Condensates in Neutron Star Interiors
... On July 4th 1054, a supernova went off in the constellation of Taurus as observed widely by astronomers on Earth (and termed as nova stella, a new star). Centuries later, in 1731, John Bevis discovered the supernova remnant, which was later christened the Crab nebula (or M1, the first entry in the M ...
... On July 4th 1054, a supernova went off in the constellation of Taurus as observed widely by astronomers on Earth (and termed as nova stella, a new star). Centuries later, in 1731, John Bevis discovered the supernova remnant, which was later christened the Crab nebula (or M1, the first entry in the M ...
neutron star
... what would happen if a star orbiting in a direction opposite the neutron’s star rotation fell onto a neutron star? ...
... what would happen if a star orbiting in a direction opposite the neutron’s star rotation fell onto a neutron star? ...
First Census of Galaxies Near Cosmic Dawn The Night Sky
... First Census of Galaxies Near Cosmic Dawn ...
... First Census of Galaxies Near Cosmic Dawn ...
WORD - Astrophysics
... essential questions remain for which the collecting area and angular resolution of an extremely large optical/infrared telescope will prove decisive. Many of these questions deal with the earliest and the latest stages of stellar evolution, plagued by significant unknowns. Determining the entire ste ...
... essential questions remain for which the collecting area and angular resolution of an extremely large optical/infrared telescope will prove decisive. Many of these questions deal with the earliest and the latest stages of stellar evolution, plagued by significant unknowns. Determining the entire ste ...
The fate of black hole singularities and the parameters of the
... puzzle becomes a crisis, as first realized by Hawking in 1974, because of the problem of the loss of information constituting the quantum state of the star whose collapse formed the black hole[3]. Another basic problem of physics is to understand why the masses and coupling constants of the elementa ...
... puzzle becomes a crisis, as first realized by Hawking in 1974, because of the problem of the loss of information constituting the quantum state of the star whose collapse formed the black hole[3]. Another basic problem of physics is to understand why the masses and coupling constants of the elementa ...
Word version - White dwarf stars and the Chandrasekhar limit
... and others. Sommerfeld left Chandra with some unpublished material of his, on the theory of electrons in metals. Chandra immediately launched into a study of the new material. In a few months Chandra had written a paper of his own, The Compton Scattering and the New Statistics. He felt that the pape ...
... and others. Sommerfeld left Chandra with some unpublished material of his, on the theory of electrons in metals. Chandra immediately launched into a study of the new material. In a few months Chandra had written a paper of his own, The Compton Scattering and the New Statistics. He felt that the pape ...
Interactive 4 - Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Explorer
... occurred within the first three minutes after the Big Bang. Complete the following atomic equations for the nucleosynthesis of hydrogen and helium isotopes. i) ...
... occurred within the first three minutes after the Big Bang. Complete the following atomic equations for the nucleosynthesis of hydrogen and helium isotopes. i) ...
Astrophysics Pristine CNO abundances from Magellanic Cloud B stars
... in what follows. The CNO abundances of the remaining three MS stars are confronted with the most recent measurements from H ii regions in Table 1: While the consistency among determinations of O abundances is very high, there is a significant positive offset ('0.7 dex) of B-star N abundances with re ...
... in what follows. The CNO abundances of the remaining three MS stars are confronted with the most recent measurements from H ii regions in Table 1: While the consistency among determinations of O abundances is very high, there is a significant positive offset ('0.7 dex) of B-star N abundances with re ...
Determining Distances to Other Galaxies
... position angle of these ellipses vary with radius, a spiral-shaped density wave can be formed from a set of nested ovals. Density wave theory is really based on the premise that mutual gravitational attraction of stars and gas clouds at different radii can offset the spiral’s tendency to wind-up. Th ...
... position angle of these ellipses vary with radius, a spiral-shaped density wave can be formed from a set of nested ovals. Density wave theory is really based on the premise that mutual gravitational attraction of stars and gas clouds at different radii can offset the spiral’s tendency to wind-up. Th ...
A search for a new class of pulsating DA white dwarf stars in the DB
... has nearly doubled the number known, adding eight new V777 Her stars to the nine known previously (Nitta et al., in preparation). The current range in temperature of the known V777 Her stars is 27 800 ≥ T eff ≥ 21 800 K. Pulsating white dwarfs have the potential to examine astrophysics and high-ener ...
... has nearly doubled the number known, adding eight new V777 Her stars to the nine known previously (Nitta et al., in preparation). The current range in temperature of the known V777 Her stars is 27 800 ≥ T eff ≥ 21 800 K. Pulsating white dwarfs have the potential to examine astrophysics and high-ener ...
Spiral structure of the Third Galactic Quadrant and the solution to the
... The clusters’ basic parameters (reddening, distance and age) have been derived via Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) and isochrone fits to the cluster sequences in different photometric diagrams. This is a standard and solid method that has been used in open cluster studies for several decades. From the ...
... The clusters’ basic parameters (reddening, distance and age) have been derived via Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) and isochrone fits to the cluster sequences in different photometric diagrams. This is a standard and solid method that has been used in open cluster studies for several decades. From the ...
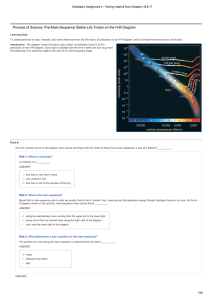
Process of Science: PreMainSequence Stellar Life Tracks on the HR
... If you watch the position of the red dot on the HR diagram as the interactive figure plays, you will see that the dot is highest — meaning the object is most luminous— when it is a protostar and therefore does not yet have internal fusion. This fact can be a little surprising, but do not forget tha ...
... If you watch the position of the red dot on the HR diagram as the interactive figure plays, you will see that the dot is highest — meaning the object is most luminous— when it is a protostar and therefore does not yet have internal fusion. This fact can be a little surprising, but do not forget tha ...
... Parallax to Barnard’s Star - If we take photographs or images of nearby stars at different times of the year, then the motion of the Earth about the Sun causes our observing location to be different and the nearby stars will show parallax motions. Barnard’s star is one such nearby star. But, in addi ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.
![Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014331057_1-996ec6eddf93071c5e835624d4620c7e-300x300.png)