Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
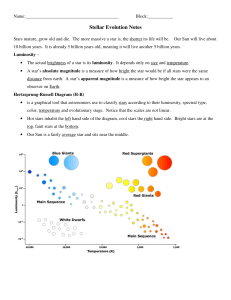
ref H-R Spectral types
... In this Activity we have had a look at the Balmer series, and how its occurrence in the photospheres of stars will vary with temperature. The temperature, and hence the colour and spectral line strength characteristics of stars, is used to classify them into types O, B, A, F, G, K and M-type stars. ...
... In this Activity we have had a look at the Balmer series, and how its occurrence in the photospheres of stars will vary with temperature. The temperature, and hence the colour and spectral line strength characteristics of stars, is used to classify them into types O, B, A, F, G, K and M-type stars. ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
Document
... • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core. • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and ...
... • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core. • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and ...
read in advance to speed your work
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... Occur only in stars whose masses are greater than 8 M. At the end of its life, massive stars form an iron core by fusing silicon. The iron core forms in a few days. Fusion ends at this point. The core has a mass of about 2 M. The iron core cannot support itself and collapses, from a size of ...
... Occur only in stars whose masses are greater than 8 M. At the end of its life, massive stars form an iron core by fusing silicon. The iron core forms in a few days. Fusion ends at this point. The core has a mass of about 2 M. The iron core cannot support itself and collapses, from a size of ...
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY
... The Milky Way (MW) is the name given to the faint band of light visible in the night sky. This light is the sum of billions of stars comprising our home galaxy. Today, we understand that the Milky Way is a flattened, rotating disk of stars, gas and dust, about 100,000 light years in diameter. The de ...
... The Milky Way (MW) is the name given to the faint band of light visible in the night sky. This light is the sum of billions of stars comprising our home galaxy. Today, we understand that the Milky Way is a flattened, rotating disk of stars, gas and dust, about 100,000 light years in diameter. The de ...
File
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... supernova type II explosion. You should know the details of how and why this occurs. You should also distinguish between this type of supernova explosion and a type Ia. VI. ...
... supernova type II explosion. You should know the details of how and why this occurs. You should also distinguish between this type of supernova explosion and a type Ia. VI. ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... They burn very slowly and have estimated lifetimes of 100 billion years. Proxima Centauri and Barnard's Star are red dwarfs. ...
... They burn very slowly and have estimated lifetimes of 100 billion years. Proxima Centauri and Barnard's Star are red dwarfs. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... Emitted energy per unit surface area è ...
... Emitted energy per unit surface area è ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
Learning Objectives Weeks 9-11 . 1. Know that star birth can begin
... Novae and thermonuclear supernovae both occur in close binary systems with a white dwarf, but a while a nova can recur a supernova is a one-shot event. 17. Like a white dwarf, a neutron star has an upper limit on its mass. For a neutron star to collapse, gravity must overwhelm both degeneracy pressu ...
... Novae and thermonuclear supernovae both occur in close binary systems with a white dwarf, but a while a nova can recur a supernova is a one-shot event. 17. Like a white dwarf, a neutron star has an upper limit on its mass. For a neutron star to collapse, gravity must overwhelm both degeneracy pressu ...
Chapter2
... IV. The Motion of the Planets A. The Moving Planets B. Astrology V. Astronomical Influences on Earth's Climate A. The Hypothesis B. The Evidence ...
... IV. The Motion of the Planets A. The Moving Planets B. Astrology V. Astronomical Influences on Earth's Climate A. The Hypothesis B. The Evidence ...
3. Stellar Formation and Evolution
... condition of hydrostatic equilibrium, a protostar forms at the core. • These pre-main sequence stars are often surrounded by a protoplanetary disk (explain later). ...
... condition of hydrostatic equilibrium, a protostar forms at the core. • These pre-main sequence stars are often surrounded by a protoplanetary disk (explain later). ...
Name _________ Date _____________ Period ______ Skills
... COMPOSITION OF STARS _____ 5. The band of colors produced when white light passes through a prism is a(n) a. color wheel. b. emission line. c. ultraviolet light. d. spectrum. _____ 6. A hot, solid object gives off a(n) a. continuous spectrum. b. absorption spectrum. c. emission line. d. partial spec ...
... COMPOSITION OF STARS _____ 5. The band of colors produced when white light passes through a prism is a(n) a. color wheel. b. emission line. c. ultraviolet light. d. spectrum. _____ 6. A hot, solid object gives off a(n) a. continuous spectrum. b. absorption spectrum. c. emission line. d. partial spec ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... The Life of HUGE Stars • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
... The Life of HUGE Stars • As particles fall to the core they lose kinetic & potential energy and more HEAT results • This heat triggers nuclear fusion in the outer layers, and the resulting explosion is the supernova. • The energy released can fuse iron and other heavier elements, up to uranium. ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.