2007-8 Astronomy Outline
... Observation: (verbally describe what you see with the naked eye; make sketch(s)) *first night sky journal will be due on __Friday, August 19th__* Chapter 1 I. Astronomy Study of the universe Universe is the totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Measurements i. Light year ii. Astronom ...
... Observation: (verbally describe what you see with the naked eye; make sketch(s)) *first night sky journal will be due on __Friday, August 19th__* Chapter 1 I. Astronomy Study of the universe Universe is the totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Measurements i. Light year ii. Astronom ...
Star Light, Star Bright: Exploring how stars are classified
... luminosity value. 3. Make sure they understand the luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity such that a value greater than 1 means it is that many times the sun's luminosity. A value less than one means it is that fraction of the sun's value. 4. Allow time for the groups to become familiar wit ...
... luminosity value. 3. Make sure they understand the luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity such that a value greater than 1 means it is that many times the sun's luminosity. A value less than one means it is that fraction of the sun's value. 4. Allow time for the groups to become familiar wit ...
COM 2014 January
... The Double Cluster (also known as Caldwell 14) is the common name for the naked-eye open clusters NGC 869 and NGC 884 (sometimes designated h Persei and χ Persei, respectively, but those designations would really apply to both clusters and to a visually nearby star, which are close together in the c ...
... The Double Cluster (also known as Caldwell 14) is the common name for the naked-eye open clusters NGC 869 and NGC 884 (sometimes designated h Persei and χ Persei, respectively, but those designations would really apply to both clusters and to a visually nearby star, which are close together in the c ...
Problem set 2
... F = I(T⊙ ) · Ω⊙ with T⊙ = 5777 K, and calculate this value numerically. Note that to calculate the flux from a blackbody of known temperature (or other source of known specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these ...
... F = I(T⊙ ) · Ω⊙ with T⊙ = 5777 K, and calculate this value numerically. Note that to calculate the flux from a blackbody of known temperature (or other source of known specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these ...
Introduction and some basic concepts
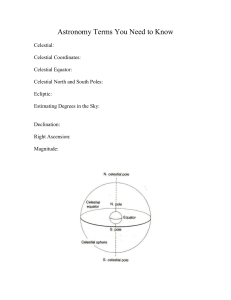
... celestial coordinates is that the Earth's turns on its axis once a day. The Sun rises and sets each day. The Moon rises and sets each day. The stars also rise and set. Their principal apparent motion is simply due to the rotation of the Earth. Thus, the elevation angle and the azimuth angle of a cel ...
... celestial coordinates is that the Earth's turns on its axis once a day. The Sun rises and sets each day. The Moon rises and sets each day. The stars also rise and set. Their principal apparent motion is simply due to the rotation of the Earth. Thus, the elevation angle and the azimuth angle of a cel ...
Name: pd: ______ Date: Constellation Scavenger Hunt! Google Sky
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
Irregular Galaxies
... • Huge clouds of dust, gas, and the new elements explode into space. • This forms a new nebula. • Once a star supernovas, the core that remains of it will become either a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... • Huge clouds of dust, gas, and the new elements explode into space. • This forms a new nebula. • Once a star supernovas, the core that remains of it will become either a neutron star or a black hole. ...
III. Contents of The Universe
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
Astronomy Terms You Need to Know
... The Geminids are usually the strongest meteor shower of the year and meteor enthusiasts are certain to circle December 13 and 14 on their calendars. This is the one major shower that provides good activity prior to midnight as the constellation of Gemini is well placed from 10pm onward. The Geminids ...
... The Geminids are usually the strongest meteor shower of the year and meteor enthusiasts are certain to circle December 13 and 14 on their calendars. This is the one major shower that provides good activity prior to midnight as the constellation of Gemini is well placed from 10pm onward. The Geminids ...
wk9 (part 1)
... • A study of the exact shape of the ZAMS in an HR diagram indicates that more massive stars have larger radii than less massive stars ...
... • A study of the exact shape of the ZAMS in an HR diagram indicates that more massive stars have larger radii than less massive stars ...
Homework #2
... 1) Supernovae are very bright, but do you think that they pose a biological hazard? Consider a typical (Type II) supernova with Lpeak = 109 solar luminosities. (This kind comes from the death of a massive star and is more common than the brighter Type Ia supernovae discussed so far in class). At wha ...
... 1) Supernovae are very bright, but do you think that they pose a biological hazard? Consider a typical (Type II) supernova with Lpeak = 109 solar luminosities. (This kind comes from the death of a massive star and is more common than the brighter Type Ia supernovae discussed so far in class). At wha ...
doc - IAC
... same way as planetary masses are measured. The most massive ones are 100 to 150 times heavier than the Sun. The most massive stars evolve more rapidly than those of low mass. Does this in any way affect the galaxies in which they are found? Indeed it does. Massive stars have very short lifetimes, at ...
... same way as planetary masses are measured. The most massive ones are 100 to 150 times heavier than the Sun. The most massive stars evolve more rapidly than those of low mass. Does this in any way affect the galaxies in which they are found? Indeed it does. Massive stars have very short lifetimes, at ...
Nights of the Heavenly G With
... Capella and moving to Castor, to Pollux, to Procyon, to Sirius, to Rigel in Orion, sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of the winter stars, and traced out a giant letter "G" taking up nearly half the starry sky! Taking a closer lo ...
... Capella and moving to Castor, to Pollux, to Procyon, to Sirius, to Rigel in Orion, sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of the winter stars, and traced out a giant letter "G" taking up nearly half the starry sky! Taking a closer lo ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.