The Life Cycle of Spiral Arm Galaxies
... The observed speed of the Smith Cloud (0.001c) may not just be a random number but might have significance. It might correspond to the speed that protons are traveling in the outer shell of th ...
... The observed speed of the Smith Cloud (0.001c) may not just be a random number but might have significance. It might correspond to the speed that protons are traveling in the outer shell of th ...
TAP 704- 8: The ladder of astronomical distances
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
Lesson 4 - Scientist in Residence Program
... Stars like humans come in different sizes and colours. However, unlike people a star’s colour and brightness is highly dependent on its size. We can get clues about how hot a star is and a star’s age from a star’s colour. Stars are often classified based on size, temperature and spectra (or its colo ...
... Stars like humans come in different sizes and colours. However, unlike people a star’s colour and brightness is highly dependent on its size. We can get clues about how hot a star is and a star’s age from a star’s colour. Stars are often classified based on size, temperature and spectra (or its colo ...
20_LectureOutline
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... Roughly how big (in A.U.) will the Sun become when it enters the red-giant phase? (3 points) A star like the Sun will evolve into a red giant with a size about 100 times its current size. This is equivalent to about 70 million km, or almost half an AU. 5. Chaisson Review and Discussion 20.8 Do all s ...
... Roughly how big (in A.U.) will the Sun become when it enters the red-giant phase? (3 points) A star like the Sun will evolve into a red giant with a size about 100 times its current size. This is equivalent to about 70 million km, or almost half an AU. 5. Chaisson Review and Discussion 20.8 Do all s ...
magnitude handout
... How do we use this table? The magnitude difference between two stars along with Table 2 gives us the brightness ratio, how many times brighter the star is. We can also work the other way. Thus if star A is 40 times brighter than star B, the table tells us that A is 4 magnitudes brighter. It is prett ...
... How do we use this table? The magnitude difference between two stars along with Table 2 gives us the brightness ratio, how many times brighter the star is. We can also work the other way. Thus if star A is 40 times brighter than star B, the table tells us that A is 4 magnitudes brighter. It is prett ...
26.4 Groups of Stars
... too dim to be seen easily from Earth but can still be detected from the motion of the other star. If one star passes in front of the other, blocking some of the light from reaching Earth, the star system is called an eclipsing binary. The brightness of an eclipsing binary varies over time in a regul ...
... too dim to be seen easily from Earth but can still be detected from the motion of the other star. If one star passes in front of the other, blocking some of the light from reaching Earth, the star system is called an eclipsing binary. The brightness of an eclipsing binary varies over time in a regul ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius (sphere surface area is 4 p R2) ...
... temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius (sphere surface area is 4 p R2) ...
objects in telescope are farther than they appear
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
Contents ISP 205 Section 2 Study Guide for Test 3 28 March 2007
... A white dwarf has about the same mass as the sun and the same size as the earth. True or false? A neutron star has about the same mass as the sun and the same size as the earth. True or false? If the temperature of the sun cooled suddenly, would the size change? If the temperature of the white dwarf ...
... A white dwarf has about the same mass as the sun and the same size as the earth. True or false? A neutron star has about the same mass as the sun and the same size as the earth. True or false? If the temperature of the sun cooled suddenly, would the size change? If the temperature of the white dwarf ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... which in turn, causes a rapid increase in the light output of the system. Such a binary is called a cataclysmic variable and can go through numerous (though not necessarily periodic) episodes of rapid brightenings. The most energetic of the cataclysmic variables are called dwarf novae. Such systems ...
... which in turn, causes a rapid increase in the light output of the system. Such a binary is called a cataclysmic variable and can go through numerous (though not necessarily periodic) episodes of rapid brightenings. The most energetic of the cataclysmic variables are called dwarf novae. Such systems ...
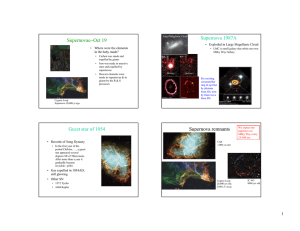
Supernovae Oct 19 − Supernova 1987A
... period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
... period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
Gizmos: H-R Diagrams
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
2014 State Test
... D6. (2 pts) The measured parallax of this star is 1.26 milliarcseconds. What is the distance to this star in parsecs? Give your answer to three significant figures. D7. (2 pts) What is the distance modulus associated with the distance you calculated in D6? If you didn’t get an answer to D6 or don’t ...
... D6. (2 pts) The measured parallax of this star is 1.26 milliarcseconds. What is the distance to this star in parsecs? Give your answer to three significant figures. D7. (2 pts) What is the distance modulus associated with the distance you calculated in D6? If you didn’t get an answer to D6 or don’t ...
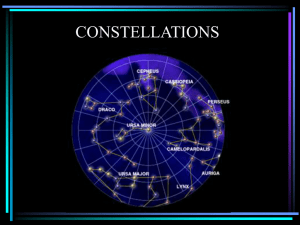
Constellations Overview
... • Follow the line made by Orion’s belt up & to the right • Aldebaran- Red star that is the eye of the bull. It is the 13th brightest in the nighttime sky ...
... • Follow the line made by Orion’s belt up & to the right • Aldebaran- Red star that is the eye of the bull. It is the 13th brightest in the nighttime sky ...
PPT - Yale University
... rotation periods) because disks are fragile and cannot sustain a large torque. Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
... rotation periods) because disks are fragile and cannot sustain a large torque. Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.