AyC10 Fall 2007: Midterm 2 Review Sheet
... depends on the observer’s distance from the source. We calculate the luminosity (same as “intrinsic energy output”) of stars by measuring their brightness (counting how many photons hit our camera chip) and their distance (via parallax or other methods we haven’t discussed in detail). Once we know t ...
... depends on the observer’s distance from the source. We calculate the luminosity (same as “intrinsic energy output”) of stars by measuring their brightness (counting how many photons hit our camera chip) and their distance (via parallax or other methods we haven’t discussed in detail). Once we know t ...
Topic Outline - Physics Rocks!
... Solve problems involving stellar parallax. Absolute and apparent magnitudes E.3.5 Describe the apparent magnitude scale E.3.4 ...
... Solve problems involving stellar parallax. Absolute and apparent magnitudes E.3.5 Describe the apparent magnitude scale E.3.4 ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... with the collapsing core and inner envelope and this shell of hydrogen can now begin fusing. The shell Hburning creates shell gamma rays that are able to deposit more energy into the star’s envelope (since they do not originate in the core) and this causes the star’s envelope to swell. The star beco ...
... with the collapsing core and inner envelope and this shell of hydrogen can now begin fusing. The shell Hburning creates shell gamma rays that are able to deposit more energy into the star’s envelope (since they do not originate in the core) and this causes the star’s envelope to swell. The star beco ...
Lecture 9a: More on Star formation and evolution 10/22
... Globular Star Clusters “fuzzy cotton ball” by eye or with modest telescope • usually dim red stars • dense with 100,000 stars in 50-300 LY region with less than LY separating stars • no heavy elements. Just Hydrogen and Helium • often outside plane of galaxy Understood as group of old stars for ...
... Globular Star Clusters “fuzzy cotton ball” by eye or with modest telescope • usually dim red stars • dense with 100,000 stars in 50-300 LY region with less than LY separating stars • no heavy elements. Just Hydrogen and Helium • often outside plane of galaxy Understood as group of old stars for ...
9J Gravity and Space
... The astrology and mythology of the constellations, especially those of the signs of the zodiac may be enjoyable, but the science behind it isn’t quite the same. Precession: Due to the moon and sun’s pull of gravity, Earth wobbles as it spins. This wobbling is called precession and it's so slow that ...
... The astrology and mythology of the constellations, especially those of the signs of the zodiac may be enjoyable, but the science behind it isn’t quite the same. Precession: Due to the moon and sun’s pull of gravity, Earth wobbles as it spins. This wobbling is called precession and it's so slow that ...
Stars
... In a star like the Sun, electron degeneracy stops the contraction of the core before the temperature gets high enough to start carbon burning. Supported against further contraction, the core cannot get any more energy by gravitational contraction. From this point on, the core cools down like an ordi ...
... In a star like the Sun, electron degeneracy stops the contraction of the core before the temperature gets high enough to start carbon burning. Supported against further contraction, the core cannot get any more energy by gravitational contraction. From this point on, the core cools down like an ordi ...
Sun - Cobb Learning
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
The Milky Way - Houston Community College System
... difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers have used their telescopes and spectrographs in clever ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. In this chapter you will find answers to five important questions about stars: • How far awa ...
... difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers have used their telescopes and spectrographs in clever ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. In this chapter you will find answers to five important questions about stars: • How far awa ...
The Northern Winter Constellations - Science
... rough hexagon of very bright stars. This is called the Winter Hexagon. Starting at Rigel, if you go counterclockwise by one, you end up at Aldebaran in Taurus. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at Capella in Auriga. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at the pair of stars Pollux ...
... rough hexagon of very bright stars. This is called the Winter Hexagon. Starting at Rigel, if you go counterclockwise by one, you end up at Aldebaran in Taurus. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at Capella in Auriga. Go counterclockwise once more and you end up at the pair of stars Pollux ...
2009_ASU_Exam
... magnitude as observed from earth. If an observer were able to move 10 pcs closer to both stars, which star will appear brighter from the new observation point? 14) Star P is a pulsating variable star. As it pulses, the apparent magnitude of Star P changes by 5 magnitudes. Assuming that its temperatu ...
... magnitude as observed from earth. If an observer were able to move 10 pcs closer to both stars, which star will appear brighter from the new observation point? 14) Star P is a pulsating variable star. As it pulses, the apparent magnitude of Star P changes by 5 magnitudes. Assuming that its temperatu ...
Final Exam, Dec. 19, 2015 - Physics@Brock
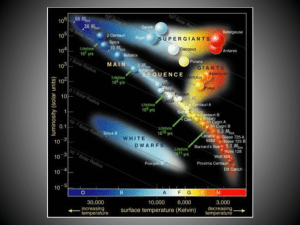
... (d) [None of the above.] 5. The spectroscopic parallax is a method of determining (a) a star’s chemical composition. (b) a star’s temperature. (c) a star’s distance from parallax angle. (d) a star’s distance using H-R diagram. 6. Which of these main sequence stars will have the shortest lifetime? (a ...
... (d) [None of the above.] 5. The spectroscopic parallax is a method of determining (a) a star’s chemical composition. (b) a star’s temperature. (c) a star’s distance from parallax angle. (d) a star’s distance using H-R diagram. 6. Which of these main sequence stars will have the shortest lifetime? (a ...
Chapter 09
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.