C - ScienceWilmeth5
... If this day continues to be sunny, what will most likely happen to the length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will de ...
... If this day continues to be sunny, what will most likely happen to the length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will de ...
October 2011 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... When at opposition Jupiter will be 50° high and will be 50 arcminutes in diameter and very bright. Jupiter always displays an almost full disc but can lose a tiny amount from the edge when it is at greatest elongation (at about 90° from the Sun as we view it from Earth). However as Jupiter is at opp ...
... When at opposition Jupiter will be 50° high and will be 50 arcminutes in diameter and very bright. Jupiter always displays an almost full disc but can lose a tiny amount from the edge when it is at greatest elongation (at about 90° from the Sun as we view it from Earth). However as Jupiter is at opp ...
Meet the Planets - Arbordale Publishing
... Young children are naturally inquisitive and are sponges for information. The whole purpose of this activity is to help children verify the information they know (or think they know) and to get them thinking “beyond the box” about a particular subject. Before reading the book, ask the children what ...
... Young children are naturally inquisitive and are sponges for information. The whole purpose of this activity is to help children verify the information they know (or think they know) and to get them thinking “beyond the box” about a particular subject. Before reading the book, ask the children what ...
FirstLight 2011-09_10_Final.pub
... launches from Cape Canaveral or any other space port. A weather balloon is common enough but it did not sit well – even in the telescope, the object appeared star-like (i.e. it had no form or "disk"). There was little or no motion – certainly a balloon would have demonstrated some drift during the t ...
... launches from Cape Canaveral or any other space port. A weather balloon is common enough but it did not sit well – even in the telescope, the object appeared star-like (i.e. it had no form or "disk"). There was little or no motion – certainly a balloon would have demonstrated some drift during the t ...
Classification_of_Stars_By_Luminosity
... Apparent magnitude • Apparent magnitude is not necessarily related to the amount of light actually produced by the star but is simply a measure of how bright it appears to be from Earth. • (Some bright stars are simply close neighbours while other giant stars may appear equally bright but are also ...
... Apparent magnitude • Apparent magnitude is not necessarily related to the amount of light actually produced by the star but is simply a measure of how bright it appears to be from Earth. • (Some bright stars are simply close neighbours while other giant stars may appear equally bright but are also ...
Oldest SN
... determination of age can be taken to be + 1000 years since the age estimates depend on the canonical interstellar medium conditions, expansion rates etc. It should be noted that no data of the apparent brightness of these supernovae at their peak exists. We assume that these are canonical supernovae ...
... determination of age can be taken to be + 1000 years since the age estimates depend on the canonical interstellar medium conditions, expansion rates etc. It should be noted that no data of the apparent brightness of these supernovae at their peak exists. We assume that these are canonical supernovae ...
Space environment
... outside Earth's magnetosphere (16 Earth radii in the sunward direction, several times this in the antisunward direction), the dose is of the order of the safe limit for astronauts, 0.5 Sv/yr, and much more in the event of solar flares. For a few-day's journey to the Moon there is little risk, but fo ...
... outside Earth's magnetosphere (16 Earth radii in the sunward direction, several times this in the antisunward direction), the dose is of the order of the safe limit for astronauts, 0.5 Sv/yr, and much more in the event of solar flares. For a few-day's journey to the Moon there is little risk, but fo ...
Lecture02: Astronomical Distance
... One ly is the distance light can travel in one year at a speed of about 3 ×105 km/s or 186,000 miles/s n 1 ly = 9.46 × 1012 km or 63,240 AU Q: What are the distances of planets to the Sun in units of AU ? q Parsec (pc) Q: 1 pc = ? Km = ? ly n the distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of 1 a ...
... One ly is the distance light can travel in one year at a speed of about 3 ×105 km/s or 186,000 miles/s n 1 ly = 9.46 × 1012 km or 63,240 AU Q: What are the distances of planets to the Sun in units of AU ? q Parsec (pc) Q: 1 pc = ? Km = ? ly n the distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of 1 a ...
Apr/May 2003 - Madison Astronomical Society
... eclipses, since the new moon overtakes the sun from west to east. This year, both eclipses move (roughly) east-to-west, that is, “backward.” Does the moon reverse its direction in 2003? The reason for the strange geometry comes from the fact that in both solar eclipses this year, the shadow falls on ...
... eclipses, since the new moon overtakes the sun from west to east. This year, both eclipses move (roughly) east-to-west, that is, “backward.” Does the moon reverse its direction in 2003? The reason for the strange geometry comes from the fact that in both solar eclipses this year, the shadow falls on ...
ASTR-100 - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... 27° (26.928474° more exactly) eastward; this is why the moon needs slightly more than two days to catch up with the sun to reach the same phase. Thus one cycle of lunar phases takes 29.53 days (Moon’s synodic [phase] period; 31). The Moon occurs within or outside of the space between the Earth and S ...
... 27° (26.928474° more exactly) eastward; this is why the moon needs slightly more than two days to catch up with the sun to reach the same phase. Thus one cycle of lunar phases takes 29.53 days (Moon’s synodic [phase] period; 31). The Moon occurs within or outside of the space between the Earth and S ...
Astronomy: Earth and Space Systems
... Movement: The Moon revolves with Earth around the Sun, but the rotation time for one complete spin of the Moon is a little over 27 Earth days; The Moon revolves around Earth in 29½ Earth days; Because the Moon rotates and revolves in nearly the same amount of time, the same side of the Moon always f ...
... Movement: The Moon revolves with Earth around the Sun, but the rotation time for one complete spin of the Moon is a little over 27 Earth days; The Moon revolves around Earth in 29½ Earth days; Because the Moon rotates and revolves in nearly the same amount of time, the same side of the Moon always f ...
ASTR-100 - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... 27° (26.928474° more exactly) eastward; this is why the moon needs slightly more than two days to catch up with the sun to reach the same phase. Thus one cycle of lunar phases takes 29.53 days (Moon’s synodic [phase] period; 33). The Moon occurs within or outside of the space between the Earth and S ...
... 27° (26.928474° more exactly) eastward; this is why the moon needs slightly more than two days to catch up with the sun to reach the same phase. Thus one cycle of lunar phases takes 29.53 days (Moon’s synodic [phase] period; 33). The Moon occurs within or outside of the space between the Earth and S ...
Uranus and Neptune
... Uranus’ radical tilt causes interesting illumination conditions. 84 year orbit. 42 years of light or dark at the poles! ...
... Uranus’ radical tilt causes interesting illumination conditions. 84 year orbit. 42 years of light or dark at the poles! ...
we can bee the change we wish to bee
... together, they “hide” and take something away that is no longer needed, thus Sun and Moon cast their shadow on the Earth, while they unite to create something new. Solar and Lunar eclipses create a consciousness that is based on the geometrical dance of the Sun, Moon and Earth. An eclipse brings the ...
... together, they “hide” and take something away that is no longer needed, thus Sun and Moon cast their shadow on the Earth, while they unite to create something new. Solar and Lunar eclipses create a consciousness that is based on the geometrical dance of the Sun, Moon and Earth. An eclipse brings the ...
Lecture 2
... from the celestial equator to the horizon? Start by asking what the length of the pink arc is? 36 degrees Now what is the sum of the pink plus orange arcs? (What is the distance in degrees from zenith to horizon?) 90 degrees So the answer to Hint #1 is 90-36 = 54 degrees Your friend’s latitude is 22 ...
... from the celestial equator to the horizon? Start by asking what the length of the pink arc is? 36 degrees Now what is the sum of the pink plus orange arcs? (What is the distance in degrees from zenith to horizon?) 90 degrees So the answer to Hint #1 is 90-36 = 54 degrees Your friend’s latitude is 22 ...
Function 1 Competence 2 - Official Website of MARINA STCW
... The Annual Publication of Database of Questionnaires is mandated in Republic Act 10635 or the Act Establishing the Maritime Industry Authority (MARINA) as the Single Maritime Administration Responsible for the Implementation and Enforcement of the 1978 International Convention on Standards of Traini ...
... The Annual Publication of Database of Questionnaires is mandated in Republic Act 10635 or the Act Establishing the Maritime Industry Authority (MARINA) as the Single Maritime Administration Responsible for the Implementation and Enforcement of the 1978 International Convention on Standards of Traini ...
The Emerald Tablet of Hermes
... polarity, and which stands symbolically for the purified soul and the self. It lifts it to heaven and into the sphere of the cosmic Sophia. As we have determined with the representation of the androgynous being, the consciousness for which it stands, though it is to be found beyond the sensual pola ...
... polarity, and which stands symbolically for the purified soul and the self. It lifts it to heaven and into the sphere of the cosmic Sophia. As we have determined with the representation of the androgynous being, the consciousness for which it stands, though it is to be found beyond the sensual pola ...
Note Packet
... b) The Direct Ray Shifts depending on the Season: -Since earth is spherical, tilted and revolving around the sun, there is just one line of latitude that receives direct insolation each day. This occurs at the latitude where the sun is at its zenith which varies based on the season due to Earth’s re ...
... b) The Direct Ray Shifts depending on the Season: -Since earth is spherical, tilted and revolving around the sun, there is just one line of latitude that receives direct insolation each day. This occurs at the latitude where the sun is at its zenith which varies based on the season due to Earth’s re ...
Earth Motions and the Heavens
... overhead at 23.5 degrees S. 150 BC- The sun rose with the constellation ...
... overhead at 23.5 degrees S. 150 BC- The sun rose with the constellation ...
Unit 12: The Formation of the Earth
... Because of its large mass, the sun dominates the motion of all the other objects in the solar system. The planets and most of the remaining matter are distributed in a plane. As seen from a vantage point far north of the solar system, the sun rotates counterclockwise about its axis. The planets and ...
... Because of its large mass, the sun dominates the motion of all the other objects in the solar system. The planets and most of the remaining matter are distributed in a plane. As seen from a vantage point far north of the solar system, the sun rotates counterclockwise about its axis. The planets and ...
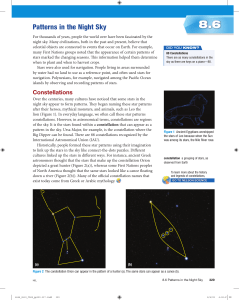
Patterns in the Night Sky
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
Seasons Challenge
... •Can be determined by calculating the length of daylight for that day and divide by two •When the Sun is at its highest point in the sky •Not always 12 o’clock noon ...
... •Can be determined by calculating the length of daylight for that day and divide by two •When the Sun is at its highest point in the sky •Not always 12 o’clock noon ...
Stars, Constellations, and the Celestial Sphere
... The horizon for an observer at O is the intersection of a plane tangent to Earth at O with the celestial sphere. Everything that the observer can see is above the tangent plane (represented by the green line in the figure). The angle between the celestial equator (yellow line) and the horizon (gree ...
... The horizon for an observer at O is the intersection of a plane tangent to Earth at O with the celestial sphere. Everything that the observer can see is above the tangent plane (represented by the green line in the figure). The angle between the celestial equator (yellow line) and the horizon (gree ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.