how mankind came to be. Scientists believe that the Solar System evolved from a giant cloud of dust and gas. They belie ...
... witness it. Our own evolution is tied closely to the evolution of the Solar System. Thus, without understanding from where the Solar System came from, it is difficult to comprehend how mankind came to be. Scientists believe that the Solar System evolved from a giant cloud of dust and gas. They belie ...
grade 7 natural sciences term 4 planet earth and beyond
... Tides are the predictable, repeated rise and fall of the sea and ocean levels. You can see the effect of the tides in the waves on the sea. During high tide, the sea level rises and the waves bring the seawater further up the beach, or raise the sea level in the harbour. During low tide, the water l ...
... Tides are the predictable, repeated rise and fall of the sea and ocean levels. You can see the effect of the tides in the waves on the sea. During high tide, the sea level rises and the waves bring the seawater further up the beach, or raise the sea level in the harbour. During low tide, the water l ...
28. Planet Earth - Brigham Young University
... (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars); they are rocky in composition, denser than the other planets, and relatively small. The Jovian planets are the next four out from the sun (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune); they are largely gaseous in composition, have low densities, and are very large. Pluto, ...
... (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars); they are rocky in composition, denser than the other planets, and relatively small. The Jovian planets are the next four out from the sun (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune); they are largely gaseous in composition, have low densities, and are very large. Pluto, ...
For Chapter 16
... Other Planetary Systems • Are there other planetary systems in the universe? • If so, we would expect to find some of these systems in different stages of formation • In other words, we should be able to find clouds of gas and dust, primordial nebula, and protosuns, etc. ...
... Other Planetary Systems • Are there other planetary systems in the universe? • If so, we would expect to find some of these systems in different stages of formation • In other words, we should be able to find clouds of gas and dust, primordial nebula, and protosuns, etc. ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... F) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear above the northern horizon at 32° altitude. G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H ...
... F) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear above the northern horizon at 32° altitude. G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H ...
December, 2012 Vol.23 No.12 The Newsletter of the Cape Cod Astronomical Society
... appears “stationary” at roughly the same altitude every night and sets about two hours after the sun all month (see uniform setting times in our Mooncusser’s Almanac table below.) ...
... appears “stationary” at roughly the same altitude every night and sets about two hours after the sun all month (see uniform setting times in our Mooncusser’s Almanac table below.) ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... Solar time is based on the position of the Sun. If the solar time is 1 p.m. at location X, at which location is the solar time ...
... Solar time is based on the position of the Sun. If the solar time is 1 p.m. at location X, at which location is the solar time ...
Earth Science 24.3 The Sun
... What are those dark areas Galileo observed? The dark regions of the photosphere that we observe are called sunspots. An individual sunspot contains a black region ringed by a lighter region. Sunspots appear dark because of their temperature, which is about 1500 K less than that of the surrounding so ...
... What are those dark areas Galileo observed? The dark regions of the photosphere that we observe are called sunspots. An individual sunspot contains a black region ringed by a lighter region. Sunspots appear dark because of their temperature, which is about 1500 K less than that of the surrounding so ...
Grade 9 Applied
... _____ 8. How many electrons can the first shell of a Bohr-Rutherford diagram hold? a) 2 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8 _____ 9. How many electrons can the second shell of a Bohr-Rutherford diagram ...
... _____ 8. How many electrons can the first shell of a Bohr-Rutherford diagram hold? a) 2 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8 _____ 9. How many electrons can the second shell of a Bohr-Rutherford diagram ...
Galileo & the Telescope— Sept 20
... http://galileo.rice.edu/images/people/galileo/g_tintoretto.gif ...
... http://galileo.rice.edu/images/people/galileo/g_tintoretto.gif ...
Venus
... Venus is also known as the "__________________________ star" or the "evening star" since it is visible and quite bright at either dawn or dusk. It is only __________________________ at dawn or __________________________ since it is closer to the __________________________ than we are. Like the moon, ...
... Venus is also known as the "__________________________ star" or the "evening star" since it is visible and quite bright at either dawn or dusk. It is only __________________________ at dawn or __________________________ since it is closer to the __________________________ than we are. Like the moon, ...
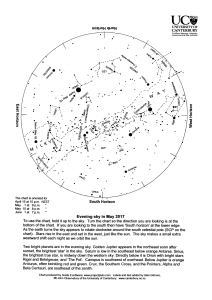
1705 Star Charts
... Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern sky. As the sky darkens ...
... Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern sky. As the sky darkens ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... The Central Problem in astronomy is distance. What we see is basically a twodimensional picture of the sky. To interpret many pieces of information available to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But B ...
... The Central Problem in astronomy is distance. What we see is basically a twodimensional picture of the sky. To interpret many pieces of information available to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But B ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.