Eclipses, Distance, Parallax, Small Angle, and Magnitude (Professor
... Partial or Total? • Our location within the Moon’s shadow determines whether we see a total or partial solar eclipse. • The Moon’s umbra makes a circle generally about 170 miles in diameter on the surface of the Earth and the Moon’s orbital motion causes that shadow to sweep rapidly along the surfa ...
... Partial or Total? • Our location within the Moon’s shadow determines whether we see a total or partial solar eclipse. • The Moon’s umbra makes a circle generally about 170 miles in diameter on the surface of the Earth and the Moon’s orbital motion causes that shadow to sweep rapidly along the surfa ...
Analemma - Stony Brook University
... Cepheus, and Cassiopeia are all to be found in the fall evening sky. • Perseus holds the head of Medusa (the variable star Algol - the Ghoul - is her eye). • As punishment for her vanity, Queen Cassiopeia, as a circumpolar constellation, is condemned to hang upside down half the year, a most undigni ...
... Cepheus, and Cassiopeia are all to be found in the fall evening sky. • Perseus holds the head of Medusa (the variable star Algol - the Ghoul - is her eye). • As punishment for her vanity, Queen Cassiopeia, as a circumpolar constellation, is condemned to hang upside down half the year, a most undigni ...
Constellation Argo Navis
... Homunculus Nebula is a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye that is being ejected by the erratic luminous blue variable star Eta Carinae, the most massive visible star known. Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstab ...
... Homunculus Nebula is a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye that is being ejected by the erratic luminous blue variable star Eta Carinae, the most massive visible star known. Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstab ...
Spiral structure of the Third Galactic Quadrant and the solution to the
... Fig. 1) has been taken as strong evidence for the existence of the CMa galaxy (Bellazzini et al. 2004; Dinescu et al. 2005; Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The BP has been modelled and interpreted as the last burst of star formation in that galaxy 1-2 Gyr ago (which, given that it is a 1-2 Gyr popul ...
... Fig. 1) has been taken as strong evidence for the existence of the CMa galaxy (Bellazzini et al. 2004; Dinescu et al. 2005; Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The BP has been modelled and interpreted as the last burst of star formation in that galaxy 1-2 Gyr ago (which, given that it is a 1-2 Gyr popul ...
Astronomy 103
... Bavaria developed the spectroscope in the early 1800's. Wollaston was the first to see dark lines in the spectrum of the Sun and by 1863, it was known that these dark lines were identical to patterns of spectral lines from particular elements found on the Earth. (One set of lines failed to match the ...
... Bavaria developed the spectroscope in the early 1800's. Wollaston was the first to see dark lines in the spectrum of the Sun and by 1863, it was known that these dark lines were identical to patterns of spectral lines from particular elements found on the Earth. (One set of lines failed to match the ...
docx - STAO
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... instructor will demonstrate the celestial pipes to you. The use of this instructional tool and your hand at arm's length as a measuring device will assist you in locating objects in the night sky. Once you have located Polaris, you can orient your star maps to find other objects. Indicate on your di ...
... instructor will demonstrate the celestial pipes to you. The use of this instructional tool and your hand at arm's length as a measuring device will assist you in locating objects in the night sky. Once you have located Polaris, you can orient your star maps to find other objects. Indicate on your di ...
Teacher Demo: Bright Star or Close Star?
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
Lecture 17 Review
... star is too large, the gas cloud condenses quite fast, is unstable, gets very hot, and either explodes or fragments into smaller clouds which form individual stars. A second question is, can the mass of the gas be too small. The answer is yes. If the mass of the cloud is too small it heats up from g ...
... star is too large, the gas cloud condenses quite fast, is unstable, gets very hot, and either explodes or fragments into smaller clouds which form individual stars. A second question is, can the mass of the gas be too small. The answer is yes. If the mass of the cloud is too small it heats up from g ...
giant molecular clouds
... Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
... Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
Absolute Magnitudes of Supernovae
... Use the value of the Hubble Law to compute the distance of the host galaxy (and the supernova) from the recession velocity. Remember that the distance = velocity / Ho. Now you can calculate the absolute magnitude from the distance and the apparent magnitude using the inverse square law. Recall that ...
... Use the value of the Hubble Law to compute the distance of the host galaxy (and the supernova) from the recession velocity. Remember that the distance = velocity / Ho. Now you can calculate the absolute magnitude from the distance and the apparent magnitude using the inverse square law. Recall that ...
Binary Star Systems - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... • An eclipsing binary system is a special type of spectroscopic binary, where the orbit of the two stars is edge-on to our line of sight. • We periodically see one star pass in front of or eclipse the other star. When this happens the total amount of light that we receive from the pair dims for a fe ...
... • An eclipsing binary system is a special type of spectroscopic binary, where the orbit of the two stars is edge-on to our line of sight. • We periodically see one star pass in front of or eclipse the other star. When this happens the total amount of light that we receive from the pair dims for a fe ...
Unit 4: Astronomy
... of these in addition to an optical telescope. Assignment #2: Pages 568, 587-588 Topics: Distances to and motion of stars Objectives: 1) Describe how astronomers were first able to measure the distances to stars. 2) Describe the unit of the length developed by astronomers to measure and describe dist ...
... of these in addition to an optical telescope. Assignment #2: Pages 568, 587-588 Topics: Distances to and motion of stars Objectives: 1) Describe how astronomers were first able to measure the distances to stars. 2) Describe the unit of the length developed by astronomers to measure and describe dist ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... – Suggested they orbited “d ark stars” Alvan Clark (1862) – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The fi ...
... – Suggested they orbited “d ark stars” Alvan Clark (1862) – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The fi ...
Some Basic Principles from Astronomy
... surface of the Earth, and what we would like to know more about is out there – thataway! [◮ Imagine I am gesturing vaguely at the ceiling as you read this ◭] • In many ways, the story of astronomy began with attempting to measure distances —how big is the Earth? how far away is the Moon? how big is ...
... surface of the Earth, and what we would like to know more about is out there – thataway! [◮ Imagine I am gesturing vaguely at the ceiling as you read this ◭] • In many ways, the story of astronomy began with attempting to measure distances —how big is the Earth? how far away is the Moon? how big is ...
What are the Spectral Lines? - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... - real knowledge only due to hard facts, e.g., laboratory science, measurements • claimed ...
... - real knowledge only due to hard facts, e.g., laboratory science, measurements • claimed ...
Part 3
... To understand the phenomena of A-type and W-type contact binaries To understand the O’connell effect in close binaries ...
... To understand the phenomena of A-type and W-type contact binaries To understand the O’connell effect in close binaries ...
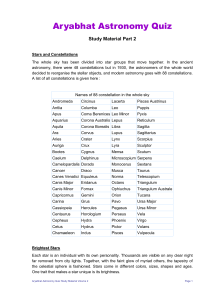
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... All stars shine but none do it like Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Aptly named, Sirius comes from the Greek word Seirius, meaning, "searing" or "scorching." Blazing at a visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation C ...
... All stars shine but none do it like Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Aptly named, Sirius comes from the Greek word Seirius, meaning, "searing" or "scorching." Blazing at a visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation C ...
Topics for Today`s Class Luminosity Equation The Heart of
... – Luminosity (or absolute magnitude) versus temperature (or spectral type) ...
... – Luminosity (or absolute magnitude) versus temperature (or spectral type) ...
Distance, Size, and Temperature of a Star
... planetary nebula they explode in what is called a super nova. Super nova explosions can be brighter than an entire galaxy, and can be seen from very far away. Because blue giant stars only live a short time, scientists use them to find places in outer space where new stars are forming. Remember when ...
... planetary nebula they explode in what is called a super nova. Super nova explosions can be brighter than an entire galaxy, and can be seen from very far away. Because blue giant stars only live a short time, scientists use them to find places in outer space where new stars are forming. Remember when ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... When a cloud starts to collapse, it should fragment. Fragments then collapse on their own, fragmenting further. End product is 100’s or 1000’s of dense clumps each destined to form star, binary star, etc. Hence a cloud gives birth to a cluster of stars. ...
... When a cloud starts to collapse, it should fragment. Fragments then collapse on their own, fragmenting further. End product is 100’s or 1000’s of dense clumps each destined to form star, binary star, etc. Hence a cloud gives birth to a cluster of stars. ...
Star Formation, HR Diagram, and the Main Sequence (Professor
... Star Form in Clusters Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Star Clusters . Our own Sun is part of an open cluster than includes other nearby stars such as Alpha Centauri and Barnard's star. ...
... Star Form in Clusters Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Star Clusters . Our own Sun is part of an open cluster than includes other nearby stars such as Alpha Centauri and Barnard's star. ...
Name - MIT
... E) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino 32) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. C) what most stars become when they die. D) an early stage of a neutron star. E) a protostar that gives ...
... E) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino 32) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. C) what most stars become when they die. D) an early stage of a neutron star. E) a protostar that gives ...
Name
... D) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino E) three helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy 31) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) what most stars become when they die. C) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. D) a ...
... D) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino E) three helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy 31) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) what most stars become when they die. C) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. D) a ...
Name - MIT
... E) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino 32) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. C) what most stars become when they die. D) an early stage of a neutron star. E) a protostar that gives ...
... E) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy and a neutrino 32) A white dwarf is ____. A) a precursor to a black hole. B) a brown dwarf that has exhausted its fuel for nuclear fusion. C) what most stars become when they die. D) an early stage of a neutron star. E) a protostar that gives ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.