Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
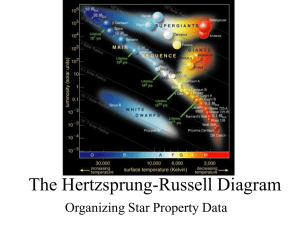
... their variety - while some are bright, some are faint; some are blue and red. The attempt to understand this vast variety eventually led to the physics of the structure of the stars. The brightness of a star is measured in magnitudes. Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer who lived a hundred and fifty year ...
... their variety - while some are bright, some are faint; some are blue and red. The attempt to understand this vast variety eventually led to the physics of the structure of the stars. The brightness of a star is measured in magnitudes. Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer who lived a hundred and fifty year ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... Up to now, there are few observational constraints on the overall mass-ratio distribution of the binary population. One of the few measures of f(q) for binary systems, comes from Fisher et al. (2005) who estimated the q distribution function from spectroscopic observations of field binaries within ...
... Up to now, there are few observational constraints on the overall mass-ratio distribution of the binary population. One of the few measures of f(q) for binary systems, comes from Fisher et al. (2005) who estimated the q distribution function from spectroscopic observations of field binaries within ...
Study Guide 4 Part A Outline
... Universe is expanding The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large amounts of energy from re ...
... Universe is expanding The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large amounts of energy from re ...
Goal: To understand how to find the brightness of stars and what
... Why is this all important? • Well, if you know how bright a star is supposed to be and how bright it appears to be you can tell how far away it is. • If you know how far away a star is, how bright it appears to be, and what its temperature is, then you can find what its actual brightness is, and wi ...
... Why is this all important? • Well, if you know how bright a star is supposed to be and how bright it appears to be you can tell how far away it is. • If you know how far away a star is, how bright it appears to be, and what its temperature is, then you can find what its actual brightness is, and wi ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... C. Density. D. Surface temperature. 2. The color of a star is MOST DIRECTLY related to its: A. mass. B. surface temperature. C. central (core) temperature. D. luminosity. 3. Assuming that stars radiate like blackbodies, you must know which of the following properties in order to infer the radius of ...
... C. Density. D. Surface temperature. 2. The color of a star is MOST DIRECTLY related to its: A. mass. B. surface temperature. C. central (core) temperature. D. luminosity. 3. Assuming that stars radiate like blackbodies, you must know which of the following properties in order to infer the radius of ...
Amanda Boyle Starstuff
... down in less than 1 second. It takes about 15 minutes for the star to build up to its supernova. The explosion itself lasts around100 seconds. The supernova creates a fantastic image too, visible for many days after the incident, sometimes over a year. In space time, these stars die faster than a bl ...
... down in less than 1 second. It takes about 15 minutes for the star to build up to its supernova. The explosion itself lasts around100 seconds. The supernova creates a fantastic image too, visible for many days after the incident, sometimes over a year. In space time, these stars die faster than a bl ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars - Sierra College Astronomy Home
... A star’s color is determined by its temperature. An absorption spectrum - the absorption of radiation at various wavelengths - can be used to determine a star’s temperature. Harvard astronomers, lead by Edward Pickering and his women “computers” developed the first stellar classification system usin ...
... A star’s color is determined by its temperature. An absorption spectrum - the absorption of radiation at various wavelengths - can be used to determine a star’s temperature. Harvard astronomers, lead by Edward Pickering and his women “computers” developed the first stellar classification system usin ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.