HR Diagram
... 4. Are any of the stars that you plotted on the H-R diagram white dwarf stars? What is the evidence for your answer? ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Our sun has a surface temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Plot the Sun on the H ...
... 4. Are any of the stars that you plotted on the H-R diagram white dwarf stars? What is the evidence for your answer? ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Our sun has a surface temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Plot the Sun on the H ...
Due: January 15, 2014 Name
... a. the spherical cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion. b. the disk of material in which planets are forming around a star other than the Sun. c. a shell of ejected gases, glowing by fluorescence caused by ultraviolet light from a hot but dying central star. d. a gas cloud surrounding a ...
... a. the spherical cloud of hot gas produced by a supernova explosion. b. the disk of material in which planets are forming around a star other than the Sun. c. a shell of ejected gases, glowing by fluorescence caused by ultraviolet light from a hot but dying central star. d. a gas cloud surrounding a ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Click Stars: Lights in the Sky and write out the questions and answers to the following on a sheet of white construction paper to be turned in. Be sure your name and period are on it. 1) What is the name of the brightest star in our night sky? What is the name of the brightest star in all of the kno ...
... Click Stars: Lights in the Sky and write out the questions and answers to the following on a sheet of white construction paper to be turned in. Be sure your name and period are on it. 1) What is the name of the brightest star in our night sky? What is the name of the brightest star in all of the kno ...
SIERRA STAR GAZERS
... been filled with moonlight and hung before them in a net woven of the glint of frosty stars.” Even amongst the Messier objects, this one is a keeper. Messier 28 is a 7th magnitude globular cluster drifting about 20,000 light years away. With an apparent diameter of only 10’. M28 is just a shade of M ...
... been filled with moonlight and hung before them in a net woven of the glint of frosty stars.” Even amongst the Messier objects, this one is a keeper. Messier 28 is a 7th magnitude globular cluster drifting about 20,000 light years away. With an apparent diameter of only 10’. M28 is just a shade of M ...
Questions for this book (Word format)
... Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydrogen fusion to occur ...
... Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydrogen fusion to occur ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... two bands, B − V (B minus V ), was called the B-V color index. Hot stars have a negative index and cooler stars a positive index since in the magnitude system, fainter measurements have greater magnitudes. The B-V color index depends only on a star’s Temperature. Modern astronomers use two other sys ...
... two bands, B − V (B minus V ), was called the B-V color index. Hot stars have a negative index and cooler stars a positive index since in the magnitude system, fainter measurements have greater magnitudes. The B-V color index depends only on a star’s Temperature. Modern astronomers use two other sys ...
Chapter 19 Notes Stars Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
Unit 2-1 Life Cycle of the Sun
... magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approximately 32 light years away from the Earth. One of the stars you will observe will be a medium s ...
... magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approximately 32 light years away from the Earth. One of the stars you will observe will be a medium s ...
PDF copy
... The discovery of the mechanism of fasting and feasting process is the breakthrough that many were looking forward to and given important inputs for further theoretical understanding of these binaries. Says Dr Bhalerao: “This allows us to better understand how massive stars form, to study how binarie ...
... The discovery of the mechanism of fasting and feasting process is the breakthrough that many were looking forward to and given important inputs for further theoretical understanding of these binaries. Says Dr Bhalerao: “This allows us to better understand how massive stars form, to study how binarie ...
Page 1 Astronomy 110 Homework #08 Assigned: 03/13/2007 Due
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... see from Earth. A hot, large star that is very far from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
... see from Earth. A hot, large star that is very far from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
HR Diagram
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ ...
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ ...
Stars with mass less than 0.5 solar masses
... So, the hottest, brightest stars are at the top left while the coolest, faintest stars are at the bottom right. The diagonal band of stars running from the upper left to lower right is known as the Main Sequence and includes those stars which are converting hydrongen into helium in their cores under ...
... So, the hottest, brightest stars are at the top left while the coolest, faintest stars are at the bottom right. The diagonal band of stars running from the upper left to lower right is known as the Main Sequence and includes those stars which are converting hydrongen into helium in their cores under ...
Sep 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... A Light Year (ly) is a unit of length and is equal to the discan be seen with the naked eye. tance light travels in one year. Since light moves at the rate of Our 186,282 miles a second, one light year is nearly 6 trillion miles Double Stars Moon long. The closest nighttime star visible to the naked ...
... A Light Year (ly) is a unit of length and is equal to the discan be seen with the naked eye. tance light travels in one year. Since light moves at the rate of Our 186,282 miles a second, one light year is nearly 6 trillion miles Double Stars Moon long. The closest nighttime star visible to the naked ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
IB Precalculus
... Richter magnitude 5.0. Approximately how many times more intense was the 1944 earthquake in New York than the 1975 earthquake in Minnesota. 2. The most intense recorded earthquake in Texas occurred in 1931; it had Richter magnitude 5.8. If an earthquake were to strike Texas next year that was three ...
... Richter magnitude 5.0. Approximately how many times more intense was the 1944 earthquake in New York than the 1975 earthquake in Minnesota. 2. The most intense recorded earthquake in Texas occurred in 1931; it had Richter magnitude 5.8. If an earthquake were to strike Texas next year that was three ...
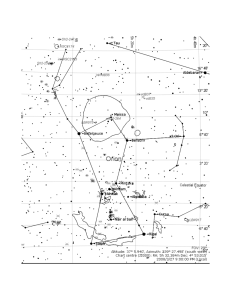
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.