Astronomy Club of Asheville June 2016 Sky Events
... Corvus, the famous Sombrero Galaxy (M104) is often observed in small telescopes, and it is one of the brightest galaxies in the sky as seen from Earth. But mostly overlooked are 3 other wonderful celestial objects that are all located within 1½° of the Sombrero Galaxy. These wonders include 2 re ...
... Corvus, the famous Sombrero Galaxy (M104) is often observed in small telescopes, and it is one of the brightest galaxies in the sky as seen from Earth. But mostly overlooked are 3 other wonderful celestial objects that are all located within 1½° of the Sombrero Galaxy. These wonders include 2 re ...
Comets, Meteors, and Meteoroids
... A falling star is a meteor. Meteors are streaks of light in the sky. The light is caused by a small speck of dust burning when it enters the Earth's atmosphere. The dust comes from comets. These pieces of comet dust are called meteoroids. Most meteoroids are smaller than a grain of sand. The flash o ...
... A falling star is a meteor. Meteors are streaks of light in the sky. The light is caused by a small speck of dust burning when it enters the Earth's atmosphere. The dust comes from comets. These pieces of comet dust are called meteoroids. Most meteoroids are smaller than a grain of sand. The flash o ...
Star Magnitude - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... are of Greek and Latin origins and Vega, Rigel, Aldebaran are Arabic derivations. In some cases two names are given to a star because some stars are referred to with multiple names. The designation column gives the star's designation by Johann Bayer's letter and John Flamsteed's number. Johann Bayer ...
... are of Greek and Latin origins and Vega, Rigel, Aldebaran are Arabic derivations. In some cases two names are given to a star because some stars are referred to with multiple names. The designation column gives the star's designation by Johann Bayer's letter and John Flamsteed's number. Johann Bayer ...
Magnitudes lesson plan
... that he could see from his latitude into six classes of brightness. His idea of six classes probably came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ...
... that he could see from his latitude into six classes of brightness. His idea of six classes probably came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ...
Variable star information
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
Celestial Distances
... Their periods are always less than one day, and their changes in brightness are typically less than about a factor of 2 From observations, astronomers have concluded that RR Lyrae variables all have nearly the same intrinsic luminosity, of about 50 times that of the Sun Thus, they are like standard ...
... Their periods are always less than one day, and their changes in brightness are typically less than about a factor of 2 From observations, astronomers have concluded that RR Lyrae variables all have nearly the same intrinsic luminosity, of about 50 times that of the Sun Thus, they are like standard ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. ...
... stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • the core of a red giant star, revealed when the outer layers are shed during the planetary nebula phase. • a white dwarf star that has cooled to a low temperature over its long lifetime. Stars with masses less that 8% of that of the Sun remain as long-lived, dim brown objects, never brightening li ...
... • the core of a red giant star, revealed when the outer layers are shed during the planetary nebula phase. • a white dwarf star that has cooled to a low temperature over its long lifetime. Stars with masses less that 8% of that of the Sun remain as long-lived, dim brown objects, never brightening li ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
Name: Period: ___ Date: ______ Light-year Calculation
... Light-year Calculation Practice Astronomy Distances are so great in space that a special unit of measurement is used. It is called a light-year. This sounds like a measurement of time, but it is a unit used to measure distance. By definition a light-year is the distance that light travels in one yea ...
... Light-year Calculation Practice Astronomy Distances are so great in space that a special unit of measurement is used. It is called a light-year. This sounds like a measurement of time, but it is a unit used to measure distance. By definition a light-year is the distance that light travels in one yea ...
antarctic and associated exploration book collection
... ۞ In mid-January this year, NASA highlighted a new book Touch the Invisible Sky, by Noreen Grice, Simon Steel and Doris Daou, specially written for able sighted and blind readers. With 60 pages of NASA color images of nebulae, stars, galaxies and some of the telescopes that captured the images, Brai ...
... ۞ In mid-January this year, NASA highlighted a new book Touch the Invisible Sky, by Noreen Grice, Simon Steel and Doris Daou, specially written for able sighted and blind readers. With 60 pages of NASA color images of nebulae, stars, galaxies and some of the telescopes that captured the images, Brai ...
every star in the cluster.
... But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
... But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
Distance
... Ques4ons • How much does the apparent brightness of stars we see in the sky vary? Why? • Stars have different colors? So is the amount of light at different wavelengths the same? • Can we tell the difference between a very luminous star that is far away and in intrinsically low luminosity st ...
... Ques4ons • How much does the apparent brightness of stars we see in the sky vary? Why? • Stars have different colors? So is the amount of light at different wavelengths the same? • Can we tell the difference between a very luminous star that is far away and in intrinsically low luminosity st ...
1) The following questions refer to the HR diagram
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...
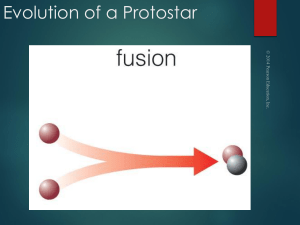
Evolution of a Protostar
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
... A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion. ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.









![David`s Mapping the Heavens[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008084229_1-877ead4b57cbb51d927fdcd6d06ce5c8-300x300.png)